Hazard And Risk Management.pdf
- 1. Presented By: Miss. Mohini Tawade, First Year M. Pharmacy, Department of Quality Assurance, Guided By: Dr. (Mrs.) Shubhangi Pharande, Dr. D.Y. Patil College of Pharmacy, Akurdi, Pune. Hazard And Risk Management
- 2. 8/03/20XX PITCH DECK 2 INTRODUCTION Hazard: ÔÉòSituation that posses a level of threat to life, health, property, or environment ÔÉòHazard Management involves identifying hazard, assessing the hazard, and controlling the risk. Risk: ÔÉòRisk = Probability + Severity ÔÉòRisk management involves risk identification, assessment, mitigation, elimination and communication.
- 3. Importance of Risk Assessment and Risk Management: ÔÇß Identifying and understanding potential risk ÔÇß Prioritizing Risks/ Risk Ranking ÔÇß Preventing or minimizing the negative impact on the organization ÔÇß Enhancing decision-making ÔÇß Ensuring compliance with regulations and standards ÔÇß Supporting continues improvement ÔÇß Cost-effective resource allocation ÔÇß Corrective and Preventive Action
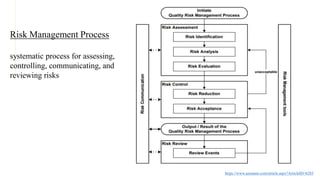
- 4. Risk Management Process systematic process for assessing, controlling, communicating, and reviewing risks https://www.azonano.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=6283
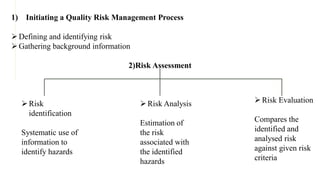
- 5. 1) Initiating a Quality Risk Management Process ÔÉòDefining and identifying risk ÔÉòGathering background information 2)Risk Assessment ÔÉòRisk identification Systematic use of information to identify hazards ÔÉòRisk Analysis Estimation of the risk associated with the identified hazards ÔÉòRisk Evaluation Compares the identified and analysed risk against given risk criteria
- 6. 3) Risk Control ÔÉòRisk Reduction: Reduce the risk to an acceptable level. ÔÉòRisk acceptance 4) Risk Communication ÔÉòSharing the information of risk and risk management documents between the decision- makers and others 5) Risk Review ÔÉòThe output/results of the risk management process should be reviewed
- 7. Risk Management Methods and Tools: ÔÉòBasic Risk Management Facilitation Methods For example Flowcharts; Check Sheets; Process Mapping; Cause and Effect Diagrams (also called an Ishikawa diagram or fishbone diagram) ÔÉòFailure Mode Effects Analysis (FMEA) Used to evaluate failure mode for processes and its effect on results or product performance. ÔÉòFailure Mode, Effects, and Criticality Analysis (FMECA) Investigation of the degree of severity of the outcomes, their respective probabilities of occurrence, and their detectability. ÔÉòFault Tree Analysis (FTA) Determines the possible causes and probability of occurrence of an unexpected event.
- 8. 8 ÔÉòHazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) It is a systematic, proactive, and preventive tool for assuring product quality, reliability, and safety ÔÉòPreliminary Hazard Analysis (PHA) Analysis based on applying prior experience or knowledge of a hazard or failure to identify future hazards ÔÉòRisk Ranking and Filtering ÔÉòSupporting Statistical Tools Enable effective data assessment and facilitate more reliable decision making
- 9. 9 Preliminary Hazard Analysis: Preliminary hazard analysis (PHA) is a semi-quantitative analysis that is performed to: ÔÉòIdentify all potential hazards and accidental events that may lead to an accident ÔÉòRank the identified accidental events according to their severity ÔÉòIdentify required hazard controls measures and follow-up actions ÔÉòAs an initial step of a detailed risk analysis of a system concept or an existing system.
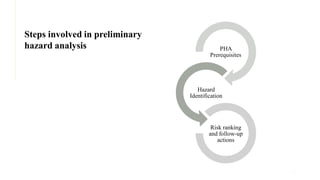
- 10. 10 PHA Prerequisites Hazard Identification Risk ranking and follow-up actions Steps involved in preliminary hazard analysis