Hbo leadership
- 1. EULOGIO “AMANG” RODRIGUEZ INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (EARIST) TOPIC: LEADERSHIP SUBMITTED TO: DR. DIOSDADO MEDINA SUBMITTED BY: JANET ESPORLAS LINQUICO
- 2. Leadership LEADERS ARE CALLED TO STAND IN THAT LONELY PLACE BETWEEN NO LONGER AND THE NOT YET AND INTENTIONALLY MAKE DECISIONS THAT WILL BIND, FORGE, MOVE AND CREATE HISTORY. WE ARE NOT CALLED TO BE POPULAR, WE ARE NOT CALLED TO BE SAFE, WE ARE NOT CALLED TO FOLLOW, WE ARE THE ONES CALLED TO TAKE RISKS, WE ARE THE ONES CALLED TO CHANGE ATTITUDES; TO RISK DISPLEASURES WE ARE THE ONES CALLED TO GAMBLE OUR LIVES, FOR A BETTER WORLD MARY LOU ANDERSON, APRIL 1970
- 3. LEAD To guide or conduct by showing the way To direct and govern To show the method of attaining an objective To entice, allure, induce, influence To go before and show the way
- 4. LEADER One who leads or conducts A guide or point of reference
- 5. LEADERSHIP The position, office, term, or function of a leader The capacity to be a leader The ability to lead The act or instance of leading The "people side" of the job
- 6.  MANAGE  To handle  To have under control  To conduct, carry on, guide  To move or use in the desired manner  To be cautious and use good judgment with people  To be concerned with all aspects of the organization
- 7. MANAGER The one who manages The one who has the guidance or direction over everything The one who is at the head of an undertaking
- 8.  MANAGEMENT  The act, manner, or practice of managing, handling, directing, or controlling something  The person/persons who manage a place, business, establishment, organization, or institution  Skill in managing  Executive ability  The technical/academic side of being a teacher or administrator
- 9. ď‚—Managers involves power by position. ď‚—Leaders involves power by influence.
- 10. Abraham Zaleznik (1977) ď‚—leaders as inspiring visionaries, concerned about substance ď‚—managers he views as planners who have concerns with process
- 11. Warren Bennis (1989) ď‚— Managers administer, leaders innovate ď‚— Managers ask how and when, leaders ask what and why ď‚— Managers focus on systems, leaders focus on people ď‚— Managers do things right, leaders do the right things ď‚— Managers maintain, leaders develop ď‚— Managers rely on control, leaders inspire trust
- 12. ď‚— Managers have a short-term perspective, leaders have a longer-term perspective ď‚— Managers accept the status-quo, leaders challenge the status-quo ď‚— Managers have an eye on the bottom line, leaders have an eye on the horizon ď‚— Managers imitate, leaders originate ď‚— Managers emulate the classic good soldier, leaders are their own person ď‚— Managers copy, leaders show originality
- 13. Paul Birch (1999) ď‚—managers concerned themselves with tasks ď‚—leaders concerned themselves with people
- 14. Bruce Lynn ď‚—A Leader optimizes upside opportunity ď‚—Manager minimizes downside risk.
- 15. PATRICIA PITCHER (1994)  Three Types of Leaders 1. Artists – imaginative, inspiring, visionary, entrepreneurial, intuitive, daring, emotional 2. Craftsmen – well-balanced, steady, reasonable, sensible, predictable 3. Technocrats – cerebral, detail-oriented, fast, uncomprising, hard-headed
- 16. LEADERSHIP •DEFINED AS A PROCESS OF INFLUENCING THE ACTIVITIES OF FORMAL AND INFORMAL WORK GROUPS IN THEIR TASKS OF GOAL SETTING AND GOAL ACHIEVEMENT. •IT IS THE ART OR PROCESS OF INFLUENCING PEOPLE SO THAT THEY WILL STRIVE WILLINGLY AND ENTHUSIASTICALLY TOWARD TO ATTAINMENT OF GROUP GOALS. •IT IS COORDINATING AND MOTIVATING INDIVIDUALS AND GROUPS TO ACHIEVE DESIRED ENDS
- 17. Hemphill and Coons, 1967 LEADERSHIP IS THE BEHAVIOR OF AN INDIVIDUAL WHEN HE IS DIRECTING THE ACTIVITIES OF A GROUP TOWARD A SHARED GOAL.
- 18. Tannenbaum, Wesler & Massrik, 1967 LEADERSHIP IS INTERPERSONAL INFLUENCE, EXERCISED IN A SITUATION AND DIRECTED, THROUGH THE COMMUNICATION PROCESS, TOWARD THE ATTAINMENT OF A SPECIAL GOAL OR GOALS.
- 19. Stogdill, 1974 LEADERSHIP IS INITIATION AND MAINTENANCE OF STRUCTURE IN EXPECTATION AND INTERACTION.
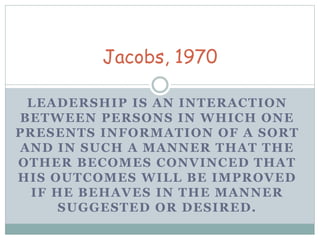
- 20. Jacobs, 1970 LEADERSHIP IS AN INTERACTION BETWEEN PERSONS IN WHICH ONE PRESENTS INFORMATION OF A SORT AND IN SUCH A MANNER THAT THE OTHER BECOMES CONVINCED THAT HIS OUTCOMES WILL BE IMPROVED IF HE BEHAVES IN THE MANNER SUGGESTED OR DESIRED.
- 21. Janda, 1987 LEADERSHIP IS A PARTICULAR TYPE OF POWER RELATIONSHIP CHARACTERIZED BY A G ROU P MEMB E R ’ S P E R C E P T I ON THA T ANOTHER GROUP MEMBER HAS THE RIGHT TO PRESCRIBE BEHAVIOR PATTERNS FOR THE FORMER REGARDING HIS ACTIVITY AS A GROUP MEMBER.
- 22. Kochan, Schmit & Coties, 1975 LEADERSHIP IS AN INFLUENCE PROC ES S WHEREBY O’ S AC T ION CHANGED P ’ S BEHAVIOR AND P VIEW THE INFLUENCE ATTEMPT AS BEING LEGITIMATE AND THE CHANGE AS BEING CONS I S TENT WI TH P ’ S GOAL .
- 23. Katz, & Khan, 1978 LEADERSHIP IS THE INFLUENTIAL INCREMENT OVER AND ABOVE MECHANICAL COMPLIANCE WITH THE ROUTINE DIRECTIVES OF THE ORGANIZATION.
- 24. Leadership Effectiveness 1 . LEADERSHIP INVOLVES THE MOST VITAL RESOURCES OF ANY ORGANIZATION THE PEOPLE. 2. POWER DISTRIBUTION BETWEEN LEADERS AND GROUP MEMBERS IS UNEQUAL. 3. LEADERSHIP INVOLVES THE USE OF DIFFERENT FORMS OF POWER TO INFLUENCE THE BEHAVIOR OF FOLLOWERS. 4. LEADERSHIP IS ABOUT VALUES.
- 25. Dimensions of Leadership Behavior 1. THE ABILITY TO USE POWER EFFECTIVELY AND IN A RESPONSIBLE MANNER. 2. THE ABILITY TO COMPREHEND THAT HUMAN BEINGS HAVE DIFFERENT MOTIVATION FORCES AT DIFFERENT TIMES AND IN DIFFERENT SITUATIONS.
- 26. Theories of Leadership TRAIT THEORY – THE LEADER IS CONCEIVED TO B E A “ G R E A T MA N ” WH O S E S U P E R I O R ENDOWMENTS INDUCE OTHERS TO FOLLOW HIM. ENVIRONMENT THEORY - IT EXPLAINS LEADERSHIP ON THE BASIS OF SITUATIONS AND CRISES THAT PROVIDES OPPORTUNITIES FOR THE PEOPLE. PERSONAL-ENVIRONMENTAL THEORY – MAINTAINS THAT CHARACTERISTICS OF A LEADER, THE FOLLOWERS AND THE SITUATIONS THAT INTERACT DETERMINE WHO WILL BE THE LEADER.
- 27. Theories of Leadership EXCHANGE THEORY – IT SUGGEST THAT GROUP INTERACTION REPRESENTS AN EXCHANGE PROCESS IN WHICH LEADERSHIP IS CONFERRED UPON THE MEMBER WHOSE EFFORTS APPEARS MORE LIKELY TO REWARD OTHER MEMBERS FOR THEIR EFFORT ON BEHALF OF THE GROUP. HUMANISTIC THEORY – IT IS BASED ON THE HYPOTHESIS THAT GROUPS WILL BE MORE EFFECTIVE AND MEMBERS WILL BE BETTER SATISFIED WHEN THE LEADER ALLOWS FOLLOWERS FREEDOM TO SATISFY THEIR NEEDS FOR ACHIEVEMENT AND SELF - ACTUALIZATION.
- 28. Theories of Leadership EXCEPTIONAL THEORY – IT MAINTAINS THAT LEADERSHIP IS MOST LIKELY TO BE ACHIEVED BY THE MEMBER WHO SUCCEEDS IN INITIATING AND RE-ENFORCING THE EXPECTATIONS THAT HE WILL MAINTAIN THE ROLE OF STRUCTURE AND GOAL DIRECTION OF THE GROUP. CONTINGENCY THEORY – IT PROPOSES THAT A GIVEN PATTERN OF LEADERSHIP BEHAVIOR WILL LEAD TO EFFECTIVE GROUP PERFORMANCE IN SOME CIRCUMSTANCES, AND INEFFECTIVE, IN SOME CASES
- 29. Theories of Leadership PATH-GOAL THEORY – IT SUGGEST THAT CERTAIN PATTERNS OF LEADER BEHAVIOR FACILITATE THE CLARIFICATION OF THE GROUP GOAL WHILE OTHER PATTERNS OF BEHAVIOR STIMULATE EFFECTIVE INSTRUMENTS AND RESPONSE ON THE FOLLOWER GROUP.
- 30. Styles of Leadership 1 . TASK-ORIENTED LEADERSHIP – THE LEADERS LOOK TOWARD ACHIEVING GOOD INTERPERSONAL RELATION BY WAY OF ATTAINING A POSITION OF PERSONAL PROMINENCE IN THE ORGANIZATION. 2. PEOPLE-ORIENTED LEADERSHIP – THE RELATION OF LEADER PERSONALITY AND BEHAVIOR TO THE FOLLOWER AND GROUP RESPONSE.
- 31. Styles of Leadership Based on the Use of Authority 1. AUTOCRATIC LEADER • DEMOCRATIC OR PARTICIPATIVE LEADER • BENEVOLENT-AUTOCRAT • LIBERAL LEADER OR FREE-REIN LEADER
- 32. Styles of Leadership Based on the Use of Authority 2. LAISSEZ-FAIRE – TO LET PEOPLE DO AS THEY CHOOSE. NO LEADERSHIP AT ALL 3. MANIPULATED-INSPIRATIONAL – THE LEADER OF THE GROUP OF LEADERS SETS THE RULES AND INTERPRETS THEM AS THEY SEE.
- 33. Ten Powerful Tools of Leadership 1. PERSUASION 2. PATIENCE 3. GENTLENESS 4. TEACHABLE 5. ACCEPTANCE
- 34. Ten Powerful Tools of Leadership 6. KINDNESS 7 . COMPASSIONATE CONFRONTATION 8. CONSISTENCY 9. OPENNESS 10. INTEGRITY
- 35. The Art of Leadership 1 . THE LEADER IS A GREAT SERVANT. 2 . THE LEADER SEES THINGS THROUGH THE EYES OF HIS FOLLOWERS. 3. T H E L E A D E R D O E S N O T S A Y , “ G E T G O I N G ! , I N S T E A D T H E S A Y S . “ L E T S G O ” A N D L E A D S T H E WAY. 4 . THE LEADER DUPLICATES HIMSELF IN THE OTHERS. 5 . THE LEADER DOES NOT HOLD PEOPLE DOWN, HE LIFTS THEM UP.
- 36. The Art of Leadership 6. THE LEADER HAS FAITH IN PEOPLE. 7. THE LEADER USES HIS HEART AS WELL AS HIS HEAD. 8. THE LEADER IS A SELF STARTER. 9. THE LEADER HAS A SENSE OF HUMOR 10. THE LEADER CAN BE LEAD. 1 1 . THE LEADER KEEPS HIS EYES ON HIS GOALS.
- 37. Traits of a Leader 1 . KNOWLEDGE 2 . BEARING 3 . COURAGE 4 . ENDURANCE 5 . ENTHUSIASM
- 38. Traits of a Leader 6. INTEGRITY 7 . DECISIVENESS 8. DEPENDABILITY 9. FORCE 10 HUMILITY
- 39. Traits of a Leader 1 1 . HUMOR 12. INITIATIVE 13. JUDGMENT 14. JUSTICE 1 5 . LOYALTY
- 40. Traits of a Leader 16. SYMPATHY 1 7 . EMPATHY 18. TACT 19. UNSELFISHNESS 20. WIT
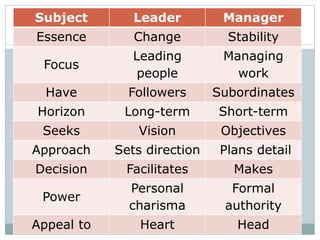
- 41. Subject Leader Manager Essence Change Stability Focus Leading people Managing work Have Followers Subordinates Horizon Long-term Short-term Seeks Vision Objectives Approach Sets direction Plans detail Decision Facilitates Makes Power Personal charisma Formal authority Appeal to Heart Head
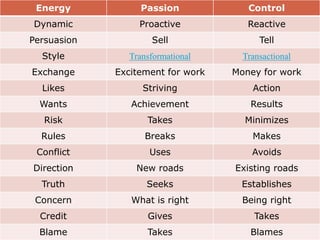
- 42. Energy Passion Control Dynamic Proactive Reactive Persuasion Sell Tell Style Transformational Transactional Exchange Excitement for work Money for work Likes Striving Action Wants Achievement Results Risk Takes Minimizes Rules Breaks Makes Conflict Uses Avoids Direction New roads Existing roads Truth Seeks Establishes Concern What is right Being right Credit Gives Takes Blame Takes Blames
- 43. Leadership Questionnaire Instructions Objective: To determine the degree that a person likes working with tasks and people. ď‚— never sometimes always ď‚— 0 1 2 3 4 5 ď‚— ď‚— _______ I encourage my team to participate when it comes decision making time and I try to implement their ideas and suggestions. ď‚— ď‚— _______ Nothing is more important than accomplishing a goal or task. ď‚— ď‚— _______ I closely monitor the schedule to ensure a task or project will be completed in time. ď‚— ď‚— _______ I enjoy coaching people on new tasks and procedures. ď‚— ď‚— _______ The more challenging a task is, the more I enjoy it.
- 44. Leadership Questionnaire ď‚— _______ I encourage my employees to be creative about their job. ď‚— ď‚— _______ When seeing a complex task through to completion, I ensure that every detail is accounted for. ď‚— ď‚— _______ I find it easy to carry out several complicated tasks at the same time. ď‚— ď‚— _______ I enjoy reading articles, books, and journals about training, leadership, and psychology; and then putting what I have read into action. ď‚— ď‚— _______ When correcting mistakes, I do not worry about jeopardizing relationships. Instructions Objective: To determine the degree that a person likes working with tasks and people.
- 45. Leadership Questionnaire Instructions Objective: To determine the degree that a person likes working with tasks and people. ď‚— _______ I manage my time very efficiently. ď‚— ď‚— _______ I enjoy explaining the intricacies and details of a complex task or project to my employees. ď‚— ď‚— _______ Breaking large projects into small manageable tasks is second nature to me. ď‚— ď‚— _______ Nothing is more important than building a great team. ď‚— ď‚— _______ I enjoy analyzing problems.
- 46. Leadership Questionnaire Instructions Objective: To determine the degree that a person likes working with tasks and people. ď‚— _______ I honor other people's boundaries. ď‚— ď‚— _______ Counseling my employees to improve their performance or behavior is second nature to me. ď‚— ď‚— _______ I enjoy reading articles, books, and trade journals about my profession; and then implementing the new procedures I have learned.
- 47. Scoring Section After completing the Questionnaire, transfer your answers to the spaces below: ď‚— People ď‚— Question ď‚— 1.______ ď‚— 4.______ ď‚— 6.______ ď‚— 9.______ ď‚— 10.______ ď‚— 12.______ ď‚— 14.______ ď‚— 16.______ ď‚— 17.______ ď‚— TOTAL ________ ď‚— X 0.2 = ________ ď‚— (multiple the Total by 0.2 to get your final score) ď‚— Task ď‚— Question ď‚— 2.______ ď‚— 3.______ ď‚— 5.______ ď‚— 7.______ ď‚— 8.______ ď‚— 11.______ ď‚— 13.______ ď‚— 15.______ ď‚— 18.______ ď‚— TOTAL ________ ď‚— X 0.2 ________ ď‚— (multiple the Total by 0.2 to get your final score)
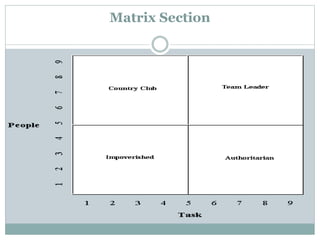
- 48. Matrix Section