Guidelines 0n Pump Vibration First edition Final July 2013 (1).pdf
- 1. EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF PUMP MANUFACTURERS ASSOCIATION EUROP?ENNE DES CONSTRUCTEURS DE POMPES EUROP?ISCHE VEREINIGUNG DER PUMPENHERSTELLER PUMP VIBRATION STANDARDS GUIDELINES First edition - 15 July 2013
- 2. Pump vibration standards 2 INTRODUCTION The diversity of standards applicable to the pump industry is probably greater on the subject of vibration than any other field. These standards can appear to be conflicting in that they present machine vibration limits in different ways and with different limiting values. The purpose of these guidelines is to present, in one document, the essential points of each standard and to explain where each standard tends to be used. This document is not an alternative to studying the full content of the standard with which compliance is required, and because it is a summary, does not contain all the conditional statements and explanations which are in the standard itself. A previous Europump guideline written some years ago, before the diversity of national and international standards occurred, recommended vibration limits for pumps. Europump is withdrawing this guideline because it does not want to add to the diversity of pump vibration standards. SCOPE The standards included in these guidelines are applicable to rotodynamic pumps only and do not include guidance or vibration levels of drivers that may be part of the pump set. The vibration limits apply to pumps with multi-vaned impellers. Pumps specifically designed for solids handling and waste water applications will experience higher out of balance forces and pressure pulsations with subsequently increased vibration levels.
- 3. Pump vibration standards 3 Contents 1. SUMMARY OF STANDARDS..............................................................................................................5 1.1. ISO 9908 - Technical specification for centrifugal pumps ¨C Class 3....................................5 1.1.1. Application of this Standard............................................................................................5 1.2. ISO 5199 ¨CTechnical specification for centrifugal pumps Class II.......................................5 1.2.1. Application of this Standard............................................................................................6 1.3. ISO 9905 - Technical specification for centrifugal pumps ¨C Class 1....................................6 1.3.1. Application of this Standard............................................................................................7 1.4. ISO 10816-3 - Mechanical vibration ¨C Evaluation of machine vibration by measurements on non rotating parts......................................................................................................................7 1.4.1. Application of this Standard............................................................................................7 1.5. BS ISO 10816-7 - Mechanical vibration - Evaluation of machine vibration by measurements on non-rotating parts.............................................................................................8 1.5.1. Application of this Standard............................................................................................9 1.6. ISO 13709 2009 Centrifugal pumps for petroleum, petrochemical and natural gas industries also a dually numbered as API 610 ..............................................................................10 1.6.1. Application of this Standard..........................................................................................12 2. COMPARISON OF PERMITTED VIBRATION LEVELS ........................................................................13
- 4. Pump vibration standards 4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Permission to reproduce extracts from British Standards is granted by The British Standards Institution (BSI). No other use of this material is permitted. British Standards can be obtained in PDF or hard copy formats from the BSI online shop: www.bsigroup.com/Shop or by contacting BSI Customer Services for hard copies only: Tel: +44 (0)20 8996 9001, Email: cservices@bsigroup.com Extracts shall not be used as part of any other work. Only English Language use of the extracts is permitted. The publication including the extracts is only available for download from Europump website ( http://www.europump.org/ ) The standards are also EN Standards and are issued as standards from European National Standards Organizations, but because this guide is in English, extracts are taken from BS EN ISO versions. The guide is based on the version of the standards which were current at the date of publishing.
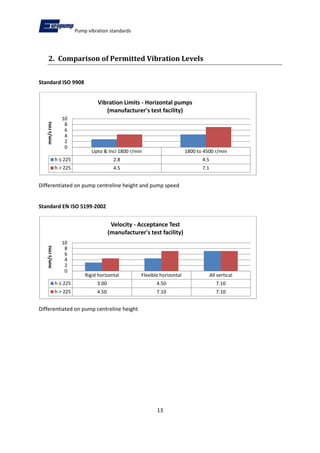
- 5. Pump vibration standards 5 1. Summary of Standards 1.1. ISO 9908 - Technical specification for centrifugal pumps ¨C Class 3 This standard covers requirements for centrifugal pumps of single stage, multistage, horizontal or vertical construction (coupled or close coupled) Class 3 requirements considered less severe than ISO 5199. Conditions: A) Vibration severity refers measurements at test facility B) Differentiates between pumps with centreline heights above and below 225 mm and speeds up to 1800 rpm and 1800 to 4500 rpm C) Values measured radially at bearing housing at a single operating point at rated speed (+/- 5%) and rated flow (+/- 5%) operating without cavitation D) Vertical lineshaft pumps have readings at the top flange when rigid couplings are employed and near the top pump bearing for pumps with flexible couplings E) Limits for both rolling and sleeve bearing pumps shall not exceed a velocity of 7.1 mm/s 1.1.1. Application of this Standard This standard is applied to any light duty centrifugal pump, but is most commonly associated with end suction pumps to EN733. 1.2. ISO 5199 ¨CTechnical specification for centrifugal pumps Class II This standard covers Class II centrifugal pumps of single stage, multistage, horizontal or vertical construction with any drive and any installation for general application. Pumps used in the chemical industry are typical of those covered by this standard.
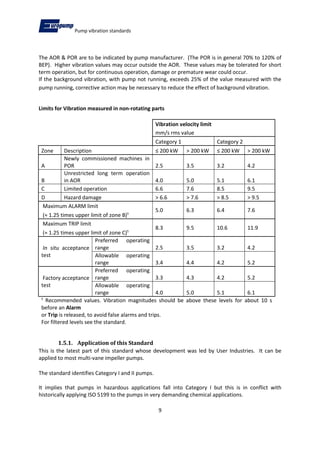
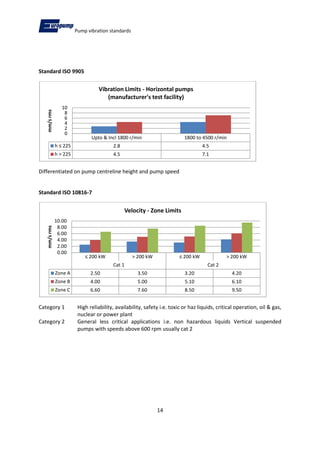
- 6. Pump vibration standards 6 Conditions: A) All major rotating components shall be balanced B) Vibration limits should be achieved by balance to grade G6.3 of ISO 1940-1 C) Vibration severity refers measurements at test facility D) Differentiates between pumps with centreline heights above and below 225 mm, and also :- 1) Rigid horizontal 2) Flexible horizontal 3) All vertical Rms velocity mm/s Rigid horizontal Flexible horizontal All vertical C/L height ¡Ü 225 mm 3.00 5.50 7.10 C/L height > 225 mm 4.50 7.10 7.10 1.2.1. Application of this Standard This standard is applied to any medium duty centrifugal pump, but is most commonly associated with end suction pumps to ISO 2858, which are used in chemical and industrial applications, including aggressive, toxic, high temperature duties. 1.3. ISO 9905 - Technical specification for centrifugal pumps ¨C Class 1 This standard covers the Class I (most severe) requirements for centrifugal pumps in various industries, but does not apply to pumps used in petroleum, petrochemical or natural gas applications. Conditions: A) All major rotating components shall be balanced. B) Vibration limits should be achieved by balance to grade G6.3 of ISO 1940-1. C) Vibration severity refers measurements at test facility D) Pump and driver vibration performance will be as good on permanent foundation as on test stand.
- 7. Pump vibration standards 7 E) Differentiates between pumps with centreline heights above and below 225 mm and speeds up to 1800 rpm and 1800 to 4500 rpm. F) Values measured radially at bearing housing at a single operating point at rated speed (+/- 5%) and rated flow (+/- 5%) operating without cavitation. Vertical lineshaft pumps have readings at top flange when rigid couplings are employed and near the top pump bearing for pumps with flexible couplings. Limits for both rolling and sleeve bearing pumps shall not exceed a velocity of 7.1 mm/s. 1.3.1. Application of this Standard This standard is applied to heavy duty centrifugal pumps for arduous duties such as high temperature or high pressure, but the standard is not intended for petroleum, oil and gas industries. 1.4. ISO 10816-3 - Mechanical vibration ¨C Evaluation of machine vibration by measurements on non rotating parts Part 3 ¨C Industrial machines with nominal power above 15 kW and nominal speeds between 120 r/min & 15000 r/min when measured in situ. 1.4.1. Application of this Standard This Part of ISO 10816 is no longer to be used as the vibration standard for pumps; it has now been superseded by part 7.
- 8. Pump vibration standards 8 1.5. BS ISO 10816-7 - Mechanical vibration - Evaluation of machine vibration by measurements on non-rotating parts Part 7: Rotodynamic pumps for industrial applications, incl. measurements on rotating shafts. The standard covers rotodynamic pumps for industrial applications with nominal power above 1kW. It includes vibration measurement on rotating and non-rotating parts (bearing housing vibration) and provides guidance for vibration severity in situ and at the manufacturer¡¯s facility for ¡®Preferred¡¯ and ¡®Allowable¡¯ operating ranges. The differentiation between solid & flexible mountings which was used in part 3, is not made. Pumps are classified in two categories: Category I Pumps required to have a high level of reliability, availability or safety reasons, (e.g. pumps for toxic and/or hazardous liquids, for critical application, oil & gas, special chemical nuclear or power plant applications). Category II Pumps for general or less critical applications (e.g. pumps for non-hazardous liquids). Vertical suspended pumps with speeds above 600 rpm usually Category II The standard defines Zone limits for vibration of non-rotating parts of rotodynamic pumps, with power above 1 kW, and impeller vanes greater than 3. The zone descriptions are: Zone A Vibration of newly commissioned machines. Zone B Acceptable for unrestricted long-term operation. Zone C Unsatisfactory for long term continuous operation Zone D Vibration of sufficient severity to cause damage to machine. Operating ranges:
- 9. Pump vibration standards 9 The AOR & POR are to be indicated by pump manufacturer. (The POR is in general 70% to 120% of BEP). Higher vibration values may occur outside the AOR. These values may be tolerated for short term operation, but for continuous operation, damage or premature wear could occur. If the background vibration, with pump not running, exceeds 25% of the value measured with the pump running, corrective action may be necessary to reduce the effect of background vibration. Limits for Vibration measured in non-rotating parts Vibration velocity limit mm/s rms value Category 1 Category 2 Zone Description ¡Ü 200 kW > 200 kW ¡Ü 200 kW > 200 kW A Newly commissioned machines in POR 2.5 3.5 3.2 4.2 B Unrestricted long term operation in AOR 4.0 5.0 5.1 6.1 C Limited operation 6.6 7.6 8.5 9.5 D Hazard damage > 6.6 > 7.6 > 8.5 > 9.5 Maximum ALARM limit 5.0 6.3 6.4 7.6 (¡Ö 1.25 times upper limit of zone B)? Maximum TRIP limit 8.3 9.5 10.6 11.9 (¡Ö 1.25 times upper limit of zone C)? In situ acceptance test Preferred operating range 2.5 3.5 3.2 4.2 Allowable operating range 3.4 4.4 4.2 5.2 Factory acceptance test Preferred operating range 3.3 4.3 4.2 5.2 Allowable operating range 4.0 5.0 5.1 6.1 ? Recommended values. Vibration magnitudes should be above these levels for about 10 s before an Alarm or Trip is released, to avoid false alarms and trips. For filtered levels see the standard. 1.5.1. Application of this Standard This is the latest part of this standard whose development was led by User Industries. It can be applied to most multi-vane impeller pumps. The standard identifies Category I and II pumps. It implies that pumps in hazardous applications fall into Category I but this is in conflict with historically applying ISO 5199 to the pumps in very demanding chemical applications.
- 10. Pump vibration standards 10 Major manufacturers in Europump recommend that chemical pumps to ISO 2858 which generally comply with the technical feature in other parts of ISO 5199 should also comply with the vibration levels in ISO 5199 or, if ISO10816 part 7 is used, then Category II is the appropriate part. The standard defines that vertical pumps are in Category II. This standard and category may impose unnecessarily low limits for some vertical pump designs and applications or where operation is intermittent or non-demanding. Here again ISO 5199 is the appropriate standard. 1.6. ISO 13709 2009 Centrifugal pumps for petroleum, petrochemical and natural gas industries also a dually numbered as API 610 In this standard, vibration limits are applied during the performance tests and reference is made to the Preferred Operating range and the Allowable Operating range in the relationship between flow and vibration. The allowable operating region is to be stated. If the allowable operating region is limited by a factor other than vibration, then that factor is to be stated.
- 11. Pump vibration standards 11 a) Vibration limits for overhung and between bearings pumps, power up to 300 kW per stage, speed up to 3600 r/min for all bearing types, measured on the bearing housing b) Vibration limits for overhung and between bearings pumps, for hydrodynamic journal bearings, measured on the pump shaft The above criteria show the allowable increase in vibration of 30%, at flows outside the preferred range but within the allowable operating region. c) Vibration limits for vertically suspended pumps, for all bearing types measured on the thrust bearing housing d) Vibration limits for vertically suspended pumps, for hydrodynamic journal bearings measured on the shaft The above criteria show the allowable increase in vibration of 30%, at flows outside the preferred range but within the allowable operating region. Velocity (mm/s RMS) POR AOR Overall 3.0 3.9 Discrete frequencies 2.0 2.6 Amplitude (?m peak to peak) Not to exceed Overall 50.00 Discrete frequencies 16.50 Velocity (mm/s RMS) POR AOR Overall 5.0 6.5 Discrete frequencies 3.4 4.4 Amplitude (?m peak to peak) Not to exceed Overall 100.00 Discrete frequencies 75.00
- 12. Pump vibration standards 12 e) Vibration Limits for Horizontal pumps absorbing more than 300 kW per stage or running above 3600 r/min. For all pump and bearing types: ? At any speed greater than max continuous speed, up to and including trip speed, the vibration shall not exceed 150% of the max value recorded at maximum continuous speed. ? Variable speed pumps shall operate over their specified speed range without exceeding the vibration limits stated for this standard. 1.6.1. Application of this Standard This is the widely used standard for centrifugal pumps for petroleum, petrochemical and gas industry process services. The vibration and test requirements of this standard are sometimes applied to pumps which do not comply with the other technical requirement of the standard, for example ISO 2858 or ANSI B73.1 pumps used in the above industries. Users should consider if this is adding unnecessary costs to these pumps when other industries accept less stringent standards.
- 13. Pump vibration standards 13 2. Comparison of Permitted Vibration Levels Standard ISO 9908 Differentiated on pump centreline height and pump speed Standard EN ISO 5199-2002 Differentiated on pump centreline height Upto & Incl 1800 r/min 1800 to 4500 r/min h ¡Ü 225 2.8 4.5 h > 225 4.5 7.1 0 2 4 6 8 10 mm/s rms Vibration Limits - Horizontal pumps (manufacturer's test facility) Rigid horizontal Flexible horizontal All vertical h ¡Ü 225 3.00 4.50 7.10 h > 225 4.50 7.10 7.10 0 2 4 6 8 10 mm/s rms Velocity - Acceptance Test (manufacturer's test facility)
- 14. Pump vibration standards 14 Standard ISO 9905 Differentiated on pump centreline height and pump speed Standard ISO 10816-7 Category 1 High reliability, availability, safety i.e. toxic or haz liquids, critical operation, oil & gas, nuclear or power plant Category 2 General less critical applications i.e. non hazardous liquids Vertical suspended pumps with speeds above 600 rpm usually cat 2 Upto & Incl 1800 r/min 1800 to 4500 r/min h ¡Ü 225 2.8 4.5 h > 225 4.5 7.1 0 2 4 6 8 10 mm/s rms Vibration Limits - Horizontal pumps (manufacturer's test facility) ¡Ü 200 kW > 200 kW ¡Ü 200 kW > 200 kW Cat 1 Cat 2 Zone A 2.50 3.50 3.20 4.20 Zone B 4.00 5.00 5.10 6.10 Zone C 6.60 7.60 8.50 9.50 0.00 2.00 4.00 6.00 8.00 10.00 mm/s rms Velocity - Zone Limits
- 15. Pump vibration standards 15 ¡Ü 200 kW > 200 kW ¡Ü 200 kW > 200 kW Cat 1 Cat 2 POR 3.30 4.30 4.20 5.20 AOR 4.00 5.00 5.10 6.10 0.00 2.00 4.00 6.00 8.00 10.00 mm/s rms Velocity - Factory Acceptance Test ¡Ü 200 kW > 200 kW ¡Ü 200 kW > 200 kW Cat 1 Cat 2 POR 2.50 3.50 3.20 4.20 AOR 3.40 4.40 4.20 5.20 0.00 2.00 4.00 6.00 8.00 10.00 mm/s rms Velocity - In situ Acceptance Alarm Shutdown Cat 1 ¡Ü 200 kW 5.00 8.30 Cat 1 > 200 kW 6.30 9.50 Cat 2 ¡Ü 200 kW 6.40 10.60 Cat 2 > 200 kW 7.60 11.90 0.00 2.00 4.00 6.00 8.00 10.00 12.00 14.00 16.00 mm/s rms Alarm & Shutdown Limits
- 16. Pump vibration standards 16 Standard ISO 13709 For pumps up to 300kW per stage and 3600rpm¡¯ POR AOR Overall 3.00 3.90 Descrete f 2.00 2.60 0.00 2.00 4.00 6.00 8.00 10.00 mm/s rms Velocity - Factory Acceptance Test overhung & between bearings pumps POR AOR Overall 5.00 6.50 Descrete f 3.35 4.35 0.00 2.00 4.00 6.00 8.00 10.00 mm/s rms Velocity - Factory Acceptance Test vertically suspended pumps
- 17. Pump vibration standards 17 Disclaimer: This Europump Guide is a free guide and intends to help the pump industry and its customers to present the essential points of each standard regarding vibration. While it attempts to provide accurate information, we make no warranty or representation of any kind with respect to the information included herein or its completeness or accuracy. We are not responsible for any action taken as a result of relying on or in any way using the information contained in this guide and in no event shall be liable for any damages resulting from reliance on or use of this information. We also make no representations as to the accuracy of the information provided in any of the guides linked to this and obviously cannot be responsible for any information contained in those guides. Users should, as with all information or reference material, use their own best judgment as to the usefulness and accuracy of any information presented. This Guide could contain inaccuracies, and changes to the information contained herein may be made at any time. This publication may be freely reproduced, except for advertising, endorsement or commercial purposes. Please acknowledge the source as Europump aisbl. All rights reserved 1st edition July 2013