Hci week1 stamford edit
- 1. CChhaapptteerr 11 ÓĖøÓĖÅÓĖÅÓĖ┤ÓĖ┤ÓĖ¬ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒ÓĖ▒ÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ×ÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖśÓĖśÓ╣īÓ╣īÓĖŻÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖ░ÓĖ½ÓĖ¦ÓĖ¦Ó╣łÓĖ▓Ó╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖ£ÓĖ£ÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓ╣āÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓ╣āÓĖŖÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓ╣üÓ╣ēÓ╣üÓĖźÓĖźÓĖ░ÓĖ░ ÓĖäÓĖŁÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ×ÓĖ┤ÓĖ¦ÓĖ┤ÓĖ¦Ó╣ĆÓ╣ĆÓĖĢÓĖĢÓĖŁÓĖŻÓĖŻÓ╣īÓ╣ī HHuummaann--CCoommppuutteerr IInntteerrffaaccee [[HHCCII]] IITTEE 225544 bbyy ÓĖŁ..ÓĖ¬ÓĖ¬ÓĖ┤ÓĖ┤ÓĖŻÓĖŻÓĖ┤ÓĖ×ÓĖ┤ÓĖ×ÓĖŻ ÓĖæÓĖæÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ░ÓĖ░ÓĖźÓĖźÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖ×ÓĖ×ÓĖ╣ÓĖÖÓĖ╣ÓĖÖ ssiirriippoorrnntthhiittaa@@ggmmaaiill..ccoomm
- 2. Lecturer ŌĆó ÓĖŁ.ÓĖ¬ÓĖ┤ÓĖŻÓĖ┤ÓĖ×ÓĖŻ ÓĖæÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ░ÓĖźÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖ×ÓĖ╣ÓĖÖ ŌĆó Education ŌĆō B.Sc in Computer Science, Silpakorn University ŌĆō M.Sc in Computer Management, Mahidol University ŌĆō Ph.D. in Management Science, Silpakorn University, 2013 - now
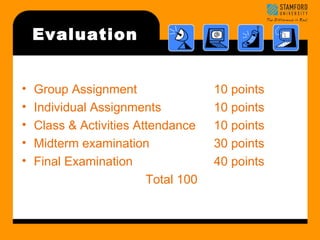
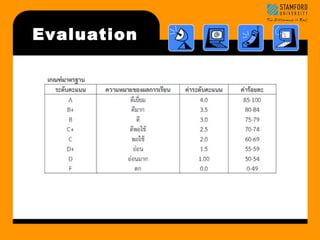
- 3. Evaluation ŌĆó Group Assignment 10 points ŌĆó Individual Assignments 10 points ŌĆó Class & Activities Attendance 10 points ŌĆó Midterm examination 30 points ŌĆó Final Examination 40 points Total 100
- 4. Evaluation
- 5. Materials Yvonne Rogers, Helen Sharp, Jenny Preece, Interaction Design: Beyond Human - Computer Interaction, 3rd Edition, John Wiley & Sons, April 2011 Shneiderman, B. and Plaisant, C., Designing the U ser Interface: Strategies for E ffective Human-Computer Int eraction:.
- 6. TodayŌĆÖs Topics 1. Introduction - What is HumanŌĆōcomputer interface ? 2. Importance of user Interface 3. Importance of good design 4. Benefits of good design 5. Good and Poor Designs 6. The User Experience 7. The Process of Interaction Design 8. Assignments
- 7. Introduction HumanŌĆōcomputer interface (HCI),alternatively man machine interaction (MMI) or computerŌĆōhuman inter action (CHI) is the study of interaction between peo ple (users) and computers.
- 8. Introduction With today's technology and tools, and our motivation to create really effective and usable interfaces and screens, why do we continue to produce systems that are inefficient and confusing or, at worst, just plain unusable? Is it because: 1. We don't care? 2. We don't possess common sense? 3. We don't have the time? 4. We still don't know what really makes good design?
- 9. Definition ACM ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ the Association for Computer Machinery Ó╣äÓĖöÓ╣ēÓĖÖÓĖ┤ÓĖóÓĖ▓ÓĖĪ HCI ÓĖ¦Ó╣łÓĖ▓ ÓĖäÓĖĘÓĖŁ ÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖäÓ╣īÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖŻÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣ł Ó╣ĆÓĖüÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖ¦ÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖŁÓĖŁÓĖüÓ╣üÓĖÜÓĖÜ ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░Ó╣ĆÓĖĪÓĖÖÓĖ┤ÓĖ£ÓĖź Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖÖÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣äÓĖøÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖÜÓĖÜÓĖäÓĖŁÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ┤ÓĖ¦Ó╣ĆÓĖĢÓĖŁÓĖŻÓ╣īÓ╣üÓĖÜÓĖÜÓĖĪÓĖĄÓĖøÓĖÅÓĖ┤ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒ÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖśÓ╣ī ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖĪÓĖÖÓĖĖÓĖ®ÓĖóÓ╣ī Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ÓĖ©ÓĖČÓĖüÓĖ®ÓĖ▓Ó╣ĆÓĖüÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖ¦ÓĖüÓĖÜÓĖ▒ ÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖÅÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖōÓ╣īÓĖĢÓĖ▓Ó╣łÓĖćÓ╣å ÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣ł Ó╣ĆÓĖüÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖ¦ÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖć Ó╣éÓĖöÓĖóÓĖ¬ÓĖŻÓĖĖÓĖø HCI ÓĖ½ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓĖ¢ÓĖćÓĖČ ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ©ÓĖČÓĖüÓĖ®ÓĖ▓Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ÓĖ¦ÓĖ┤Ó╣ĆÓĖäÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖ░ÓĖ½Ó╣ī Ó╣ĆÓĖüÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖ¦ÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÜ ÓĖøÓĖÄÓĖ¬ÓĖ┤ÓĖ▒ÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖśÓ╣ī ÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖ½ÓĖ¦Ó╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖŁÓĖĖÓĖøÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖōÓ╣īÓĖäÓĖŁÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ┤ÓĖ¦Ó╣ĆÓĖĢÓĖŁÓĖŻÓ╣ī ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖÜÓĖÜÓĖäÓĖŁÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ┤ÓĖ¦Ó╣ĆÓĖĢÓĖŁÓĖŻÓ╣ī ÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓĖ£ÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖćÓĖ▓ÓĖÖ Ó╣ĆÓĖ×ÓĖŁÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖĢÓĖŁÓĖÜÓ╣éÓĖłÓĖŚÓĖóÓ╣ī ÓĖ¦Ó╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖŁÓĖóÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓ╣äÓĖŻÓĖłÓĖČÓĖćÓĖłÓĖ░ÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣āÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓ╣ēÓĖ░ÓĖÜÓĖÜÓĖäÓĖŁÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ┤ÓĖ¦Ó╣ĆÓĖĢÓĖŁÓĖŻÓ╣ī Ó╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖćÓĖ▓ÓĖÖ ÓĖćÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖó ÓĖĪÓĖøÓĖĄÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖ¬ÓĖŚÓĖ┤ÓĖśÓĖ┤ÓĖĀÓĖ▓ÓĖ× Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖ¬ÓĖŚÓĖ┤ÓĖśÓĖ┤ÓĖ£ÓĖź Ó╣éÓĖöÓĖóÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖóÓĖĖÓĖüÓĖĢÓ╣īÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ē
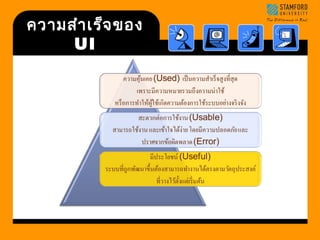
- 11. Goals of HCI FFuunnccttiioonnaall SSaaffee UUssaabbllee ŌĆóŌĆóEEaassyy ttoo lleeaarrnn ŌĆóŌĆóEEaassyy ttoo uussee Ó╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ēÓĖ▓ÓĖ½ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖć HCI ÓĖäÓĖĘÓĖŁ ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ£ÓĖźÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖÜÓĖÜÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖøÓĖÅÓĖ┤ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒ÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖśÓ╣īÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖ½ÓĖ¦Ó╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖĪÓĖÖÓĖĖÓĖ®ÓĖóÓ╣īÓ╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ÓĖäÓĖŁÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ┤ÓĖ¦Ó╣ĆÓĖĢÓĖŁÓĖŻÓ╣īÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖĪÓĖĄÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖøÓĖźÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖĀÓĖ▒ÓĖó(Safety) ,ÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ē ÓĖĪÓĖĄÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░Ó╣éÓĖóÓĖŖÓĖÖÓ╣īÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓ╣äÓĖöÓ╣ēÓĖłÓĖŻÓĖ┤ÓĖć (Utility) ,ÓĖĪÓĖĄÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖ¬ÓĖ┤ÓĖŚÓĖśÓĖ┤ÓĖ£ÓĖźÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓ╣äÓĖöÓ╣ēÓ╣ĆÓĖŻÓ╣ćÓĖ¦(Effectiveness), ÓĖĪÓĖĄÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖ¬ÓĖ┤ÓĖŚÓĖśÓĖ┤ÓĖĀÓĖ▓ÓĖ×Ó╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖŚÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖ×ÓĖóÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖäÓĖĖÓ╣ēÓĖĪ ÓĖäÓ╣łÓĖ▓(Efficiency) Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ¢ÓĖÖÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣äÓĖøÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓ╣äÓĖöÓ╣ēÓĖłÓĖŻÓĖ┤ÓĖć ÓĖćÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓĖĢÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖĄÓĖóÓĖÖÓĖŻÓĖ╣Ó╣ē Ó╣éÓĖöÓĖóÓĖĪÓĖĄÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖ¬ÓĖ┤ÓĖŚÓĖśÓĖ┤ÓĖĀÓĖ▓ÓĖ× +ÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖ¬ÓĖ┤ÓĖŚÓĖśÓĖ┤ÓĖ£ÓĖź ( Usability)
- 12. ÓĖéÓĖ▒Ó╣ēÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖŁÓĖÖÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖłÓĖ░ÓĖÖÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣äÓĖøÓĖ¬ÓĖ╣Ó╣łÓ╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ēÓĖ▓ ÓĖ½ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖć HCI Ō£ż Understand : Ó╣ĆÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖ▓Ó╣āÓĖłÓ╣āÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖłÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ¦ÓĖ┤ÓĖŚÓĖóÓĖ▓ Ō£ż Develop : ÓĖ×ÓĖ▒ÓĖÆÓĖÖÓĖ▓Ó╣ĆÓĖäÓĖŻÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖĪÓĖĘÓĖŁÓ╣üÓĖźÓĖ░Ó╣ĆÓĖŚÓĖäÓĖÖÓĖ┤ÓĖä Ō£ż Achieve : ÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖøÓĖÅÓĖ┤ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒ÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖśÓ╣īÓ╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓĖĪÓĖĄÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖ¬ÓĖŚÓĖ┤ÓĖśÓĖ┤ÓĖĀÓĖ▓ÓĖ×
- 14. Why is HCI important? 1. User-centered design is getting a crucial role! 2. Users lose time with badly designed products and services 3. Users even give up using bad interface
- 15. The Importance of the User Interface ŌĆó A well-designed interface and screen is terribly important to our users. It is their window to view the cap abilities of the system. ŌĆó It is also the vehicle through which many critical tasks are presented. These tasks often have a direct impact o n an organization's relations with its customers, and its profitability. (Facebook VS Hi5)
- 16. The Importance of the User Interface (Cont.) ŌĆó A screen's layout and appearance affect a person in a variety of ways. If they are con-fusing and inefficient, people will have greater difficulty in doing their jobs and will make more mistakes. ŌĆó Poor design may even chase some people away from a system permanently. It can also lead to aggravation, frustration, and increased stress.
- 17. ÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣äÓĖĪÓĖĢÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖćÓ╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖĄÓĖóÓĖÖ HCI ŌĆó Ó╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓĖ¬Ó╣łÓĖ¦ÓĖÖÓĖ¬ÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖäÓĖ▒ÓĖŹÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖĢÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖøÓĖÅÓĖ┤ÓĖÜÓĖ▒ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ÓĖłÓĖŻÓĖ┤ÓĖćÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖć Ó╣éÓĖøÓĖŻÓ╣üÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖĪ ŌĆó Ó╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖ▓Ó╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓĖ£ÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓĖ¬ÓĖŻÓ╣ēÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓ╣éÓĖøÓĖŻÓ╣üÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖĪÓĖ¬ÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓĖ£ÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖÖÓ╣å Ó╣äÓĖĪÓ╣łÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣łÓĖĢÓĖ▒ÓĖ¦Ó╣ĆÓĖŁÓĖć ŌĆó User Interface (UI) ÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓ╣äÓĖĪÓ╣łÓĖöÓĖĄÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓĖäÓ╣łÓĖ▓Ó╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ē ÓĖłÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓ╣āÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖøÓĖÅÓĖ┤ÓĖÜÓĖ▒ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ÓĖćÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖ×ÓĖ┤Ó╣łÓĖĪÓĖéÓĖČÓ╣ēÓĖÖ ŌĆó Ó╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖóÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓ╣āÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖŁÓĖŁÓĖüÓ╣üÓĖÜÓĖÜ UI ÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖöÓĖĄ ŌĆōÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣ĆÓĖöÓĖ▓Ó╣āÓĖłÓĖäÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓĖ¬ÓĖ┤Ó╣łÓĖćÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣äÓĖöÓ╣ēÓĖóÓĖ▓ÓĖü
- 18. The Benefits of Good Design The benefits of a well designed screen have also been under experimental scrutiny for many years. ŌĆō One researcher, for example, attempted to improve screen clarity and readability by making screens less crowded. ŌĆō Separate items, which had been combined on the same display line to conserve space, were placed on separate lines instead. ŌĆō The result screen users were about 20 percent more productive with the less crowded version.
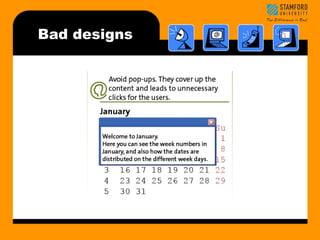
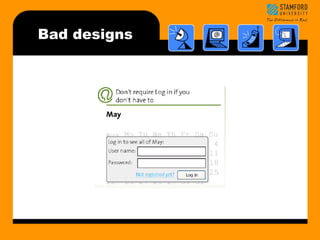
- 19. Bad Designs Bad designs ŌĆóElevator controls and labels on the bottom row all look the same, so it is easy to push a label by mistake instead of a control button ŌĆóPeople do not make same mistake for the labels and buttons on the top row. Why not? From: www.baddesigns.com
- 20. Good and bad design ŌĆó What is wrong with the right hand remote? ŌĆó Why is the left hand remote so much better designed? ŌĆō Peanut shaped to fit in hand ŌĆō Logical layout and color-coded, distinctive buttons ŌĆō Easy to locate buttons
- 21. My Choice iPod ŌĆóPros: ŌĆō portable ŌĆō power ŌĆō ease of use ŌĆóCons: ŌĆō scratches easily ŌĆō no speech for car use ŌĆō proprietary
- 22. Bad designs
- 23. Bad designs
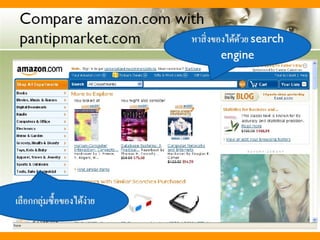
- 27. Website Performance Trade-offs ŌĆó 72 pixel ÓĖüÓ╣ĆÓ╣ćÓĖ×ÓĖĄÓĖóÓĖćÓĖ×ÓĖŁÓ╣üÓĖźÓ╣ēÓĖ¦ ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖüÓĖ¦Ó╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓĖĄÓ╣ē ÓĖłÓĖ░ÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓĖöÓĖ▓ÓĖ¦ÓĖÖÓ╣īÓ╣éÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖöÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖ▓ ŌĆó ÓĖŁÓĖóÓ╣łÓĖ▓Ó╣āÓĖ¬Ó╣łÓ╣ĆÓĖ¬ÓĖĄÓĖóÓĖćÓĖÜÓĖÖÓĖ½ÓĖÖÓ╣ēÓĖ▓Ó╣éÓĖ«ÓĖĪÓ╣ĆÓĖ×ÓĖł ŌĆó ÓĖĪÓĖĄÓĖ¦ÓĖ┤ÓĖśÓĖĄÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖłÓĖ░ÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓĖ¢ÓĖ╣ÓĖüÓ╣ĆÓĖźÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖüÓĖłÓĖ▓ÓĖü Search Engine ÓĖöÓĖĄÓĖéÓĖČÓ╣ēÓĖÖÓ╣üÓĖźÓĖ░Ó╣ĆÓĖŻÓ╣ćÓĖ¦ ŌĆó Ó╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖ¤ÓĖ¤ÓĖ┤ÓĖäÓĖćÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓ╣å ŌĆó Ó╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖ¬ÓĖĄÓ╣äÓĖĪÓ╣łÓ╣ĆÓĖüÓĖ┤ÓĖÖ 216 ÓĖ¬ÓĖĄÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖÉÓĖ▓ÓĖÖ ŌĆó Ó╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖ¬ÓĖĄÓ╣üÓĖÜÓĖÜÓ╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓ╣éÓĖäÓ╣ēÓĖö Ó╣üÓĖŚÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖŖÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁ ÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖćÓ╣å ŌĆó Ó╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓĖüÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖ½ÓĖÖÓĖöÓĖéÓĖÖÓĖ▓ÓĖöÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖ¤ÓĖ¤ÓĖ┤ÓĖäÓ╣ĆÓĖźÓĖó ŌĆó ÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖźÓĖöÓĖéÓĖÖÓĖ▓ÓĖöÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖŻÓĖ╣ÓĖøÓĖüÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖÖÓĖöÓ╣ēÓĖ¦ÓĖó Tools Ó╣ĆÓĖŖÓ╣łÓĖÖ PS ŌĆó Ó╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖ¬ÓĖĄÓĖŖÓ╣łÓĖ¦ÓĖóÓ╣āÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖłÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖöÓĖĄÓĖéÓĖÖÓĖČÓ╣ē Ó╣ĆÓĖŖÓ╣łÓĖÖ IBM ÓĖłÓĖ░Ó╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖ¬ÓĖĄÓĖ¤Ó╣ēÓĖ▓ ŌĆó ÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖ½ÓĖ¦Ó╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖć GIF, JPEG ÓĖ¢Ó╣ēÓĖ▓Ó╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓĖŻÓĖ╣ÓĖøÓ╣ĆÓĖŖÓ╣łÓĖÖ Ó╣ĆÓĖ¬Ó╣ēÓĖÖ ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖøÓĖĖÓ╣łÓĖĪÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓĖźÓĖ░Ó╣ĆÓĖŁÓĖĄÓĖóÓĖöÓ╣äÓĖĪÓ╣ł ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŻ Ó╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ē GIF ÓĖ¢Ó╣ēÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓĖźÓĖ░Ó╣ĆÓĖŁÓĖĄÓĖóÓĖöÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ē JPEG ŌĆó Ó╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖ¬ÓĖĄÓĖÖÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖó ÓĖłÓĖ░ÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖĪÓĖ¦ÓĖźÓĖ£ÓĖźÓ╣äÓĖöÓ╣ēÓ╣ĆÓĖŻÓ╣ćÓĖ¦ ÓĖéÓĖČÓ╣ēÓĖÖ ŌĆó Ó╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ē Animated GIF Ó╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓĖÖÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖ¬ÓĖĖÓĖö ŌĆó ÓĖ¢Ó╣ēÓĖ▓Ó╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ē Animation ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓ╣äÓĖøÓĖłÓĖ░ÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ē Ó╣ĆÓĖüÓĖ┤ÓĖöÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖŻÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖäÓĖ▓ÓĖŹ ŌĆó ÓĖźÓĖöÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓ╣éÓĖäÓ╣ēÓĖöÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓ╣äÓĖĪÓ╣łÓĖłÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓĖźÓĖć ŌĆó Ó╣āÓĖ¬Ó╣ł / ÓĖĢÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖźÓĖ┤ÓĖćÓĖäÓ╣īÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓĖ¬ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ¢Ó╣ĆÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖ▓ ÓĖ¢ÓĖČÓĖćÓ╣äÓĖöÓ╣ēÓ╣ĆÓĖŻÓ╣ćÓĖ¦ÓĖéÓĖČÓ╣ēÓĖÖ ŌĆó Ó╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ē Netmechanic.com Ó╣ĆÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖ¦ÓĖł ÓĖ¬ÓĖŁÓĖÜÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖ¬ÓĖ┤ÓĖŚÓĖśÓĖ┤ÓĖĀÓĖ▓ÓĖ× ŌĆó Ó╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēhttp://ÓĖŻÓĖ╣ÓĖøÓ╣ĆÓĖöÓĖ┤ÓĖĪwww.Ó╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓ╣āÓĖÖnetmechanic.ÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓ╣åÓĖĢÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣üÓĖ½com ÓĖÖÓ╣łÓĖć Ó╣ĆÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓ╣ĆÓĖüÓ╣ćÓĖÜÓ╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖ Cache Ó╣āÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖäÓĖŻÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ē Ó╣éÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖöÓ╣äÓĖ¦ÓĖéÓĖČÓ╣ēÓĖÖ
- 28. Understanding usersŌĆÖ needs ŌĆō Need to take into account what people are good and bad at ŌĆō Listen to what people want and get them involved ŌĆō Use tried and tested user-centered methods
- 29. Activity ŌĆó How does making a call differ when using a: ŌĆō Cell phone VS ŌĆō Public phone box? ŌĆó Consider the kinds of user, type of activity and context of use
- 30. Human vs Computer Computers ŌĆó Fast ŌĆó Efficient ŌĆó Rigid ŌĆó finite. Humans ŌĆó Slower ŌĆó Inefficient ŌĆó Flexible ŌĆó expansive.
- 31. ÓĖ¬Ó╣łÓĖ¦ÓĖÖÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖüÓĖŁÓĖÜÓĖ¬ÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖäÓĖ▒ÓĖŹ 5 ÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻ Ó╣āÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖäÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓĖČÓĖćÓĖ¢ÓĖČÓĖćÓĖ£ÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ē Ó╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓĖ¬ÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖäÓĖ▒ÓĖŹ 1.ÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖóÓĖ░Ó╣ĆÓĖ¦ÓĖźÓĖ▓Ó╣āÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖĄÓĖóÓĖÖÓĖŻÓĖ╣Ó╣ē (Time to Learn) 2.ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖŻÓĖ¦ÓĖöÓ╣ĆÓĖŻÓ╣ćÓĖ¦Ó╣āÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖĪÓĖ¦ÓĖźÓĖ£ÓĖź(Speed of Performance) 3.ÓĖŁÓĖ▒ÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖ£ÓĖ┤ÓĖöÓĖ×ÓĖźÓĖ▓ÓĖöÓĖłÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖćÓĖ▓ÓĖÖ(Rate of Errors) 4.ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖĄÓĖóÓĖÖÓĖŻÓĖ╣Ó╣ē (Retention Over Time) 5.ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ¦ÓĖ▒ÓĖöÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖČÓĖćÓĖ×ÓĖŁÓ╣āÓĖłÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ£ÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ē (Subjective Satisfaction)
- 32. Usability Motivations ŌĆó Life-critical system ŌĆó Industrial and commercial uses ŌĆó Home & Entertain ŌĆó Exploratory, Creative ŌĆó Sociotechnical system
- 33. What to design ŌĆó Need to take into account: ŌĆō Who the users are ŌĆō What activities are being carried out ŌĆō Where the interaction is taking place ŌĆó Need to optimize the interactions users have with a product ŌĆō So that they match the usersŌĆÖ activities and needs
- 34. Interaction Styles 1. Batch interface 2. Command-line user interface 3. Graphical user interface 4. Direct manipulation
- 35. Batch interface ŌĆó non-interactive user interfaces ŌĆó ÓĖ£Ó╣āÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖüÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖ½ÓĖÖÓĖöÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓĖźÓĖ░Ó╣ĆÓĖŁÓĖĄÓĖóÓĖöÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖćÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓĖźÓ╣łÓĖ¦ÓĖćÓĖ½ÓĖÖÓ╣ēÓĖ▓Ó╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓ╣üÓĖüÓ╣ł batch processing Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÜ output Ó╣ĆÓĖĪÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓ╣ĆÓĖ¬ÓĖŻÓ╣ćÓĖłÓĖ¬ÓĖÖÓĖ┤Ó╣ē ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖĪÓĖ¦ÓĖźÓĖ£ÓĖź ÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖĄ ŌĆóÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣äÓĖöÓ╣ēÓĖćÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖó ÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖ½ÓĖóÓĖ▒ÓĖö ŌĆóÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖćÓ╣äÓĖøÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖćÓĖĪÓĖ▓ ÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓ╣ĆÓĖ¬ÓĖĄÓĖó ŌĆóÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖ▓ ŌĆóÓ╣äÓĖĪÓ╣łÓ╣ĆÓĖ½ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖ░ÓĖ¬ÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÜ non-expert user
- 36. Command line user interface ŌĆó ÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖĄ ŌĆó ÓĖóÓĖĘÓĖöÓĖ½ÓĖóÓĖĖÓ╣łÓĖÖÓ╣äÓĖöÓ╣ē ŌĆó expert users. ŌĆó ÓĖ¬ÓĖÖÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓĖ¬ÓĖÖÓĖĖÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ē script ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ macros. ŌĆó Ó╣ĆÓĖ½ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖ░ÓĖ¬ÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻ ÓĖøÓĖÅÓĖ┤ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒ÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖśÓ╣īÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÜ ÓĖäÓĖŁÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ┤ÓĖ¦Ó╣ĆÓĖĢÓĖŁÓĖŻÓ╣īÓĖÜÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖäÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ ÓĖéÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖĪÓĖĄÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓ╣ĆÓĖŻÓ╣ćÓĖ¦Ó╣āÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻ ÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓĖ¬Ó╣łÓĖćÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖĪÓĖźÓĖ╣ (bandwidth) ÓĖĢÓĖ│Ó╣łÓĖ▓ Ó╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣éÓĖĢÓ╣ēÓĖĢÓĖŁÓĖÜÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖÜÓĖÜÓ╣éÓĖöÓĖóÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖ£ÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖłÓĖ░ÓĖĢÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖć ÓĖ×ÓĖ┤ÓĖĪÓĖ×Ó╣īÓĖäÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒Ó╣łÓĖćÓĖźÓĖćÓ╣āÓĖÖÓĖŖÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖøÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖÖÓĖäÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒Ó╣łÓĖć Ó╣ĆÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁ ÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖĢÓĖĖÓ╣ēÓĖÖÓ╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓ╣ĆÓĖüÓĖ┤ÓĖöÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓ╣āÓĖÖÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖÜÓĖÜÓĖ£ÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖłÓĖ░ ÓĖĢÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖłÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖäÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒Ó╣łÓĖć Ó╣äÓĖ¦ÓĖóÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖōÓ╣ī Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ÓĖüÓĖÄÓ╣ĆÓĖüÓĖōÓĖæÓ╣ī ÓĖĢÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓ╣åÓ╣ĆÓĖŖÓ╣łÓĖÖ ÓĖ£ÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖŖÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓĖ▓ÓĖŹÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖÜÓĖÜ ÓĖøÓĖÅÓĖ┤ÓĖÜÓĖ▒ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻ DOS
- 37. Command line user interface ŌĆó ÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓ╣ĆÓĖ¬ÓĖĄÓĖó ŌĆó ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻ error ÓĖ¬ÓĖćÓĖ╣ ŌĆó Ó╣äÓĖĪÓ╣ĆÓ╣łÓĖ½ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖ░ÓĖ¬ÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÜ non-expert user
- 38. Form Filling ŌĆó ÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖĄ ŌĆó ÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖäÓĖĄÓĖóÓ╣īÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖĪÓĖ╣ÓĖźÓ╣ĆÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖ▓ ÓĖćÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖó ŌĆó ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ¢ÓĖüÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖ½ÓĖÖÓĖöÓĖäÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖźÓ╣łÓĖ¦ÓĖć ÓĖ½ÓĖÖÓ╣ēÓĖ▓Ó╣äÓĖöÓ╣ē ŌĆó ÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓ╣ĆÓĖ¬ÓĖĄÓĖó ŌĆó Ó╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣ēÓĖÖÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖÜÓĖÖÓĖ½ÓĖÖÓ╣ēÓĖ▓ÓĖłÓĖŁÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖü
- 39. Menu Selection ŌĆó ÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖĄ ŌĆó ÓĖ¬ÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓĖ£ÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖŚÓĖ▒Ó╣łÓĖ¦Ó╣äÓĖø ŌĆó ÓĖöÓĖČÓĖćÓĖöÓĖ╣ÓĖö expert userÓĖ¢ÓĖ▓Ó╣ē ÓĖĢÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣üÓĖ¬ÓĖöÓĖćÓ╣ĆÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁ ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣ĆÓĖźÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖüÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖŻÓĖ¦ÓĖöÓ╣ĆÓĖŻÓ╣ćÓĖ¦ ŌĆó ÓĖ¬ÓĖÖÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓĖ¬ÓĖÖÓĖĖÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ¬ÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ¦ÓĖłÓĖäÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒Ó╣łÓĖć ŌĆó ÓĖŖÓ╣łÓĖ¦ÓĖóÓ╣āÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖĢÓĖ▒ÓĖöÓĖ¬ÓĖ┤ÓĖÖÓ╣āÓĖł ŌĆó ÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓ╣ĆÓĖ¬ÓĖĄÓĖó ŌĆó Ó╣ĆÓĖĪÓĖÖÓĖ╣ overload
- 40. Direct Manipulation Ó╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖłÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓ╣ĆÓĖŁÓĖ▓ÓĖ¬ÓĖ┤Ó╣łÓĖćÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣ł user ÓĖĢÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓ╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖłÓĖ░ÓĖÖÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ Ó╣ĆÓĖ¬ÓĖÖÓĖŁÓĖĪÓĖ▓Ó╣äÓĖ¦Ó╣ēÓĖŻÓĖ¦ÓĖĪÓĖüÓĖÖÓĖ▒ ÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖĄ ŌĆóÓ╣ĆÓĖ½Ó╣ćÓĖÖÓĖĀÓĖ▓ÓĖ×ÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖö ŌĆóÓĖćÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓĖĢÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖĄÓĖóÓĖÖÓĖŻÓĖ╣Ó╣ē ŌĆóÓĖ¬ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ¢ÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖĄÓĖüÓ╣ĆÓĖźÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖć ErrorsÓ╣äÓĖöÓ╣ēÓĖćÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖó ŌĆóÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖĢÓĖĖÓ╣ēÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ¬ÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ¦ÓĖł ŌĆóÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖČÓĖćÓĖ×ÓĖŁÓ╣āÓĖłÓĖ¬ÓĖ╣ÓĖć ŌĆóÓĖŖÓ╣łÓĖ¦ÓĖóÓĖŚÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖöÓ╣ēÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖłÓĖ│ÓĖ▓
- 41. Direct Manipulation ŌĆó ÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓ╣ĆÓĖ¬ÓĖĄÓĖó ŌĆó ÓĖóÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓ╣āÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣ĆÓĖéÓĖĄÓĖóÓĖÖ Ó╣éÓĖøÓĖŻÓ╣üÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖĪ ŌĆó Ó╣äÓĖĪÓ╣łÓ╣ĆÓĖ½ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖ░ÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣üÓĖ¬ÓĖöÓĖć ÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖ¤ÓĖ┤ÓĖüÓĖéÓĖÖÓĖ▓ÓĖöÓ╣ĆÓĖźÓ╣ćÓĖü ŌĆó ÓĖÜÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖäÓĖŻÓĖ▒Ó╣ēÓĖćÓĖ£ÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓ╣äÓĖĪÓ╣łÓĖŖÓĖŁÓĖÜ ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖÖÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣ĆÓĖ¬ÓĖÖÓĖŁ ŌĆó Expert user ÓĖŁÓĖ▓ÓĖłÓ╣äÓĖĪÓ╣ł ÓĖŖÓĖŁÓĖÜ
- 42. ÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓ╣äÓĖćÓĖ¢ÓĖČÓĖćÓĖŁÓĖŁÓĖüÓ╣üÓĖÜÓĖÜÓ╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓĖĪÓĖĄ ÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖ¬ÓĖ┤ÓĖŚÓĖśÓĖ┤ÓĖĀÓĖ▓ÓĖ× ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖøÓĖźÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖĀÓĖ▒ÓĖó ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪ Ó╣ĆÓĖŖÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖ¢ÓĖĘÓĖŁ Ó╣üÓĖüÓ╣łÓĖ£ÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖ¬ÓĖ╣ÓĖćÓĖ¬ÓĖĖÓĖö? HCI ÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÜ USER INTERFACE
- 43. user-friendly; easy to use; accessible; comprehensible GOOD USER INTERFACE = USABILITY ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░Ó╣éÓĖóÓĖŖÓĖÖÓ╣ī Ó╣äÓĖöÓ╣ē
- 44. UUsseerr--cceenntteerreedd ddeessiiggnn ŌĆó ŌĆ£Know the usersŌĆØ ÓĖŻÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓĖłÓĖ▒ÓĖüÓĖ£ÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ē ŌĆō Novice ÓĖ¬ÓĖĪÓĖ▒ÓĖäÓĖŻÓ╣ĆÓĖźÓ╣łÓĖÖ ŌĆō Expert ÓĖ£ÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓ╣ĆÓĖŖÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖ¦ÓĖŖÓĖ▓ÓĖŹ ŌĆó Cognitive abilities ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖ¬ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ¢ ŌĆō visual & aural perception Ó╣ĆÓĖ½Ó╣ćÓĖÖ ÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖć ŌĆō physical manipulation ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻ ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖÜÓĖäÓĖĖÓĖĪÓĖŻÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖó ŌĆō memory ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖłÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ ŌĆó Organizational / job abilities ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻ ÓĖłÓĖ▒ÓĖöÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻ ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖ▓ÓĖÖ ŌĆó Keep users involved throughout project Ó╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓĖ£ÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖĪÓĖĄÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓ╣ĆÓĖüÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖ¦ÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖć ÓĖĢÓĖźÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖ▓ÓĖÖ
- 45. Assignmen ts 1. Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖüÓ╣éÓĖŚÓĖŻÓĖ©ÓĖ▒ÓĖ×ÓĖŚÓ╣īÓĖĪÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖ¢ÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓ╣ĆÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖÖ ÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖĢÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖóÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓĖŁÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÖ Ó╣éÓĖöÓĖóÓ╣äÓĖĪÓ╣łÓ╣äÓĖöÓ╣ē Ó╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖĄÓĖóÓĖÖÓĖŻÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖćÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓĖłÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓ╣ĆÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖÖÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ ÓĖäÓĖ╣Ó╣łÓĖĪÓĖĘÓĖŁ Ó╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓĖŚÓĖöÓĖźÓĖŁÓĖćÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓ╣éÓĖŚÓĖŻÓĖ©ÓĖ▒ÓĖ×ÓĖŚÓ╣īÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖ¬ÓĖ┤Ó╣łÓĖćÓĖĢÓ╣łÓĖŁÓ╣äÓĖøÓĖÖÓĖĄÓ╣ē ŌĆóÓĖłÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖ½ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓ╣ĆÓĖźÓĖéÓ╣éÓĖŚÓĖŻÓĖ©ÓĖ▒ÓĖ×ÓĖŚÓ╣īÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓ╣ĆÓĖäÓĖŻÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓ╣üÓĖźÓĖüÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓ╣ĆÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖÖ ÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣éÓĖŚÓĖŻÓ╣äÓĖøÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣ł Ó╣ĆÓĖÜÓĖŁÓĖŻÓ╣īÓĖöÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓĖźÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖ¦ Ó╣éÓĖöÓĖóÓ╣äÓĖĪÓ╣łÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖĪÓĖ╣ÓĖźÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓ╣ĆÓĖüÓĖÜÓ╣ćÓ╣āÓĖÖ memory ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓ╣ĆÓĖäÓĖŻÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖć ŌĆóÓ╣ĆÓĖŖÓ╣ćÓĖäÓĖöÓĖ╣ÓĖ¦Ó╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖĄ message (SMS) Ó╣āÓĖ½ÓĖĪÓ╣łÓ╣ĆÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁÓ╣äÓĖĪÓ╣ł ŌĆóÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖŁÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖÖ message ÓĖźÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖ¬ÓĖĖÓĖö 3 ÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣üÓĖŻÓĖüÓ╣āÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖäÓĖŻÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖć ŌĆóÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ¬Ó╣łÓĖć SMS ÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪ Hello I am testing the m-phone usability. Ó╣äÓĖøÓĖóÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓ╣ĆÓĖäÓĖŻÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓ╣üÓĖźÓĖüÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓ╣ĆÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖÖ ŌĆóÓ╣ĆÓĖøÓĖźÓĖóÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖÖ ringtone ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓ╣ĆÓĖäÓĖŻÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖć ŌĆóÓĖĢÓĖ▒Ó╣ēÓĖćÓ╣ĆÓĖ¦ÓĖźÓĖ▓Ó╣ĆÓĖĢÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖÖ/ÓĖøÓĖźÓĖĖÓĖü //Ó╣āÓĖÖÓĖéÓĖōÓĖ░ÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓ╣ĆÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖÖÓĖäÓĖÖÓĖ½ÓĖÖÓĖČÓ╣łÓĖćÓĖüÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖźÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖŚÓĖöÓĖźÓĖŁÓĖćÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣ł Ó╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓĖŁÓĖĄÓĖüÓĖäÓĖÖÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓ╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖ Ó╣ĆÓĖłÓ╣ēÓĖ▓ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖäÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓ╣ĆÓĖüÓĖĢÓĖ×ÓĖżÓĖĢÓĖ┤ÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖŻÓĖĪÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ē Ó╣éÓĖöÓĖóÓĖ×ÓĖóÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓ╣äÓĖĪÓ╣łÓ╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ē ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖŖÓ╣łÓĖ¦ÓĖóÓ╣ĆÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖĘÓĖŁÓ╣āÓĖö Ó╣å ÓĖÖÓĖŁÓĖüÓĖłÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖłÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖ ÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖłÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓ╣ĆÓĖ¦ÓĖźÓĖ▓ÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ē Ó╣āÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖŚÓĖ│ÓĖ▓Ó╣üÓĖĢÓ╣łÓĖźÓĖ░ÓĖŁÓĖóÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖéÓ╣ēÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖĢÓ╣ēÓĖÖ ÓĖłÓĖöÓĖÜÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖŚÓĖČÓĖüÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓ╣ĆÓĖ½Ó╣ćÓĖÖÓ╣āÓĖÖÓ╣üÓĖćÓ╣łÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪ
- 46. Assignmen ts 2. Ó╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓĖÖÓĖ▒ÓĖüÓĖ©ÓĖČÓĖüÓĖ®ÓĖ▓Ó╣ĆÓĖźÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖüÓ╣ĆÓĖ¦Ó╣ćÓĖÜÓ╣äÓĖŗÓĖĢÓ╣īÓĖŚÓ╣ĆÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖ▒ÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖóÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖć HCI ÓĖŚÓĖöÓĖĄÓĖĄÓ╣ł ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ 1 Ó╣ĆÓĖ¦Ó╣ćÓĖÜÓ╣äÓĖŗÓĖĢÓ╣ī Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░Ó╣ĆÓĖ¦Ó╣ćÓĖÜÓ╣äÓĖŗÓĖĢÓ╣īÓĖŚÓ╣ĆÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖ▒ÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖóÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖć HCI ÓĖŚÓ╣äÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖĪÓ╣łÓĖöÓĖĄ ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ 1 Ó╣ĆÓĖ¦Ó╣ćÓĖÜÓ╣äÓĖŗÓĖĢÓ╣ī ÓĖ×ÓĖŻÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖĪÓĖŚÓĖćÓĖ▒Ó╣ēÓĖÜÓĖŁÓĖüÓ╣ĆÓĖ½ÓĖĢÓĖĖÓĖ£ÓĖźÓ╣üÓĖźÓĖ░Ó╣üÓĖÖÓĖ¦ÓĖŚÓĖ▓ÓĖć Ó╣üÓĖüÓ╣ēÓ╣äÓĖé

![CChhaapptteerr 11
ÓĖøÓĖÅÓĖÅÓĖ┤ÓĖ┤ÓĖ¬ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒ÓĖ▒ÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ×ÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖśÓĖśÓ╣īÓ╣īÓĖŻÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖ░ÓĖ½ÓĖ¦ÓĖ¦Ó╣łÓĖ▓Ó╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖ£ÓĖ£ÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓ╣āÓĖ╣Ó╣ēÓ╣āÓĖŖÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓ╣üÓ╣ēÓ╣üÓĖźÓĖźÓĖ░ÓĖ░
ÓĖäÓĖŁÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ×ÓĖ┤ÓĖ¦ÓĖ┤ÓĖ¦Ó╣ĆÓ╣ĆÓĖĢÓĖĢÓĖŁÓĖŻÓĖŻÓ╣īÓ╣ī
HHuummaann--CCoommppuutteerr
IInntteerrffaaccee [[HHCCII]]
IITTEE 225544 bbyy ÓĖŁ..ÓĖ¬ÓĖ¬ÓĖ┤ÓĖ┤ÓĖŻÓĖŻÓĖ┤ÓĖ×ÓĖ┤ÓĖ×ÓĖŻ ÓĖæÓĖæÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ░ÓĖ░ÓĖźÓĖźÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖ│ÓĖ▓ÓĖ×ÓĖ×ÓĖ╣ÓĖÖÓĖ╣ÓĖÖ
ssiirriippoorrnntthhiittaa@@ggmmaaiill..ccoomm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hciweek1stamfordedit-141109220953-conversion-gate02/85/Hci-week1-stamford-edit-1-320.jpg)