Guilford's structure of intellect model
- 1. J.P. GuilfordŌĆÖs STRUCTURE OF INTELLECT MODEL / Three dimensional model (Revised) by Dr. Bonnie Amonge Crerar Assistant Professor, Assam Donbosco University, Guwahati
- 2. ŌĆó It is the result of Factor analytic research conducted by Guilford and his associates in the Psychological Laboratory, at the University of Southern California, USA. ŌĆó According to him an individuals performance on an intelligence test can be traced back to underlying mental abilities or factors of intelligence which are 180 in number and can be organized under the following three dimensions: ’āśOperations: act of thinking/ Psychological Process ’āśContent: content/ material i.e. nature of information on which one works ’āś Products: Outcome of the working of Operations on Content
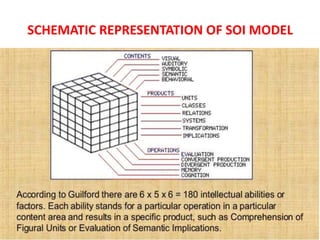
- 3. (Brain Operates) Operations (6) Contents (5) Products (6) Operat ions (6) ŌĆó Cognition : Becoming aware, discover, comprehend ŌĆó Memory recording: Encoding Information ŌĆó Memory retention: Ability to recall information ŌĆó Divergent thinking: Ability to generate multiple solutions ŌĆó Convergent thinking: Producing single solution ŌĆó Evaluation : Ability to judge similarity, differences and the best Conten ts (5) ŌĆó Visual: Information perceived through seeing ŌĆó Auditory: Information perceived through hearing ŌĆó Symbolic: Symbols and signs that have no meaning in themselves ŌĆó Semantic: Words/ sentences ŌĆō oral/ written or in oneŌĆÖs mind ŌĆó Behavioural: Acts of individual/ individuals Produc ts (6) ŌĆó Units: Single items of knowledge- words, shapes, facial expression ŌĆó Classes: Organizing units into groups based on shared attributes ŌĆó Relations: Linking units either as opposites, associates, sequences or analogues ŌĆó Systems: Multiple relation between units to create a network/ structures ŌĆó Transformations: Changes, perspectives, mutations to knowledge ŌĆó Implications: Predictions, inferences, consequences
- 4. SCHEMATIC REPRESENTATION OF SOI MODEL
- 5. EDUCATIONAL IMPLICATIONS OF THE SOI MODEL i. Intellect is a matter of skills and hence can be improvised through training. ii. Must consider individual differences among students. iii. Ability to judge peopleŌĆÖs behaviour . iv. Curriculum should be such that a combination of operations, content and product is made for the development of intellect.
- 6. References: /fraaanceee/structure-of- intelligence https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RnxGcmPlSVM /veerabalajikumar/intellig ence-testing Mangal. S. K. (2003). Advanced educational psychology. New Delhi: Prentice Hall.
Editor's Notes
- #4: These dimensions when multiplied 6x5x6 = 180 factors of intelligence.