Heart diseases during pregnancy
- 1. CARDIAC DISEASES DURING PREGNANCY AMALA JOHN College of nursing AIIMS , New Delhi
- 2. CARDIAC CHANGES DURING PREGNANCY • There is significant rise in cardiac output (30- 50%), heart rate, plasma volume (40-45%) and red blood cell volume (15-20%) during normal pregnancy.
- 3. Clinical indicators of heart diseases during pregnancy • Symptoms – Progressive dyspnea – Orthopnea – Chest Pain – Hemptysis – Syncope
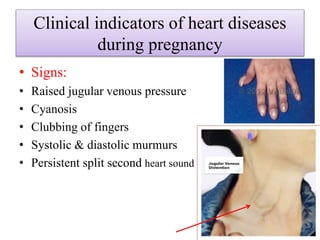
- 4. Clinical indicators of heart diseases during pregnancy • Signs: • Raised jugular venous pressure • Cyanosis • Clubbing of fingers • Systolic & diastolic murmurs • Persistent split second heart sound
- 5. Diagnosis of heart disease in pregnancy • Chest X-ray(with lead apron shield over abdomen) – Cardiomegaly – Enlargement of pulmonary veins – Enlarged pulmonary vascular markings • Electrocardiography (ECG)- cardiac arrythmia • Echocardiography – Non invasive & accurate method. It detects varous anomalies and lesions
- 6. Diagnosis of heart disease in pregnancy
- 8. MANAGEMENT OF PREGNANCY •PRE PREGNANCY COUNSELLING •ANTENATAL CARE •INTRANATAL CARE •POSTNATAL CARE
- 9. PRE PREGNANCY COUNSELLING • All women with heart disease should have pre-conceptional counseling. • The women with contraindication of pregnancy(eg: Eisenmenger’s syndrome) should be advised against pregnancy • With valvular disease- should conceive when they are in NYHA class I & II. • With mitral stenosis & CHD needing surgery should have done surgery before they venture for pregnancy.
- 10. ANTENATAL CARE • ANTENATAL CONSULTATIONS • DIET • REST • THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT
- 11. ANTENATAL VISITS Whenever cardiac diseases are diagnosed in pregnancy, the women should be referred to a tertiary care centre where she should be seen by an obstetrician and cardiologist. a. She should be seen every 2 weeks until 30 weeks of pregnancy and then every week until delivery. b. Should be checked for PR, B.P, RR, weight gain, jugular venous distension etc – cardiac failure c. At each visit she should be monitored for increase in dyspnea or limitation of activity, fine crepitations on base of lungs
- 12. DIET •Iron rich diet- to compact anemia •Avoid fatty foods •Avoid added salts •Avoid much weight gain during pregnancy •Avoid alcohol consumption
- 14. Therapeutic management • Iron & folic acid supplementation • Careful vigilance and treatment for pre- eclampsia, if present • Early diagnosis and management of any infections like UTI,RTI or dental infections. • All women with RHS should recive pencillin prophylaxis to avoid bacterial endocarditis (Inj. Benzanthyl pencillin, Penidura LA 1.2 mega units) by deep IM every 3 weeks through out pregnancy
- 15. MANAGEMENT OF PREGNANCY • INTRANATAL CARE
- 16. Principles in conducting delivery in heart disease complicated pregnancy • Induction of labour is best avoided and will wait for spontaneous onset of labour • Oxytocin , IV methergin following delivery of anterior shoulder is also not to be done. • Cut short the duration of second stage of labour. • Avoid lithotomy position & plan in semi-recumbent position
Editor's Notes
- #12: increase in dyspnea or limitation of activity, fine crepitations on base of lungs she should be monitored for increase in dyspnea or limitation of activity, fine crepitations on base of lungs and orthopnea- signs of cardiac failure
- #13: increase in dyspnea or limitation of activity, fine crepitations on base of lungs she should be monitored for increase in dyspnea or limitation of activity, fine crepitations on base of lungs and orthopnea- signs of cardiac failure