Hemraj community ppt
- 1. Community programme planning & Resource mobilization Presented by Hemraj jangir 2013msw008 Presented to Dr. jagdish jadhav HOD Department of social work
- 2. What is community? A Community is a place where people come together to share common interests and resources. The origin of ŌĆ£communityŌĆØ is from the Latin word ŌĆ” "The word "community" is derived from the Old French communit├® which is derived from the Latin communitas (cum, "with/together" + munus, "gift"), a broad term for fellowship or organized society.ŌĆØ "Community: The origin of the word "community" comes from the Latin munus, which means the gift, and cum, which means together, among each other. So community literally means to give among each other."
- 3. Refers to a process beginning with objectives defining strategies, policies, and plans to achieve them; achieving an organization to implement decisions and including a review of performance and feedback to introduce a new planning style. ( Steiner) Deciding in advance what to do, how to do it, when to do it, and who to do it. ( Alexander) Planning
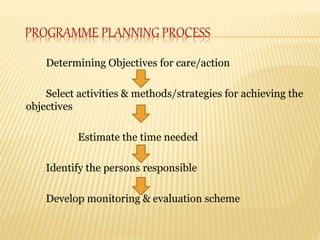
- 4. PROGRAMME PLANNING PROCESS Determining Objectives for care/action Select activities & methods/strategies for achieving the objectives Estimate the time needed Identify the persons responsible Develop monitoring & evaluation scheme
- 5. ’āÆ Identify what is to be done & what outcomes might be expected from the program/projects/services implemented/rendered ’āÆ Criteria for setting objectives: ’ā╝ Realistically achievable ’ā╝ Specifically Stated ’ā╝ Flexible enough to allow for change ’ā╝ Closely related to the problems/needs/concerns identified & felt by the client Determining objectives for care/action
- 6. ’āÆ Variety of Activities ’āÆ Home visit ’āÆ Conferences/demonstrations ’āÆ Service delivery ’āÆ Group discussion/Education ’āÆ Information dissemination ’āÆ Selecting Activities ’āÆ Consider needs/capabilities of client ’āÆ Identify target client ’āÆ Review traditional activities ’āÆ Bear in mind that a balanced program is far more effective than those which are unbalanced or biased Selecting activities & methods/strategies for achieving the objectives
- 7. ’āÆ Determine how much time is needed to accomplish each activity/program/project Estimate the time needed
- 8. ’āÆ Who will take the lead or participate in the implementation of the program plan ’āÆ Remember to involve people in the program Identify the persons responsible
- 9. ’āÆ Determine methods, tools, strategies for monitoring and evaluation ’āÆ Self-evaluation ’āÆ Peer evaluation ’āÆ Evaluation by superiors ’āÆ Analysis of statically reports ’āÆ Use of Standards ’āÆ Records review ’āÆ Use of tests ’āÆ Case discussion Develop monitoring and evaluation scheme
- 10. PROGRAMME INPLIMENTATION ’āÆ In this phase, plans are actually carried out, resources are actually mobilized to meet objectives set
- 11. ’üĮ Resources are the financial and non-financial supplies that help to fulfil organizational needs. They include money, the skills, time contributions and services of humans, and equipment and materials.
- 12. ’āś Resource mobilization is the process of identifying and obtaining resources for the organization. ’āś A continuous process of identifying and using a wide range of available resources to address identified problems. ’āś It involves action oriented resource gathering that provides a means to take action to address problems. ’āś It reflects coordinated, cooperated efforts of government and non-governmental entitles to provide systematic and sustainable change ŌĆó .
- 13. ŌĆó COMMUNITY RESOURCES ŌĆó INCLUDE: ’āśNatural Resources ’āśHuman Resources ’āśFinancial Resources ’āśInfrastructural Resources
- 14. NATURAL RESOURCES ARE ALL THE THINGS THAT NATURE PROVIDES SUCH AS: ’āś Land, air and water ’āś Minerals and surface/subsurface metals and ores ’āś Oil, gas and petroleum ’āś Trees and other plants ’āś Wildlife ’āś The standards, legislation and policies relating to the above.
- 15. ’āśHuman resources are about people. People are at the heart of all community matters and, as such, they are critical to success. ’āśIt is important to have the right people in the right jobs with the right skills, knowledge and abilities.
- 16. HUMAN RESOURCES INCLUDE: ’āś Healthy families and lifestyles ’āś Skills building, education and training ’āś Career planning and employment ’āś Effective and legal hiring practices ’āś Workers compensation and pensions ’āś Human rights and labor laws.
- 17. FINANCIAL RESOURCES MEANS MONEY AND IT OFTEN IMPLIES HAVING THE ABILITY TO ACQUIRE IT. FINANCIAL RESOURCES INCLUDE: ’āś Family or Earned Income ’āś Fundraising and grant-seeking ’āś Banks and other financial institutions ’āś Community loan funds and lending circles ’āś Access to capital and investment funding
- 18. Infrastructure is part of the resources needed to be effective in community development and includes such obvious things as: ’āś Physical buildings and structures ’āś Transportation and access ’āś Communication systems ’āś Electrical, hydro, sewage, garbage and heating.
- 19. Infrastructure also refers to the political systems and leadership needed to support a community.
- 20. ’āÆ Assessment of the current situation ’āÆ Identifying required resources for the project ’āÆ Comparing what is needed and what is available to determine the gaps ’āÆ Identifying potential sources of needed resources ’āÆ Outlining best strategies for approaching stakeholders (donors and partners) ’āÆ Outlining monitoring and review mechanisms. ’āÆ Documentation of all activities