Group13
- 1. PSG COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY 20MX15 - UNIX ARCHITECTURE AND PROGRAMMING By 21MX124 - Sandhiya M. 21MX207 - Karpaga Prasanth K. 21MX210 - Maheash Kumar M. 21MX213 - Om Raju V. Ms. A. Kalyani Asst.Professor MCA (PSG)
- 2. The ŌĆścdŌĆÖ Command The ŌĆścdŌĆÖ Command is used to change the current directory to another directory. Syntax: cd [directory path]
- 3. The ŌĆśbcŌĆÖ Command ŌĆó bc command is used for command line calculator. It is similar to basic calculator by using which we can do basic mathematical calculations. Arithmetic operations are the most basic in any kind of programming language. Linux or Unix operating system provides the bc command and expr command for doing arithmetic calculations. You can use these commands in bash or shell script also for evaluating arithmetic expressions. Syntax: Bs [-hlwsqv] [more options] [fileŌĆ”]
- 4. bc - Supports ŌĆó Arithmetic operators. ŌĆó Increment or Decrement operators. ŌĆó Assignment operators. ŌĆó Comparison or Relational operators. ŌĆó Logical or Boolean operators. ŌĆó Math functions. ŌĆó Conditional statements. ŌĆó Iterative statements.
- 5. The ŌĆśmanŌĆÖ Command ŌĆó Man command in Linux is used to display the user manual of any command that we can run on the terminal. provides a detailed view of the command which includes NAME, SYNOPSIS, DESCRIPTION, OPTIONS, EXIT STATUS, RETURN VALUES, ERRORS, FILES, VERSIONS, EXAMPLES, AUTHORS and SEE ALSO. Syntax: $man [options] [command name]
- 7. The ŌĆśwhoŌĆÖ Command ŌĆó The Linux "who" command lets you display the users currently logged in to your UNIX or Linux operating system. Whenever a user needs to know about how many users are using or are logged-in into a particular Linux-based operating system, he/she can use the "who" command to get that information.
- 8. The ŌĆśwhoamiŌĆÖ Command ŌĆó It displays the username of the current user when this command is invoked. ŌĆó Displays user, group and privileges information for the user who is currently logged on to the local system. If used without parameters, whoami displays the current domain and user name.
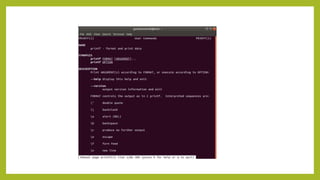
- 9. The ŌĆśpwdŌĆÖ Command ŌĆó pwd stands for Print Working Directory. It prints the path of the working directory, starting from the root. pwd is shell built-in command(pwd). ŌĆó Options: pwd -l : Prints the symbolic path. pwd ŌĆōp : Prints the Actual path.
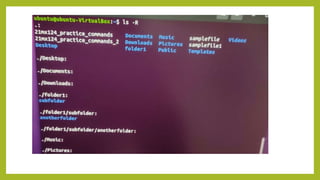
- 10. The ŌĆśmkdirŌĆÖ Command ŌĆó Mkdir stands for make directory . ŌĆó The ŌĆ£mkdirŌĆØ command is used to create a directory. ŌĆó -p: option create a hierarchy of directories. Syntax: mkdir [directory path] ubuntu@ubuntu-VirtualBox:~$ mkdir folder ubuntu@ubuntu-VirtualBox:~$ mkdir folder1 ubuntu@ubuntu-VirtualBox:~$ mkdir -p folder1/subfolder/anotherfolder
- 11. The ŌĆśrmdirŌĆÖ Command Rmdir stands for remove directory. The ŌĆ£rmdirŌĆØ command is used to remove directory. ŌĆó Syntax: rmdir [directory path] ŌĆó ubuntu@ubuntu-VirtualBox:~$ rmdir folder
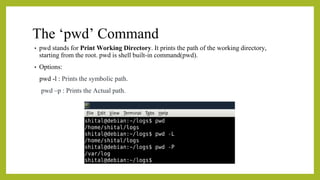
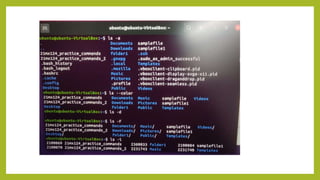
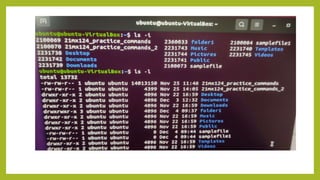
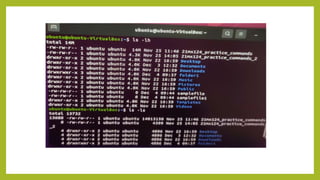
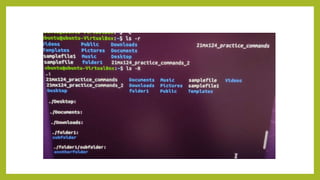
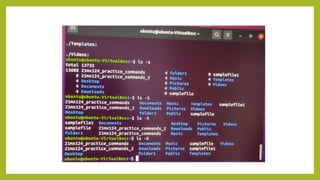
- 12. The ŌĆślsŌĆÖ Command The Linux ls command allows you to view a list of the files and folders in a given directory. You can also use this command to display details of a file, such as the owner of the file and the permissions assigned to the file. ŌĆó ubuntu@ubuntu-VirtualBox:~$ ls ŌĆó 21mx124_practice_commands Documents Music samplefile Videos ŌĆó 21mx124_practice_commands_2 Downloads Pictures samplefile1 ŌĆó Desktop folder1 Public Templates
- 20. The ŌĆśTouchŌĆÖ Command The touch command is a standard command used in UNIX/Linux operating system which is used to create, change and modify timestamps of a file. ŌĆó Syntax: Touch [File_name] ŌĆó ubuntu@ubuntu-VirtualBox:~$ touch samplefile ŌĆó ubuntu@ubuntu-VirtualBox:~$ touch samplefile1 ŌĆó ubuntu@ubuntu-VirtualBox:~$ ls ŌĆó 21mx124_practice_commands Documents Music samplefile Videos ŌĆó 21mx124_practice_commands_2 Downloads Pictures samplefile1 ŌĆó Desktop folder1 Public Templates
- 21. The ŌĆśmvŌĆÖ Command mv stands for move. mv is used to move one or more files or directories from one place to another in a file system like UNIX. It has two distinct functions. ŌĆó It renames a file or folder. ŌĆó It moves a group of files to a different directory.
- 22. The ŌĆśdateŌĆÖ Command ŌĆó Date command is used to display the system date and time. It is also used to set date and time of the system. ŌĆó By default the date command displays the date in the time zone on which unix operating system is configured. ŌĆó You must be the super-user to change the date and time. Syntax: $date
- 23. The ŌĆścatŌĆÖ Command Cat command stands for concatenate. It reads data from the file and gives their content as output. It helps us to create, view, and concatenate files. Frequently used cat commands: ŌĆó To view a single file . Command: $cat filename ŌĆó To view multiple files Command: $cat file1 file2
- 24. ŌĆó Create a file Command: $ cat >newfile ŌĆó Copy the contents of one file to another file. Command: $cat [filename-whose-contents-is-to-be-copied] > [destination-filename]
- 25. The ŌĆśMoreŌĆÖ Command ŌĆó more command is used to view the text files in the command prompt, displaying one screen at a time in case the file is large. ŌĆó The more command also allows the user do scroll up and down through the page. ŌĆó When the output is large, we can use more command to see output one by one. ŌĆó Another application of more is to use it with some other command after a pipe.
- 26. Syntax: The syntax along with options and command is as follows. more [-options] [-num] [+/pattern] [+linenum] [file_name] [-options]: any option that you want to use in order to change the way the file is displayed. (-d, -l, -f, -p, -c, -s, -u) [-num]: type the number of lines that you want to display. [+/pattern]: replace the pattern with any string that you want to find in the text file. [+linenum]: use the line number from where you want to start displaying the text content. [file_name]: name of the file containing the text that you want to display on the screen.
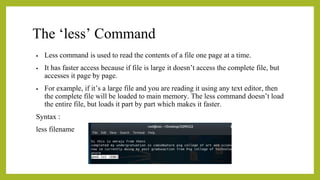
- 27. The ŌĆślessŌĆÖ Command ŌĆó Less command is used to read the contents of a file one page at a time. ŌĆó It has faster access because if file is large it doesnŌĆÖt access the complete file, but accesses it page by page. ŌĆó For example, if itŌĆÖs a large file and you are reading it using any text editor, then the complete file will be loaded to main memory. The less command doesnŌĆÖt load the entire file, but loads it part by part which makes it faster. Syntax : less filename
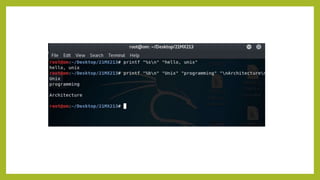
- 28. The ŌĆśprintŌĆÖ Command ŌĆó printf command is used to display the given string, number or any other format specifier on the terminal. ŌĆó It works the same way as ŌĆ£printfŌĆØ works in programming languages like C. Syntax: $printf [-v var] format [arguments] The most commonly used printf specifiers are %s, %b, %d, %x and %f. 1) %s : It is basically a string specifier for string output. $printf "%sn" "Hello, World!" 2) %b : It is same as string specifier but it allows us to interpret escape sequences with an argument. printf "%sn" "Hello, World! n" "From Geeks For Geeksn" 3) %d specifier: It is an integer specifier for showing the integral values.
- 30. The ŌĆśechoŌĆÖ Command ŌĆó echo command in linux is used to display line of text/string that are passed as an argument . This is a built in command that is mostly used in shell scripts and batch files to output status text to the screen or a file. Syntax: Echo [option] [string]
- 31. The ŌĆślpŌĆÖ Command ŌĆó The lp command in Linux stands for 'Line printer' which lets you print the files through the terminal. There is no need to change or manage the settings through the GUI. You can simply manage the printers using lp command. This command is also known as the printer management command Linux. ŌĆó This command is also known as the printer management command Linux. The lp command in Linux is one of the CUPS i.e. Common Unix Printing System. Syntax: lp [filename]
- 32. Options of lp command ŌĆó d: to print the file using a particular printer. ŌĆó -n: print multiple copies of the document. ŌĆó -q: Set the priority of the printer in the printer queue. ŌĆó -t: to assign a name to the job. ŌĆó -o: assigns one or more job. ŌĆó -i: specifies an existing job to modify. ŌĆó -m: notifies the recipient when the job is completed. ŌĆó -h: denotes the hostname of the server. ŌĆó -E: forces the encryption while connecting to the server.
- 33. The ŌĆśrmŌĆÖCommand ŌĆó The 'rm' means remove. This command is used to remove a file. The command line doesn't have a recycle bin or trash unlike other GUI's to recover the files. Hence, be very much careful while using this command. Once you have deleted a file, it is removed permanently. ŌĆó Syntax: rm <filename> ŌĆó Example: rm myfile1
- 34. Options in rm ŌĆó rm *extension - Used to delete files having same extension. ŌĆó rm -r or R - To delete a directory recursively. ŌĆó rm ŌĆōi - Remove a file interactively. ŌĆó rm ŌĆōrf - Remove a directory forcefully.
- 35. The ŌĆścpŌĆÖ Command ŌĆó cp stands for copy. This command is used to copy files or group of files or directory. It creates an exact image of a file on a disk with different file name. cp command require at least two filenames in its arguments. Syntax: cp [Source file] [destination file]
- 36. cp ŌĆōR : If the command contains two directory names, cp copies all files of the source directory to the destination directory, creating any files or directories needed. This mode of operation requires an additional option, typically R, to indicate the recursive copying of directories. ŌĆó Syntax: cp -R [Src_dir] [des_dir] cp -i : i stands for Interactive copying. With this option system first warns the user before overwriting the destination file. cp prompts for a response, if you press y then it overwrites the file and with any other option leave it uncopied. ŌĆó Synatx: cp ŌĆōI [Src_file] [des_file]

![The ŌĆścdŌĆÖ Command
The ŌĆścdŌĆÖ Command is used to change the current
directory to another directory.
Syntax: cd [directory path]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group13-211211050820/85/Group13-2-320.jpg)
![The ŌĆśbcŌĆÖ Command
ŌĆó bc command is used for command line calculator. It is similar to basic calculator
by using which we can do basic mathematical calculations.
Arithmetic operations are the most basic in any kind of programming language.
Linux or Unix operating system provides the bc command and expr
command for doing arithmetic calculations. You can use these commands in bash
or shell script also for evaluating arithmetic expressions.
Syntax:
Bs [-hlwsqv] [more options] [fileŌĆ”]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group13-211211050820/85/Group13-3-320.jpg)

![The ŌĆśmanŌĆÖ Command
ŌĆó Man command in Linux is used to display the user manual of any command that we
can run on the terminal. provides a detailed view of the command which
includes NAME, SYNOPSIS, DESCRIPTION, OPTIONS, EXIT STATUS,
RETURN VALUES, ERRORS, FILES, VERSIONS, EXAMPLES,
AUTHORS and SEE ALSO.
Syntax:
$man [options] [command name]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group13-211211050820/85/Group13-5-320.jpg)


![The ŌĆśmkdirŌĆÖ Command
ŌĆó Mkdir stands for make directory .
ŌĆó The ŌĆ£mkdirŌĆØ command is used to create a directory.
ŌĆó -p: option create a hierarchy of directories.
Syntax: mkdir [directory path]
ubuntu@ubuntu-VirtualBox:~$ mkdir folder
ubuntu@ubuntu-VirtualBox:~$ mkdir folder1
ubuntu@ubuntu-VirtualBox:~$ mkdir -p folder1/subfolder/anotherfolder](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group13-211211050820/85/Group13-10-320.jpg)
![The ŌĆśrmdirŌĆÖ
Command
Rmdir stands for remove directory.
The ŌĆ£rmdirŌĆØ command is used to remove
directory.
ŌĆó Syntax: rmdir [directory path]
ŌĆó ubuntu@ubuntu-VirtualBox:~$ rmdir folder](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group13-211211050820/85/Group13-11-320.jpg)


![The ŌĆśTouchŌĆÖ
Command
The touch command is a standard command used in
UNIX/Linux operating system which is used to create,
change and modify timestamps of a file.
ŌĆó Syntax: Touch [File_name]
ŌĆó ubuntu@ubuntu-VirtualBox:~$ touch samplefile
ŌĆó ubuntu@ubuntu-VirtualBox:~$ touch samplefile1
ŌĆó ubuntu@ubuntu-VirtualBox:~$ ls
ŌĆó 21mx124_practice_commands Documents Music samplefile
Videos
ŌĆó 21mx124_practice_commands_2 Downloads Pictures
samplefile1
ŌĆó Desktop folder1 Public Templates](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group13-211211050820/85/Group13-20-320.jpg)



![ŌĆó Create a file
Command:
$ cat >newfile
ŌĆó Copy the contents of one file to another file.
Command:
$cat [filename-whose-contents-is-to-be-copied] > [destination-filename]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group13-211211050820/85/Group13-24-320.jpg)

![Syntax:
The syntax along with options and command is as follows.
more [-options] [-num] [+/pattern] [+linenum] [file_name]
[-options]: any option that you want to use in order to change the way the file is
displayed.
(-d, -l, -f, -p, -c, -s, -u)
[-num]: type the number of lines that you want to display.
[+/pattern]: replace the pattern with any string that you want to find in the text file.
[+linenum]: use the line number from where you want to start displaying the text
content.
[file_name]: name of the file containing the text that you want to display on the
screen.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group13-211211050820/85/Group13-26-320.jpg)
![The ŌĆśprintŌĆÖ Command
ŌĆó printf command is used to display the given string, number or any other format specifier on the
terminal.
ŌĆó It works the same way as ŌĆ£printfŌĆØ works in programming languages like C.
Syntax:
$printf [-v var] format [arguments]
The most commonly used printf specifiers are %s, %b, %d, %x and %f.
1) %s : It is basically a string specifier for string output. $printf "%sn" "Hello, World!"
2) %b : It is same as string specifier but it allows us to interpret escape sequences with an argument.
printf "%sn" "Hello, World! n" "From Geeks For Geeksn"
3) %d specifier: It is an integer specifier for showing the integral values.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group13-211211050820/85/Group13-28-320.jpg)
![The ŌĆśechoŌĆÖ Command
ŌĆó echo command in linux is used to display line of text/string that are passed as an
argument . This is a built in command that is mostly used in shell scripts and
batch files to output status text to the screen or a file.
Syntax:
Echo [option] [string]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group13-211211050820/85/Group13-30-320.jpg)
![The ŌĆślpŌĆÖ Command
ŌĆó The lp command in Linux stands for 'Line printer' which lets you print the files
through the terminal. There is no need to change or manage the settings through
the GUI. You can simply manage the printers using lp command. This command
is also known as the printer management command Linux.
ŌĆó This command is also known as the printer management command Linux. The lp
command in Linux is one of the CUPS i.e. Common Unix Printing System.
Syntax:
lp [filename]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group13-211211050820/85/Group13-31-320.jpg)



![The ŌĆścpŌĆÖ
Command
ŌĆó cp stands for copy. This
command is used to copy files or
group of files or directory. It
creates an exact image of a file on
a disk with different file
name. cp command require at
least two filenames in its
arguments.
Syntax: cp [Source file]
[destination file]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group13-211211050820/85/Group13-35-320.jpg)
![cp ŌĆōR : If the command contains two directory names, cp copies all files of the source
directory to the destination directory, creating any files or directories needed. This mode of
operation requires an additional option, typically R, to indicate the recursive copying of
directories.
ŌĆó Syntax: cp -R [Src_dir] [des_dir]
cp -i : i stands for Interactive copying. With this option system first warns the user before
overwriting the destination file. cp prompts for a response, if you press y then it overwrites
the file and with any other option leave it uncopied.
ŌĆó Synatx: cp ŌĆōI [Src_file] [des_file]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group13-211211050820/85/Group13-36-320.jpg)