GSM Network Protocols
- 1. Chapter 5 Network Protocols Eng. Ahmed Khaled
- 2. Main RR procedures: ïžPower control ïžChannel quality monitoring ïžHandover ïžFrequency hopping ïžDiscontinuous transmission ïžTiming advance. MS, BTS and BSC are Concerned with transmission
- 3. Power Control: ïžEnables power adaptation of MS and BTS. ïžMain reasons for power control: ïžSaving MS battery Power ïžImprove CIR. ïžCan be enabled or disabled. ïžPerformed separately for uplink and DL. ïžMeasurements on UL and DL are sent to BSC every 480 ms. ïžMeasurements in terms of: ïžSignal strength in dBm. ïžSignal quality in BER.
- 4. Power Control: Distance Power Increase Step MS Power (dBm) Max. Transmitted Power Distance Upper Threshold Lower Threshold Power Control Increase Command Signal Strength Measured at BTS
- 5. Handover Control: ïžAutomatic switching of a call from one TCH to another. ïžCan be within the cell or between cells. ïžReasons for intra-cell handover: ïžreduction of co-channel interference. ïžMaintenance activity ïžHandover occurs on TCH when call is in speech stage. ïžOnly started if power control is not helpful. Unique feature of mobile network.
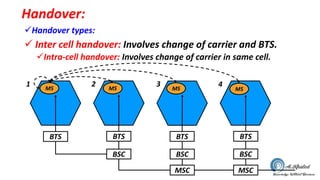
- 6. Handover: ïžHandover types: ïž Inter cell handover: Involves change of carrier and BTS. ïžIntra-cell handover: Involves change of carrier in same cell. MS MS MS MS BTS BTS BTS BTS BSC BSC BSC MSC MSC 1 2 3 4
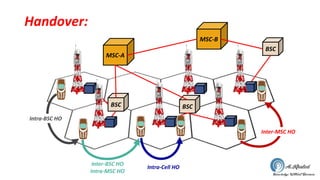
- 7. Handover: BSC MSC-A BSC BSC MSC-B Inter-MSC HO Intra-Cell HO Inter-BSC HO Intra-MSC HO Intra-BSC HO
- 8. Handover: ïžRequirements for Handover ïžExecution speed ïžReliability âĒ No excessive HO âĒ No delayed HO âĒ No early HO ïžTransparent to users (not aware) ïžService-dependent (voice, data)
- 9. Handover: ïžCriteria for Handover ïžBSC receives measurement data from BTS and MS. ïžThe MS measures DL: ïžSignal strength (dBm) ïžSignal quality (BER) ïžSignal strength of neighboring BTSs downlink ïžThe BTS measures UL: ïžSignal strength received from MS. ïžSignal quality received from MS. ïžDistance between BTS and MS.
- 11. 1 2 ð ð ð Handling of Handover: ïžReserved channel concept ïžSome channels are reserved for HO New Calls Handover
- 12. Handover: ïžN times retry ïžMultiple request for Handover ïžHandover queue ïžHO wait for a free channel. ïžSub-rating algorithm ïžFull rate TCH is split into 2 half rate TCHs.
- 13. Intra-BSC (Inter-cell) HO: Old BTS New BTS 2 34 5 6 1 5 2 BSC
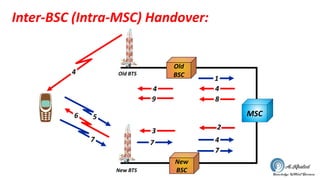
- 14. Inter-BSC (Intra-MSC) Handover: MSC New BSC Old BSCOld BTS New BTS 2 4 7 4 9 3 7 1 4 8 4 56 7
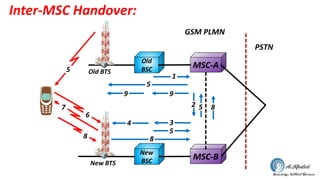
- 15. Inter-MSC Handover: MSC-A Old BSC MSC-B New BSC 1 5 99 4 3 5 8 852 5 8 6 7 New BTS Old BTS PSTN GSM PLMN
- 16. Mobility Management (MM): ïžMain task of MM is to support mobility. ïžMM activities include: ïžLocation update ïžUpdate HLR/VLR ïžTMSI re-allocation. ïžAuthentication of MS.
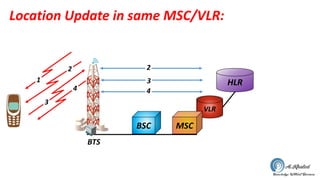
- 17. Location Update in same MSC/VLR: HLR VLR MSCBSC 1 2 3 4 2 3 4 BTS
- 18. Location Update with New MSC/VLR: New VLR New MSC BSC Old VLR HLR 4 2 3 4 Old MSC 5 BTS ïķWhen MS enters into new LA, location update. ïķLA may belong to new MSC/VLR.
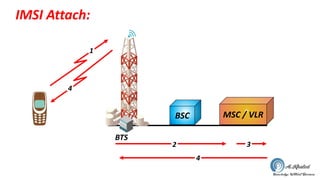
- 19. IMSI Attach: BSC MSC / VLR 4 2 3 4 1 BTS
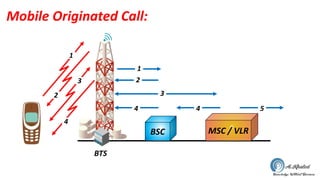
- 20. Mobile Originated Call: BSC MSC / VLR 4 3 2 4 4 5 3 2 1 BTS 1
- 22. PCH RACH AGCH SDCCH SDCCH SDCCH SDCCH SDCCH SDCCH SDCCH FACCH FACCH FACCH FACCH TCH SDCCH Paging Request Immediate Assignment Authentication Request Cipher Mode Command Setup Assignment Command Connect Acknowledge Data Channel Request Paging Response Auth. Response Cipher Mode Comp. Call Confirmed Assignment Complete Alert BSS/MSC Data Connect MS