Headaches in Ophthalmology
- 1. • Subhead Headaches in Ophthalmology HEADLINE TO GO HERE Dr Paula Berdoukas General Ophthalmologist
- 2. symptoms for the optometrist • Pain concentrated around the eye • Headache with any associated ophthalmic symptom – blur, double vision, redness, photophobia, visual aura 2
- 3. aim of assessment • Diagnose and treat ophthalmic causes of headache • Recognise benign headache patterns with ophthalmic feature • Recognise ophthalmic symptoms or signs of intracranial or systemic cause of headache • Know when to refer 3
- 4. assessment • VA • Refraction – under corrected hypermetropia, overcorrected myopia, presbyopia • Slit Lamp examination • IOP • Neurologic assessment – VF, EOM, Cranial Nerves, Pupils • Skin/Scalp – rash, temporal A 4
- 5. ophthalmic causes of headache • Visible – corneal abrasion/ infection, iritis, scleritis • Refractive error – mild frontal headache, worse with prolonged visual task • Heterophoria/ Heterotropia – mild frontal headache, intermittent blur or double vision • Angle Closure Glaucoma – Severe pain around eye, haloes, loss of vision, redness • Pigment dispersion Syndrome – intermittent blur, haloes and eye pain after exercise or pupil dilation • Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus – pain, hyperesthesia, rash or vesicles in Vi +/- ocular inflammation 5
- 6. benign headache patterns • Migraine – +/- aura, nausea, vomiting, photophobia, phonophobia • Cluster Headache – tearing, rhinorrhoea, sweating, ptosis +/- miosis • Tension headache • Sinus disease 6
- 7. What not to miss: headache with an intracranial origin • Causes – tumors, inflammation, infection (meninges or paranasal sinuses), arterial dissection or aneurysm, benign intracranial hypertension • History – recent onset or increasing severity, constant, worse with coughing, straining or lying down – normal vision, transient obscurations of vision, visual field defects •Examination – anisocoria, ptosis, disc swelling, cranial nerve palsy 7
- 8. Pupil Involving IIIrd nerve Palsy • IIIn function – EOM: MR, IR, IO, SR, Levator – PARA to iris sphincter and ciliary mm • Symptoms – Acute headache, double vision, nausea, neck stiffness • Signs – Ptosis, EOM limitation (SO and LR work unopposed), pupil dilated • Dx: Post Communicating A aneurysm – DDx: vasculopathic, GCA, demyelination, stroke, metastasis, trauma 8
- 9. “Down and out” 9 Image courtesy of www.aao.org: 4 Neuro Conditions Not to Be Missed By Marianne Doran, Miriam Karmel, and Annie Stuart
- 10. giant cell arteritis • age > 50 years • headache – recent temple/ frontal headache and tenderness • vision – acute severe vision loss, amurosis fugax, diplopia • systemic – jaw claudication, polymyalgia, malaise, weight loss, fever, sweats • Signs – field loss or blur – RAPD – swollen, pale or hyperemic disc – retinal ischemia – EOM defect – tender non-pulsatile temporal artery 10
- 11. Mr SN • 58 yr old • 1 week of headaches and right ear ache • 1 year of shoulder pain and cervical spine spurs, sees chiropractor. • On his most recent visit, prior to any manipulation, chiropractor noted L pupil was dilated and R lid droopy: referred to optom who referred to ophthl. 11
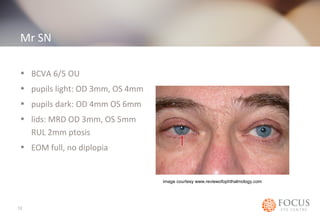
- 12. Mr SN • BCVA 6/5 OU • pupils light: OD 3mm, OS 4mm • pupils dark: OD 4mm OS 6mm • lids: MRD OD 3mm, OS 5mm RUL 2mm ptosis • EOM full, no diplopia 12 image courtesy www.reviewofophthalmology.com
- 13. Provisional Diagnosis: Horners Syndrome secondary to ICA dissection DDx: Malignancy, stroke, aneurysm, Image courtesy of younglivingforum.com 13
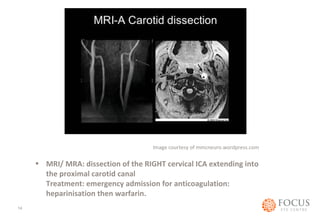
- 14. Image courtesy of mmcneuro.wordpress.com • MRI/ MRA: dissection of the RIGHT cervical ICA extending into the proximal carotid canal Treatment: emergency admission for anticoagulation: heparinisation then warfarin. 14
Editor's Notes
- #3: General History: associated neurological symptoms, nausea, vomiting, GCA symptoms, BP, medications
- #6: Refractive error: mild frontal/ ocular ache. Absent on waking. Precipitated by prolonged visual tasks. Should respond well to glasses Heterophoria/ Heterotropia: mild frontal headache, intermittent blur or double vision. Difficulty adjusting focus. Worsens through the day. Angle Closure Glaucoma: may be intermittent. Severe pain around eye, haloes, loss of vision, reddness, Elevated IOP and shallow angle Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus: pain or hyperesthesia in Trigeminal distribution. Rash or vesicles. Ocular inflammation: conjunctivitis, keratitis, iritis, elevated IOP