Heat of neutralization
- 1. Chapter 4 Thermochemistry 4.4 Heat Of Neutralization ITeach â Chemistry Form 5
- 2. Heat of neutralization Is the heat energy released when one mole of water is formed from the neutralization between one mole of hydrogen ions, H + from an acid and one mole of hydroxide ions, OH - from an alkali. Chapter 4 Thermochemistry Heat Of Neutralization ITeach â Chemistry Form 5 Energy change = mc In which, m = the mass of the aqueous reaction mixture c = the specific heat capacity of the aqueous reaction mixture = the change in temperature
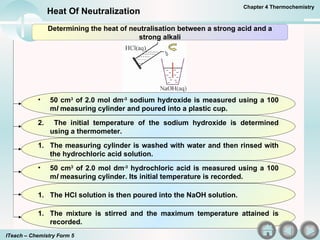
- 3. 50 cm 3 of 2.0 mol dm -3 sodium hydroxide is measured using a 100 m l measuring cylinder and poured into a plastic cup. 2. The initial temperature of the sodium hydroxide is determined using a thermometer. The measuring cylinder is washed with water and then rinsed with the hydrochloric acid solution. 50 cm 3 of 2.0 mol dm -3 hydrochloric acid is measured using a 100 m l measuring cylinder. Its initial temperature is recorded. The HCl solution is then poured into the NaOH solution. The mixture is stirred and the maximum temperature attained is recorded. Determining the heat of neutralisation between a strong acid and a strong alkali Chapter 4 Thermochemistry Heat Of Neutralization ITeach â Chemistry Form 5
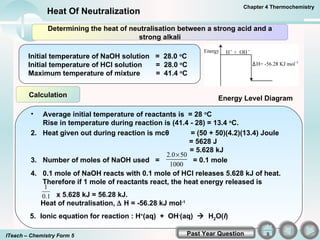
- 4. Calculation Energy Level Diagram Determining the heat of neutralisation between a strong acid and a strong alkali Initial temperature of NaOH solution = 28.0 o C Initial temperature of HCl solution = 28.0 o C Maximum temperature of mixture = 41.4 o C Average initial temperature of reactants is = 28 o C Rise in temperature during reaction is (41.4 - 28) = 13.4 o C. 2. Heat given out during reaction is mc Îļ = (50 + 50)(4.2)(13.4) Joule = 5628 J = 5.628 kJ 5. Ionic equation for reaction : H + (aq) + OH - (aq) ï H 2 O( I ) Chapter 4 Thermochemistry Heat Of Neutralization Past Year Question ITeach â Chemistry Form 5 3. Number of moles of NaOH used = = 0.1 mole 4. 0.1 mole of NaOH reacts with 0.1 mole of HCl releases 5.628 kJ of heat. Therefore if 1 mole of reactants react, the heat energy released is x 5.628 kJ = 56.28 kJ. Heat of neutralisation, ï H = -56.28 kJ mol -1
- 5. The heat of neutralisation involving a weak acid and a weak alkali A strong acid and a strong alkali ionizes completely in water. HCl(aq) ï H + (aq) + Cl - (aq) KOH(aq) ï K + (aq) + OH - (aq) When these solutions are added together the only change that occurs is the formation of water molecules. K + OH - (aq) + H + Cl - (aq) ï K + Cl - (aq) + H 2 O( l ) Hence the heat of neutralization is the heat released from the formation of 1 mole of water and its value is approximately 57.4 kJ mol -1 . H + (aq) + OH - (aq) ï H 2 O( l ) ï H= -57.4 kJ mol -1 Hence the heat of neutralization of any strong acid and strong alkali is the same. For example Na + OH - (aq) + H + NO 3 - (aq) ï Na + NO 3 - (aq) + H 2 O( l ) ï H= -57.4 kJ mol -1 Chapter 4 Thermochemistry Heat Of Neutralization Past Year Question ITeach â Chemistry Form 5
- 6. Heat energy is required to break this O-H bond before the H + can react with the OH - to form water. Thus the net heat change is less than 57 kJ mol . The heat of neutralisation involving a weak acid and a weak alkali However when weak acids or alkalis are involved, the heat of neutralization is lower than 57.4 kJ mol -1 . These weak acids or alkalis are partially dissociated in water. Some energy is needed to break the -O-H bonds to release the hydrogen ions or the hydroxide ions before they can react. Thus the net heat change will be less than 57.4 kJ/mol. For example the heat of neutralization of ethanoic acid and sodium hydroxide is only 54 kJ mol -1 . Chapter 4 Thermochemistry Heat Of Neutralization Past Year Question ITeach â Chemistry Form 5
- 7. The End i - Teach