HEAD TO TOE EXAMINATION OF NEWBORNS.pptx
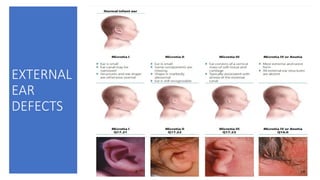
- 1. HEAD TO TOE EXAMINATION OF NEWBORN ENT ASPECTS Prof.Dr.M.Bharathimohan
- 5. HEARING ASSESSMENT IN CHILDREN Hearing assessment in children can be done by 1. Behavioral methods & 2. Physiological methods Behavioral assessment includes 3. Behavioral observation audiometry (BOA) – 0 to 6months 4. Visual reinforcement audiometry (VRA) – 6 months to 2 ½ years 5. Conditioned play audiometry – 2 1/2 to 6 years Physiological assessment includes 6. Otoacoustic emission (OAE) 7. Impedance audiometry 8. Auditory brain stem response (ABR)
- 6. Joint Committee on Infant Hearing 2019 • Physiological screening should be completed by 1month • Audiological diagnosis by 2 months • Enrollment in Early Intervention by 3 months • States who meet 1-3-6 benchmark should strive to meet 1-2-3 benchmark
- 10. Breathing and Feeding Abnormalities in Newborn • Choanal Atresia • Cleft Lip and Palate
- 11. Choanal Atresia
- 12. CT Scan
- 13. Bedside diagnosis •Neonatologist is the first person to see baby •5 FG tube passed in both nostrils to confirm diagnosis for patency
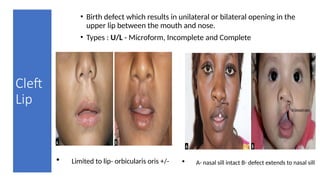
- 14. Cleft Lip • Birth defect which results in unilateral or bilateral opening in the upper lip between the mouth and nose. • Types : U/L - Microform, Incomplete and Complete • Limited to lip- orbicularis oris +/- • A- nasal sill intact B- defect extends to nasal sill
- 16. Cleft Palate • Breach in continuity of palate or a furrow in the palatal vault. A defect in the roof of mouth due to lack of tissue development. • Types : Isolated submucous and soft palate, Incomplete cleft, Complete Cleft.
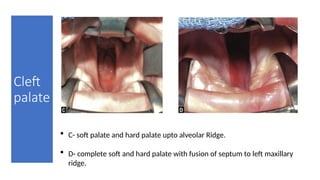
- 17. • C- soft palate and hard palate upto alveolar Ridge. • D- complete soft and hard palate with fusion of septum to left maxillary ridge. Cleft palate
- 18. Problems Associated • Airway Obstruction • Sleep disturbances • Failure to Thrive - swallowing problems, regurgitation, aspiration, LRTIs, pneumonia • SAM - reduced feeding • Hearing Loss - OME / ET dysfunction