HANS: Enabling CMY Metamers
- 1. HANS Enabling CMY Metamers J├Īn Morovi─Ź, Peter Morovi─Ź & Juan Manuel Garc├Ła-Reyero HewlettŌĆōPackard Company Barcelona, Spain Presented at ICC/HP Digital Print Day, 15th June 2011 201 ┬® HewlettŌĆōPackard Company 1
- 2. What makes printed colors? 201 ┬® HewlettŌĆōPackard Company 1
- 3. Print color formation Side view Additive Relative area coverages Neugebauer primaries 70% W 13% C 10% K 6% M Subtractive 1% CM 201 ┬® HewlettŌĆōPackard Company 1
- 4. Analog from digital 201 ┬® HewlettŌĆōPackard Company 1
- 5. From color to halftone pattern color separation color management CIE L*a*b* linearization color appearance model sRGB calibration device characterization SWOP CMYK halftoning color enhancement ... gamut mapping 201 ┬® HewlettŌĆōPackard Company 1
- 6. Controlling print color ŌĆō a ’¼ürst principles approach 201 ┬® HewlettŌĆōPackard Company 1
- 7. How do we get from color to halftone pattern? Halftone patternŌĆÖs Neugebauer Primary Halftone Source color Color management Printable color statistics pattern 20% W 30% C 20% M 0% Y 20% CM 0% CY 0% MY 0% CMY 201 ┬® HewlettŌĆōPackard Company 1
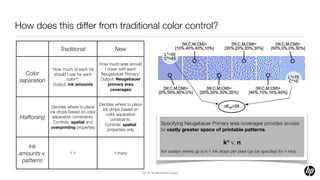
- 8. How does this differ from traditional color control? Traditional New How much area should ŌĆśHow much of each ink I cover with each Color should I use for each Neugebauer PrimaryŌĆÖ separation color?ŌĆÖ Output: Neugebauer Output: ink amounts primary area coverages Decides where to place Decides where to place ink drops based on ink drops based on color color separation Halftoning separation constraints. constraints. Controls: spatial and Specifying Neugebauer Primary area coverages provides access Controls: spatial overprinting properties properties only to vastly greater space of printable patterns. kn v. n Ink (for system where up to k-1 ink drops per pixel can be speci’¼üed for n inks) amounts v. 1:1 1:many patterns 201 ┬® HewlettŌĆōPackard Company 1
- 9. From theory to practice 201 ┬® HewlettŌĆōPackard Company 1
- 10. A minimal Halftone Area Neugebauer Separation setup (CMYK, 1bpp) Printable color 20% W 30% C 20% M 0% Y 20% CM 0% CY 0% MY 0% CMY 0% K 0% KC 0% KM 0% KY 0% KCM 0% KCY 0% KMY 0% KCMY Print & measure Compute convex Find printable Barycentric Select one NP per Neugebauer primary hull & tetrahedralize colorŌĆÖs enclosing coordinates are pixel & diffuse (NP) CIE XYZs hull NPs tetrahedron vertex NP areas NPac-NP error 201 ┬® HewlettŌĆōPackard Company 1
- 11. Optimizing HANS ŌĆó Form all polyhedra using the kn NPs ŌĆó Find all colors for which NPacs are to be optimized enclosed by each polyhedron ŌĆó Compute barycentric coordinates ŌĆó Evaluate each candidate (grain, ink use, color constancy, ...) ŌĆó Assign combined score ŌĆó Select best NPac for each color CMY 1dpp: kn=23=8 ŌåÆ 163 polyhedra CMYK 1dpp: kn=24=16 ŌåÆ 64839 polyhedra CMYKcm 2dpp: kn=36=729 ŌåÆ 2.8x10219 polyhedra 201 ┬® HewlettŌĆōPackard Company 1
- 12. Reductio ad absurdum ŌĆō the CMY case ŌĆó With traditional, colorant space control: no metamers ŌĆó each in-gamut color matched by one CMY colorant amount combination ŌĆó Even at max. 1 drop per pixel, CMY colorant set has 23=8 Neugebauer Primaries ŌĆó 3D colorimetric space to 8D NP space results in 1:many mapping ŌĆó 163 polyhedra span gamut and provide metamers ŌĆó midŌĆōgray: 115 metamers ŌĆó mean 13% ink use difference between metamer using most and least ink for each color ŌĆó More metamers still if more than one drop per pixel is used 201 ┬® HewlettŌĆōPackard Company 1
- 13. Does it work? 201 ┬® HewlettŌĆōPackard Company 1
- 14. Test setup: ŌĆśCan we ’¼ünd NPacs that use less ink?ŌĆÖ ŌĆó Printer: HP Designjet L65500 ŌĆó Inks: CMYKcm latex ŌĆó Substrate: Avery Self-Adhesive Vinyl ŌĆó Color samples: 748 Lab-uniform ISO coated v. 2 samples ŌĆó Color work’¼éows compared: ŌĆó Ink space separation, GCR optimized for low grain, ink space halftoning (current default) ŌĆó Ink space separation, maximum GCR optimized for low grain, ink space halftoning (current optimal) ŌĆó NPac space separation (optimized for minimum ink use) and halftoning (HANS) 201 ┬® HewlettŌĆōPackard Company 1
- 15. Results ŌĆō┬Āink use 201 ┬® HewlettŌĆōPackard Company 1
- 16. What next? 201 ┬® HewlettŌĆōPackard Company 1
- 17. Challenges and bene’¼üts ŌĆó Challenges: ŌĆó printer model accuracy (the more accurate the better the optimization) ŌĆó computational ef’¼üciency (weeks of computation per substrate) ŌĆó optimization (ef’¼ücient models of print attributes, ef’¼ücient traversal of NPac space) ŌĆó Bene’¼üts: ŌĆó greater & direct optimization (more from the same printer-ink-substrate) ŌĆó explicit tradeŌĆōoff among print attributes (grain v. ink use v. color constancy) ŌĆó inkset agnosticism (same process for CMY 1bpp and CMmYKkNnRGB 2bpp) ŌĆó More detail at this yearŌĆÖs IS&T/SID Color and Imaging Conference (subject to acceptance) 201 ┬® HewlettŌĆōPackard Company 1
- 18. Acknowledgements ŌĆō Lluis Abello ŌĆō Alan Lobban ŌĆō Carlos Amselem ŌĆō ├ōscar Martinez ŌĆō Xavi Bruch ŌĆō Scott Norum ŌĆō Gary Dispoto ŌĆō Michel Encrenaz ŌĆō Aleix Oriol ŌĆō I-Jong Lin ŌĆō Eduard Garcia ŌĆō Ramon Pastor ŌĆō John Recker ŌĆō Oriol Gasch ŌĆō Yvan Richard ŌĆō Ingeborg Tastl ŌĆō Rafa Gimenez ŌĆō Aurora Rubio ŌĆō Bob Ulichney ŌĆō Dudi Bakalash ŌĆō Josep Girlat ŌĆō Utpal Sarkar ŌĆō Lahav Langboim ŌĆō Rafael Goma ŌĆō Albert Serra ŌĆō Shay Maoz ŌĆō Andr├®s Gonzalez ŌĆō Jep Tarradas ŌĆō Amir Sheinman ŌĆō Jacint Hument ŌĆō Joan Uroz ŌĆō Alex Veis ŌĆō Johan Lammens ŌĆō Jordi Vilar ŌĆō Igor Yakubov 201 ┬® HewlettŌĆōPackard Company 1