Having fun with phonological awareness
- 1. HAVING FUN WITH PHONOLOGICAL AWARENESS By, Mark Smith & Jenny Kwong Shuk Wah IPG, Gaya Campus
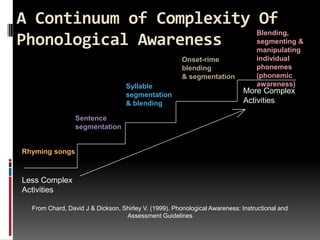
- 2. A Continuum of Complexity Of Blending, Phonological Awareness segmenting & manipulating Onset-rime individual blending phonemes & segmentation (phonemic Syllable awareness) segmentation More Complex & blending Activities Sentence segmentation Rhyming songs Less Complex Activities From Chard, David J & Dickson, Shirley V. (1999). Phonological Awareness: Instructional and Assessment Guidelines
- 3. 1.Rhyme Example Variation Row, row, row your boat ’é¦ Ba, ba, black sheep gently down the stream. Merrily, merrily, merrily, merri ly; Life is but a dream
- 4. 1.1 Sing to the tune ŌĆ£if youŌĆÖre happy and you know itŌĆ”ŌĆØ Did you ever see a cat /beŌłé/ in a hat /t╩āeŌłé/? Did you ever see a cat / beŌłé / in a hat / t╩āeŌłé/?? No, I never, no, I never, no, I never, no, I never No, I never saw a cat/ beŌłé / in a hat / t╩āeŌłé/?. Variations: A mouse in a house. A bear in a chair. An owl drying off with a towel.
- 5. 1.2 Rhyme Through Movement One potato, two potatoes, three potatoes, four Five potatoes, six potatoes, seven potatoes, more Task: In small groups, children sing the rhyme while passing around an object. The child holding the object at the end of the rhyme (on ŌĆśmoreŌĆÖ) must then state a word that begins with the same initial sound. i.e. /p/ Example: Vary with other food names such as banana /b/, papaya /p/, tomato /t/ etc.
- 6. 1.3 Make a Rhyme Example Variation Teddy Bear, Teddy Bear, ’é¦ Pussy Cat Jump around Teddy Bear, Teddy Bear, ’é¦ Daddy Dog Touch the ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ”. ’é¦ Speedy Spider Teddy Bear, Teddy Bear, Open the box ’é¦ Coco Cow Teddy Bear, Teddy Bear, ’é¦ Henny Hen Pull out the ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.. Teddy Bear, Teddy Bear, Bake a cake. Teddy Bear, Teddy Bear, Swim in the ŌĆ”ŌĆ”ŌĆ” .
- 7. 2.Sentence Segmentation Level Teacher cuts out green lily pads and places on classroom floor. Children then hop the number of times they hear words in a sentence dictated by the teacher. Alternative: Children clap the number of words heard in a sentence. Task: Practice some short sentences with your partner. Have them clap the number of words they hear. Swap roles.
- 8. 2.2 Sentence Segmentation Level Model Practise 1. Good morning children. 1. Ned has a newt in his net. 2. How are you today? 2. Penny has a penguin in her pack. 3. I am fine thank you. 3. Sally has a seal on her 4. What is your name?. seesaw. 5. Tomorrow we are going 4. Tom has a tiger in his tent. to town. 5. Alex has an ox in his box. 6. Yousef has a yak on his 6. Ahmad is working very yacht well today. 7. Zara has a zebra in her zoo.
- 9. 3. Syllable Level Objective: Students will be able to define syllables and recognise how many syllables are in a word ’é¦ ŌĆśMarkŌĆÖ : clap once (one syllable) ’é¦ ŌĆśJennyŌĆÖ: clap twice (two syllables) ’é¦ ŌĆścucumberŌĆÖ: clap thrice (three syllables)
- 10. 3.1 Syllable Level Name Game ’é¦ Write all of the childrenŌĆÖs names on index cards and place in a basket. ’é¦ Sit in a circle and pass the basket from one child to the next when the music begins. ’é¦ When the music stops, whoever is holding the basket pulls out a card and reads the childŌĆÖs name on the card. ’é¦ The class repeats the name and claps out the number of syllables or parts as they say the name (e.g. Jen-ny has 2 claps.
- 11. 3.2 Syllable Manipulation Model Practise ŌĆśSabahŌĆÖ. What ’é¦ Say robot without the ro would the word ’é¦ Say table without the ta say If I took off ’é¦ Say potato without the po the ŌĆśSaŌĆÖ? ’é¦ Say cucumber without the cu Elicit: It would say ŌĆśbahŌĆÖ and now we Other Examples?? only have 1 syllable. Source: Blevins (1997: 58)
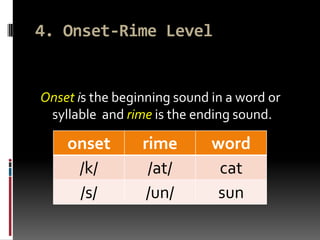
- 12. 4. Onset-Rime Level Onset is the beginning sound in a word or syllable and rime is the ending sound. onset rime word /k/ /at/ cat /s/ /un/ sun
- 13. 4.1 Developing Limericks Guided Practice Model In groups use the following words to make up your own limerick. Mat There was a young boy called ŌĆ” Who had an overly large ŌĆ” Siti, mouse, kitty, house/in/ When it chased the ŌĆ” It shook the ŌĆ” So Mat got rid of the ŌĆ” Sharing Now read your poem aloud to your friends.
- 14. 4.2 Creating Rhyming Poems Model Extension of Variations Using the word family chart ’é¦ /in/ developed by the children, create simple ’é¦ /ip/ rhyming poems. ’é¦ /op/ Eg. ’é¦ /ick/ My Cat My cat is very fat. ’é¦ /eck/ He should be chasing the rat. But instead he sits on the mat And expects a pat. Oh, my cat is very fat.
- 16. 5.2. Phoneme Matching Initial (beginning) sound Final (ending) sound Middle sound Possible Activities: ’é¦ Teacher distributes pictures to students who must then match the pictures according to the teacherŌĆÖs instructions. ’é¦ Snap.. Card Game.
- 17. 5.3. Phoneme Substitution The Teacher has students listen as he/she says a CVC word eg. ŌĆśbugŌĆÖ. ŌĆ£How many magnets will I use?ŌĆØ (3) ŌĆ”. ŌĆ£LetŌĆÖs countŌĆ”ŌĆØ ŌĆ£What about if I change the /b/ to a /m/? What is the word now? ŌĆ” ŌĆ£Now lets try ŌĆśdadŌĆÖ. How many sounds do you hear? (3) ŌĆ” So, how many magnets? (3) ŌĆ” ŌĆ£Do you hear any sounds that are the same?ŌĆØ (d)ŌĆ” So our beginning and ending sound will be the same colour. TASK: In pairs, use magnets to practice the above procedure with other 3 letter words. E.g. ŌĆśbatŌĆÖ ŌĆśtopŌĆÖ ŌĆśfatŌĆÖ etc.
- 18. 5.4. Phoneme Blending Explain to children that you are going to say a word in parts. (Robot Talk) You want them to listen carefully, and then say the word as a whole. i.e. blend the sounds. For e.g. If I say /m/ /a/ /p/, you would sayŌĆ”.. ŌĆśmapŌĆÖ. What about if I say /t/ /o/ /p/ ? TASK: In pairs practise the above procedure with the following words. Remember not to show your ŌĆśstudentŌĆÖ the letters. Practice e.gs: /m/ /o/ /p/, /f/ /i/ /t/, /s/ /u/ /n/, /c/ /a/ /t/.
- 19. 5.4 Guess It! Place picture cards in a bag and draw out one picture at a time. Tell the children I can see a /k/ an /a/ and a /t/. Show the picture card for children to check their response. Teaching points: Commence at easier level first e.g. Onset-rime and gradually increase difficulty level. E.g. I can see a /c/ /at/ BEFORE I can see a /c/ /a/ /t/. Invite children to be the ŌĆśteacherŌĆÖ.
- 20. 5.5. Phoneme Segmentation Involves children segmenting the sounds they hear in an oral word. Teacher Dialogue: IŌĆÖm going to say a word and I want you to listen very carefully and tell me all the sounds you hear in that word. For e.g. If I say the word ŌĆśmopŌĆÖ you would say /m/ /o/ /p/. Understand? TASK: In pairs , role play a teacher and student using the following words: /Hi/, /it/, /so/, /sat/, /top/, /map/ NB: This is a purely aural task. Ensure ŌĆśchildrenŌĆÖ canŌĆÖt see the words you are dictating.
- 21. 5.5 Segmentation Cheer Change the words in the 3rd line of the first stanza each time you say the cheer. Instruct children to segment the word sound by sound. Listen to my cheer. Then shout the sounds you hear. Sun! Sun! Sun! LetŌĆÖs take apart the word sun! Give me the beginning sound. (Children respond with /s/) Give me the middle sound. (Children respond with /u/) Give me the ending sound. (Children respond with /n/) ThatŌĆÖs right! /s/ /u/ /n/ - Sun! Sun! Sun!
- 22. 5.6. Phoneme Deletion & Addition Explicit Instruction: ŌĆ£IŌĆÖm going to take a word and make new words using it. I can take the /s/ off sat, put on a /p/, and I have a new word ŌĆō pat. Guided Practice: Have children replace the first sound in each word you say with a /s/. hit, well, funny, bun, mad, bend, rat, rope. NB: Once children are familiar with substituting initial sounds, move onto final sounds and finally middle sounds.
- 23. 5.6 Phoneme Deletion Exercises 1. Initial Phoneme ’é¦ Say part without the /p/ ’é¦ Say sun without the /s/ 2. Final Phoneme ’é¦ Say meat without the /t/ ’é¦ Say mop without the /p/ ’é¦ Say take without the /k/ 3. Second consonant in an initial blend ’é¦ Say spell without the /p/ ’é¦ Say clap without the /l/ Source: Blevins (1997:58)
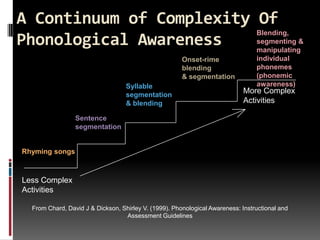
- 24. A Continuum of Complexity Of Blending, Phonological Awareness segmenting & manipulating Onset-rime individual blending phonemes & segmentation (phonemic Syllable awareness) segmentation More Complex & blending Activities Sentence segmentation Rhyming songs Less Complex Activities From Chard, David J & Dickson, Shirley V. (1999). Phonological Awareness: Instructional and Assessment Guidelines
- 25. Individual Phoneme Level Yopp & Yopp (2000) suggest 6 levels of phoneme manipulation: 1. Identification 2. Matching 3. Substitution 4. Blending 5. Segmenting 6. Deletion & Addition
- 26. List of References Chard, D. J., & Dickson, S. V. (1999). Phonological Awareness: Instructional Assessment Guidelines. Retrieved, July 31, 2007, from http://www.ldonline.org Blevins, W. (1997). Phonemic Awareness Activities For early Reading Success. Ashton Scholastic, New York. Adams, M.J.(1990). Beginning to read: Thinking & Learning about print. Cambridge, MA: MIT press. Chard, D.J. & Dickson, S.V. (1999). Phonological Awareness: Instructional and Assessment Guidelines. Retrieved, July 31, 2007 from http://www.ldonline.org Juel, C., Griffith, P.L.,& Gough, P.B. (1986). Acquisition of literacy: A Longitudinal study of children in first and second grade. Journal of Educational Psychology, 78,243-255. Yopp, H.K., & Yopp, R.H.(2000). Supporting Phonemic Awareness in the classroom. Reading Teacher, 54, 130-141.