Hepatic encephalopathy
Download as PPTX, PDF183 likes92,649 views
Hepatic encephalopathy occurs when the liver fails to detoxify toxic substances, such as ammonia, which are then able to pass into the brain. This causes neurological symptoms ranging from mild confusion to coma. Precipitating factors include gastrointestinal bleeding, infections, and certain drugs. Treatment focuses on reducing ammonia production in the gut through lactulose, antibiotics, and low-protein diets. Correcting electrolyte imbalances and removing precipitating medications or infections are also important for management of hepatic encephalopathy.
1 of 31
Downloaded 2,208 times





![Causes
• Chronic parenchymal liver disease:
• Chronic hepatitis.
• Cirrhosis.
• Fulminating hepatic failure:
• Acute viral hepatitis.
• Drugs.
• Toxins e.g. Wilson’s Disease, CCL4.
• Surgical Portal-systemic anastomoses, - portacaval
shunts, or Transjugular intrahepatic portal-systemic
shunting [TIPS]).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hepaticencephalopathy-140617003917-phpapp02/85/Hepatic-encephalopathy-6-320.jpg)























Recommended
Hepatic Encephalopathy -Pathophysiology,Evaluation And Management



Hepatic Encephalopathy -Pathophysiology,Evaluation And ManagementSantosh Narayankar
Ěý
Hepatic encephalopathy is a brain dysfunction caused by liver disease or portosystemic shunting. It presents as a wide range of neurological or psychiatric abnormalities from mild alterations to coma. The prevalence is 30-40% in those with cirrhosis and risk of first episode is 5-25% within 5 years of cirrhosis diagnosis. Recurrence risk after an initial episode is 40% within 1 year. Ammonia, systemic inflammation, manganese, genetics, and oxidative stress may all contribute to pathogenesis. Diagnosis involves clinical exam and testing like serum ammonia levels or neuropsychological tests on phone apps. Management involves treating precipitating factors, lactulose, antibiotics like rifaximin, andHepatic encephalopathy



Hepatic encephalopathyChandan N
Ěý
Portal-systemic encephalopathy is a brain disorder caused by liver dysfunction that allows toxins to reach the brain. It is characterized by alterations in mental status, neurological abnormalities, and distinctive EEG changes. The main underlying mechanism involves increased levels of ammonia in the bloodstream from the gut that are normally processed by the liver. Treatment focuses on reducing ammonia production in the colon through medications like lactulose and restricting protein intake. Prognosis depends on the underlying liver disease and can range from fully treatable acute episodes to chronic and potentially fatal cases.Hepatic failure



Hepatic failureEkta Patel
Ěý
Liver failure occurs when the liver rapidly loses its ability to function, resulting in mental status changes and coagulation abnormalities. It can be caused by viral hepatitis, drug toxicity, toxins, vascular issues, or metabolic diseases. Acute liver failure presents as a sudden onset of severe liver injury in someone without pre-existing liver disease. It requires emergency treatment and may necessitate a liver transplant if liver function cannot be reversed. Management involves supportive care, medications to treat complications, and sometimes a liver transplant.Portal hypertension



Portal hypertensionMohit Chaudhary
Ěý
Portal hypertension occurs when there is increased resistance to blood flow through the portal vein, causing elevated pressure. It is defined as a hepatic venous pressure gradient over 5 mmHg. Measurement involves catheterization of the hepatic vein. Causes include cirrhosis and other liver diseases. Complications include variceal bleeding, ascites, and encephalopathy. Treatment of acute bleeding involves vasoactive drugs, endoscopic therapy, and TIPS. Secondary prevention uses beta-blockers to reduce portal pressure and risk of rebleeding.Cholangitis



CholangitisLala Gladson Ananda Robin
Ěý
Acute cholangitis is an infection of the bile ducts caused by obstruction and bacterial overgrowth. It presents with fever, jaundice, and right upper quadrant pain (Charcot's triad). Obstruction leads to increased pressure and bacterial growth in the bile ducts. Diagnosis involves blood tests, imaging like ultrasound or CT, and testing bile if drained. Treatment is antibiotics, hydration, and relieving obstruction endoscopically or surgically. Antibiotics are continued until obstruction is fully resolved to prevent recurrence.acute pancreatitis



acute pancreatitisssn zhd
Ěý
Acute pancreatitis is a condition where pancreatic enzymes leak into the pancreas and cause its auto-digestion. Common causes include gallstones, alcohol use, and idiopathic factors. Patients present with epigastric pain radiating to the back that is exacerbated by eating or lying down. Lab tests show elevated pancreatic enzymes and imaging shows changes to the pancreas. Treatment is supportive with NPO, IV fluids, pain control and monitoring for complications like necrosis, pseudocysts, shock and respiratory failure. Severe cases may require ERCP, surgery or drainage procedures.Diabetic Ketoacidosis



Diabetic KetoacidosisCikbungazafieya Zawani
Ěý
Diabetes is a condition where the body does not properly process glucose due to lack of insulin or insulin resistance. Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) occurs when a lack of insulin causes the body to break down fat and produce ketones, leading to hyperglycemia, ketosis and acidosis. DKA treatment involves rehydration, insulin therapy to lower blood glucose and ketone levels, electrolyte replacement, and identifying/treating the precipitating cause. Complications can include infection, shock, thrombosis, pulmonary edema and cerebral edema. Prevention relies on education about sick day management to avoid DKA during illness.Pheochromocytoma



PheochromocytomaGAMANDEEP
Ěý
The document discusses pheochromocytoma, a rare tumor of the adrenal glands that secretes excess catecholamines. It causes high blood pressure, headaches, increased heart rate and metabolic changes. Diagnosis involves testing urine and plasma catecholamine levels. Treatment includes alpha-blockers to lower blood pressure before surgery to remove the tumor. Nursing care focuses on monitoring vital signs and blood pressure to prevent hypertensive crises before and after surgery.Pheochromocytoma



Pheochromocytomarashree-singh
Ěý
Phreochromocytoma : overvew, introduction, adrenal gland anatomy and physiology, adrenl gland tumor classification, epidemiology, clinical features, investigationsCholelithiasis



CholelithiasisNikhil Gupta
Ěý
This document discusses predisposing factors, pathogenesis, types, clinical features, complications, investigations, differential diagnosis, and management of gallstones. The main types are cholesterol stones, mixed stones, and pigment stones. Risk factors include obesity, female sex hormones, age, pregnancy, certain drugs, and diabetes. Gallstones can cause symptoms like biliary colic or be asymptomatic. Complications involve inflammation of the gallbladder or bile ducts. Treatment options are medical therapy with ursodeoxycholic acid for small cholesterol stones or laparoscopic cholecystectomy.Ulcerative colitis



Ulcerative colitissyed ubaid
Ěý
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that affects the colon. It is characterized by inflammation and ulcers in the lining of the rectum and colon. The causes are unknown but likely involve genetic and immune factors. Symptoms include abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, and weight loss. Diagnosis involves blood tests, colonoscopy, and biopsy. Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation through medications like mesalamine, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or biologics. Surgery to remove the colon may be needed for severe cases or cancer prevention. Complications can include toxic megacolon, colon cancer, and extraintestinal manifestations.Fulminant hepatic failure



Fulminant hepatic failureRanjithkumar Kondapaka
Ěý
Fulminant hepatic failure is a clinical syndrome resulting from massive liver cell necrosis or impairment. It is characterized by coagulopathy and encephalopathy that develops over less than 8 weeks. The liver loses its synthetic, excretory, and detoxifying functions. Causes include viral hepatitis, drugs like acetaminophen, and metabolic disorders. Presentation includes jaundice, fever, vomiting, and confusion. Treatment focuses on supportive care, treating complications, and sometimes liver transplantation. Prognosis depends on factors like age, etiology, and development of complications.Obstructive jaundice



Obstructive jaundiceBashir BnYunus
Ěý
obstructive jaundice, cholestasis, cholangitis, pancreatic head tumour, periampullary tumour, cholangiocarcinoma, Inguinal hernia



Inguinal herniafathimma sahir
Ěý
This document provides information on the anatomy of the inguinal canal and inguinal hernias. It describes the boundaries and structures that pass through the inguinal canal. It discusses the types of inguinal hernias including indirect, direct, and femoral hernias. It also covers the clinical features of inguinal hernias such as symptoms, precipitating causes, and examination findings including inspection, palpation, and tests to determine hernia type.Management of seizures



Management of seizuresPraveen Nagula
Ěý
This document discusses the management of seizures. It covers the approach to evaluating a patient with seizures, including common diagnostic tests. It then classifies traditional and newer antiepileptic drugs, describing their mechanisms of action and uses in treating different seizure disorders. The document discusses in detail several commonly used antiepileptic drugs, including phenytoin, carbamazepine, phenobarbital, vigabatrin, lamotrigine, felbamate, gabapentin, pregabalin, topiramate, and valproic acid. It also addresses status epilepticus, drug interactions, teratogenic effects, surgical treatment options, and newer drugs in development.Cholecystitis



CholecystitisVikrant Udutha
Ěý
This document provides an overview of cholecystitis, including:
1. It defines cholecystitis as the inflammatory condition of the gallbladder and describes the types of acute cholecystitis.
2. It outlines the clinical features of acute cholecystitis including symptoms like colicky pain and signs like Murphy's sign.
3. It discusses the treatment options for acute cholecystitis which include conservative treatment, early cholecystectomy, or emergency cholecystostomy depending on the severity of the case.Cushing Syndrome



Cushing SyndromeDr. Binu Babu Nursing Lectures Incredibly Easy
Ěý
Cushing syndrome is characterized by excess cortisol secretion caused by too much ACTH from the pituitary gland or excess cortisol from adrenal tumors. It presents with weight gain, thin extremities, moon face, skin changes, and metabolic complications. Diagnosis involves urine and blood tests to measure cortisol levels. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include surgery to remove tumors, radiation therapy, or medications to reduce cortisol levels. Nursing care focuses on preventing infections, injuries, skin breakdown and improving nutrition, fluid balance and body image.Liver abscess



Liver abscessJibran Mohsin
Ěý
Liver abscesses can be pyogenic (caused by bacteria), amoebic (caused by Entamoeba histolytica), or fungal. Pyogenic liver abscesses are most commonly located in the right lobe due to blood flow patterns and are usually caused by gram-negative bacteria like E. coli. Patients present with fever, right upper quadrant pain, hepatomegaly, and diarrhea in some cases of amoebic abscess. Diagnosis involves blood tests, imaging like CT or ultrasound, and abscess fluid culture. Treatment is drainage of pus combined with antibiotics, usually percutaneous catheter drainage guided by imaging. For amoebic abscess, metronidazole is usuallyChronic liver disease



Chronic liver diseasePuneet Shukla
Ěý
This document summarizes chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. It describes cirrhosis as scarring of the liver caused by chronic liver disease leading to loss of liver function. Common causes include alcohol, hepatitis B/C, NASH, and genetic disorders. Complications include ascites, variceal bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy, hepatorenal syndrome, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Management involves treating the underlying cause, vaccinations, diuretics, banding/TIPS for varices, lactulose for encephalopathy, and liver transplantation for late stage disease.chronic liver disease (CLD)



chronic liver disease (CLD)Kashif Hussain
Ěý
This lecture the whole information related to chronic liver disease, its causes, investigation and treatment.Achalasia



Achalasiafareedresidency
Ěý
Achalasia is a rare disorder of the esophagus that results from damaged nerves that control food movement. It causes difficulty swallowing and food getting stuck. The document discusses the causes, symptoms, tests used to diagnose (endoscopy, manometry), and treatments of achalasia. Treatments include medications to relax muscles, botox injections, balloon dilation procedures, and surgeries like Heller myotomy to cut the lower esophageal sphincter muscle.Esophageal varices



Esophageal varicesShweta Sharma
Ěý
This document discusses oesophageal varices, which are dilated and tortuous veins in the oesophageal wall caused by increased venous pressure. Varices are prone to rupture and bleeding. The document defines portal hypertension and discusses the epidemiology, etiology, risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic evaluations, medical and surgical management, nursing care, and conclusions regarding oesophageal varices. It also summarizes two research articles on using capsule endoscopy to diagnose varices and using blood ammonia levels to predict variceal presence and bleeding risk.RECTAL PROLAPSE 



RECTAL PROLAPSE Kushal kumar
Ěý
This document discusses rectal prolapse, which is the protrusion of the rectum outside of the body. It describes the types of rectal prolapse as partial or complete. Risk factors include weakened muscles, trauma from childbirth, and conditions that increase abdominal pressure. Treatment depends on the type and severity of prolapse, ranging from injections to repair surgery via abdominal or perineal approaches. Complications of surgery include nerve damage, infection, and recurrence of prolapse.Status Epilepticus



Status EpilepticusZeeshan Khan
Ěý
This document discusses status epilepticus, which is defined as prolonged or repeated seizures without recovery between seizures. It classifies status epilepticus, explores its pathophysiology and etiology, and outlines its presentation, differential diagnosis, workup, and management. Status epilepticus results from either failed seizure termination mechanisms or initiation of mechanisms leading to prolonged seizures. It can cause neuronal death or injury if not promptly treated. Management involves initial treatment with benzodiazepines followed by anti-seizure medications like fosphenytoin or anesthetic doses if seizures persist over 40 minutes.Obstructive jaundice



Obstructive jaundiceSilah Aysha
Ěý
This document contains information on various biliary diseases including gallstones, cholangiocarcinoma, pancreatic cancer, and biliary strictures. It discusses the clinical presentation, investigations, and management of biliary obstructions of different types including those caused by stones, tumors, strictures, and cysts. The diagnosis and treatment of choledochal cysts and sclerosing cholangitis are also covered.Pyelonephritis, ACUTE PYELONEPHRITIS, CHRONIC PYELONEPHRITIS, 



Pyelonephritis, ACUTE PYELONEPHRITIS, CHRONIC PYELONEPHRITIS, pankaj rana
Ěý
Pyelonephritis
It is the inflammation of the kidney & upper urinary tract that usually results from the bacterial infection of the bladder.
Pyelonephritis can be classified in several different catagories:
-acute pyelonephritis
-chronic pyelonephritis
-xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
Intestinal obstruction



Intestinal obstructionsyed ubaid
Ěý
Intestinal obstruction occurs when the normal passage of intestinal contents is blocked. It can involve the small intestine, large intestine, or both. Obstructions are classified as mechanical, which involve a physical blockage, or dynamic/adynamic, which involve ineffective motility without a blockage. Common causes include adhesions, hernias, tumors, and volvulus. Symptoms vary based on the location and severity of the obstruction but often include colicky abdominal pain, vomiting, distention, and constipation. Diagnosis involves physical exam findings like distention and hyperperistalsis as well as imaging tests showing gas/fluid levels and other signs of obstruction.Abdiminal tuberculosis



Abdiminal tuberculosisThorlikonda Sasidhar
Ěý
1. Abdominal tuberculosis refers to tuberculosis infection of the gastrointestinal tract, mesenteric lymph nodes, peritoneum, and organs like the liver and spleen.
2. It is commonly caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis or M. bovis bacteria and spreads via ingestion, hematogenous spread, or lymphatic spread.
3. Common presentations include abdominal pain, fever, weight loss, and the formation of masses, strictures, or ascites in the abdomen. Investigations include imaging tests, blood tests, and microbiological analysis of samples.Hepatic encephalopathy [HE]![Hepatic encephalopathy [HE]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/hepaticencephalopathy-200612174704-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Hepatic encephalopathy [HE]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/hepaticencephalopathy-200612174704-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Hepatic encephalopathy [HE]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/hepaticencephalopathy-200612174704-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Hepatic encephalopathy [HE]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/hepaticencephalopathy-200612174704-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Hepatic encephalopathy [HE]Deepak Pradeep
Ěý
Hepatic encephalopathy is a disorder of brain function caused by liver failure and the buildup of toxic substances. Ammonia produced during protein breakdown in the gut cannot be removed by the damaged liver and crosses into the brain. Symptoms range from confusion to coma. Treatment aims to reduce ammonia levels through a low-protein diet, lactulose to increase ammonia excretion, antibiotics to treat gut infections, and medications to stimulate ammonia metabolism. Prognosis depends on the severity and reversibility of the underlying liver disease.Hepatic encephalopathy



Hepatic encephalopathyArun George
Ěý
Hepatic encephalopathy in Paediatrics, Hepatology, Critical care, Pediatric Intensive care, Pediatric emegency, Gastroenterology, Acute liver failure, Fulminant hepatic failureMore Related Content
What's hot (20)
Pheochromocytoma



Pheochromocytomarashree-singh
Ěý
Phreochromocytoma : overvew, introduction, adrenal gland anatomy and physiology, adrenl gland tumor classification, epidemiology, clinical features, investigationsCholelithiasis



CholelithiasisNikhil Gupta
Ěý
This document discusses predisposing factors, pathogenesis, types, clinical features, complications, investigations, differential diagnosis, and management of gallstones. The main types are cholesterol stones, mixed stones, and pigment stones. Risk factors include obesity, female sex hormones, age, pregnancy, certain drugs, and diabetes. Gallstones can cause symptoms like biliary colic or be asymptomatic. Complications involve inflammation of the gallbladder or bile ducts. Treatment options are medical therapy with ursodeoxycholic acid for small cholesterol stones or laparoscopic cholecystectomy.Ulcerative colitis



Ulcerative colitissyed ubaid
Ěý
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that affects the colon. It is characterized by inflammation and ulcers in the lining of the rectum and colon. The causes are unknown but likely involve genetic and immune factors. Symptoms include abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, and weight loss. Diagnosis involves blood tests, colonoscopy, and biopsy. Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation through medications like mesalamine, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or biologics. Surgery to remove the colon may be needed for severe cases or cancer prevention. Complications can include toxic megacolon, colon cancer, and extraintestinal manifestations.Fulminant hepatic failure



Fulminant hepatic failureRanjithkumar Kondapaka
Ěý
Fulminant hepatic failure is a clinical syndrome resulting from massive liver cell necrosis or impairment. It is characterized by coagulopathy and encephalopathy that develops over less than 8 weeks. The liver loses its synthetic, excretory, and detoxifying functions. Causes include viral hepatitis, drugs like acetaminophen, and metabolic disorders. Presentation includes jaundice, fever, vomiting, and confusion. Treatment focuses on supportive care, treating complications, and sometimes liver transplantation. Prognosis depends on factors like age, etiology, and development of complications.Obstructive jaundice



Obstructive jaundiceBashir BnYunus
Ěý
obstructive jaundice, cholestasis, cholangitis, pancreatic head tumour, periampullary tumour, cholangiocarcinoma, Inguinal hernia



Inguinal herniafathimma sahir
Ěý
This document provides information on the anatomy of the inguinal canal and inguinal hernias. It describes the boundaries and structures that pass through the inguinal canal. It discusses the types of inguinal hernias including indirect, direct, and femoral hernias. It also covers the clinical features of inguinal hernias such as symptoms, precipitating causes, and examination findings including inspection, palpation, and tests to determine hernia type.Management of seizures



Management of seizuresPraveen Nagula
Ěý
This document discusses the management of seizures. It covers the approach to evaluating a patient with seizures, including common diagnostic tests. It then classifies traditional and newer antiepileptic drugs, describing their mechanisms of action and uses in treating different seizure disorders. The document discusses in detail several commonly used antiepileptic drugs, including phenytoin, carbamazepine, phenobarbital, vigabatrin, lamotrigine, felbamate, gabapentin, pregabalin, topiramate, and valproic acid. It also addresses status epilepticus, drug interactions, teratogenic effects, surgical treatment options, and newer drugs in development.Cholecystitis



CholecystitisVikrant Udutha
Ěý
This document provides an overview of cholecystitis, including:
1. It defines cholecystitis as the inflammatory condition of the gallbladder and describes the types of acute cholecystitis.
2. It outlines the clinical features of acute cholecystitis including symptoms like colicky pain and signs like Murphy's sign.
3. It discusses the treatment options for acute cholecystitis which include conservative treatment, early cholecystectomy, or emergency cholecystostomy depending on the severity of the case.Cushing Syndrome



Cushing SyndromeDr. Binu Babu Nursing Lectures Incredibly Easy
Ěý
Cushing syndrome is characterized by excess cortisol secretion caused by too much ACTH from the pituitary gland or excess cortisol from adrenal tumors. It presents with weight gain, thin extremities, moon face, skin changes, and metabolic complications. Diagnosis involves urine and blood tests to measure cortisol levels. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include surgery to remove tumors, radiation therapy, or medications to reduce cortisol levels. Nursing care focuses on preventing infections, injuries, skin breakdown and improving nutrition, fluid balance and body image.Liver abscess



Liver abscessJibran Mohsin
Ěý
Liver abscesses can be pyogenic (caused by bacteria), amoebic (caused by Entamoeba histolytica), or fungal. Pyogenic liver abscesses are most commonly located in the right lobe due to blood flow patterns and are usually caused by gram-negative bacteria like E. coli. Patients present with fever, right upper quadrant pain, hepatomegaly, and diarrhea in some cases of amoebic abscess. Diagnosis involves blood tests, imaging like CT or ultrasound, and abscess fluid culture. Treatment is drainage of pus combined with antibiotics, usually percutaneous catheter drainage guided by imaging. For amoebic abscess, metronidazole is usuallyChronic liver disease



Chronic liver diseasePuneet Shukla
Ěý
This document summarizes chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. It describes cirrhosis as scarring of the liver caused by chronic liver disease leading to loss of liver function. Common causes include alcohol, hepatitis B/C, NASH, and genetic disorders. Complications include ascites, variceal bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy, hepatorenal syndrome, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Management involves treating the underlying cause, vaccinations, diuretics, banding/TIPS for varices, lactulose for encephalopathy, and liver transplantation for late stage disease.chronic liver disease (CLD)



chronic liver disease (CLD)Kashif Hussain
Ěý
This lecture the whole information related to chronic liver disease, its causes, investigation and treatment.Achalasia



Achalasiafareedresidency
Ěý
Achalasia is a rare disorder of the esophagus that results from damaged nerves that control food movement. It causes difficulty swallowing and food getting stuck. The document discusses the causes, symptoms, tests used to diagnose (endoscopy, manometry), and treatments of achalasia. Treatments include medications to relax muscles, botox injections, balloon dilation procedures, and surgeries like Heller myotomy to cut the lower esophageal sphincter muscle.Esophageal varices



Esophageal varicesShweta Sharma
Ěý
This document discusses oesophageal varices, which are dilated and tortuous veins in the oesophageal wall caused by increased venous pressure. Varices are prone to rupture and bleeding. The document defines portal hypertension and discusses the epidemiology, etiology, risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic evaluations, medical and surgical management, nursing care, and conclusions regarding oesophageal varices. It also summarizes two research articles on using capsule endoscopy to diagnose varices and using blood ammonia levels to predict variceal presence and bleeding risk.RECTAL PROLAPSE 



RECTAL PROLAPSE Kushal kumar
Ěý
This document discusses rectal prolapse, which is the protrusion of the rectum outside of the body. It describes the types of rectal prolapse as partial or complete. Risk factors include weakened muscles, trauma from childbirth, and conditions that increase abdominal pressure. Treatment depends on the type and severity of prolapse, ranging from injections to repair surgery via abdominal or perineal approaches. Complications of surgery include nerve damage, infection, and recurrence of prolapse.Status Epilepticus



Status EpilepticusZeeshan Khan
Ěý
This document discusses status epilepticus, which is defined as prolonged or repeated seizures without recovery between seizures. It classifies status epilepticus, explores its pathophysiology and etiology, and outlines its presentation, differential diagnosis, workup, and management. Status epilepticus results from either failed seizure termination mechanisms or initiation of mechanisms leading to prolonged seizures. It can cause neuronal death or injury if not promptly treated. Management involves initial treatment with benzodiazepines followed by anti-seizure medications like fosphenytoin or anesthetic doses if seizures persist over 40 minutes.Obstructive jaundice



Obstructive jaundiceSilah Aysha
Ěý
This document contains information on various biliary diseases including gallstones, cholangiocarcinoma, pancreatic cancer, and biliary strictures. It discusses the clinical presentation, investigations, and management of biliary obstructions of different types including those caused by stones, tumors, strictures, and cysts. The diagnosis and treatment of choledochal cysts and sclerosing cholangitis are also covered.Pyelonephritis, ACUTE PYELONEPHRITIS, CHRONIC PYELONEPHRITIS, 



Pyelonephritis, ACUTE PYELONEPHRITIS, CHRONIC PYELONEPHRITIS, pankaj rana
Ěý
Pyelonephritis
It is the inflammation of the kidney & upper urinary tract that usually results from the bacterial infection of the bladder.
Pyelonephritis can be classified in several different catagories:
-acute pyelonephritis
-chronic pyelonephritis
-xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
Intestinal obstruction



Intestinal obstructionsyed ubaid
Ěý
Intestinal obstruction occurs when the normal passage of intestinal contents is blocked. It can involve the small intestine, large intestine, or both. Obstructions are classified as mechanical, which involve a physical blockage, or dynamic/adynamic, which involve ineffective motility without a blockage. Common causes include adhesions, hernias, tumors, and volvulus. Symptoms vary based on the location and severity of the obstruction but often include colicky abdominal pain, vomiting, distention, and constipation. Diagnosis involves physical exam findings like distention and hyperperistalsis as well as imaging tests showing gas/fluid levels and other signs of obstruction.Abdiminal tuberculosis



Abdiminal tuberculosisThorlikonda Sasidhar
Ěý
1. Abdominal tuberculosis refers to tuberculosis infection of the gastrointestinal tract, mesenteric lymph nodes, peritoneum, and organs like the liver and spleen.
2. It is commonly caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis or M. bovis bacteria and spreads via ingestion, hematogenous spread, or lymphatic spread.
3. Common presentations include abdominal pain, fever, weight loss, and the formation of masses, strictures, or ascites in the abdomen. Investigations include imaging tests, blood tests, and microbiological analysis of samples.Similar to Hepatic encephalopathy (20)
Hepatic encephalopathy [HE]![Hepatic encephalopathy [HE]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/hepaticencephalopathy-200612174704-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Hepatic encephalopathy [HE]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/hepaticencephalopathy-200612174704-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Hepatic encephalopathy [HE]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/hepaticencephalopathy-200612174704-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Hepatic encephalopathy [HE]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/hepaticencephalopathy-200612174704-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Hepatic encephalopathy [HE]Deepak Pradeep
Ěý
Hepatic encephalopathy is a disorder of brain function caused by liver failure and the buildup of toxic substances. Ammonia produced during protein breakdown in the gut cannot be removed by the damaged liver and crosses into the brain. Symptoms range from confusion to coma. Treatment aims to reduce ammonia levels through a low-protein diet, lactulose to increase ammonia excretion, antibiotics to treat gut infections, and medications to stimulate ammonia metabolism. Prognosis depends on the severity and reversibility of the underlying liver disease.Hepatic encephalopathy



Hepatic encephalopathyArun George
Ěý
Hepatic encephalopathy in Paediatrics, Hepatology, Critical care, Pediatric Intensive care, Pediatric emegency, Gastroenterology, Acute liver failure, Fulminant hepatic failureHepatic encephalopathy for student by dr Mohammed Hussien 



Hepatic encephalopathy for student by dr Mohammed Hussien Kafrelsheiekh University
Ěý
What is Hepatic Encephalopathy.
What is the Grading of Hepatic Encephalopathy.
How to Diagnose Hepatic Encephalopathy .
How to Treat Hepatic Encephalopathy. urea cycle.pptx



urea cycle.pptxSanthiMeherPeddi
Ěý
The document summarizes urea cycle disorders (UCDs), which are caused by genetic mutations that impair the urea cycle - a pathway in the liver that detoxifies ammonia. The key points are:
1) UCDs can range from severe neonatal presentation with hyperammonemia and coma to late-onset episodic symptoms.
2) Diagnosis involves measuring elevated blood ammonia and amino acid levels. Enzyme analysis or DNA testing can confirm the specific UCD.
3) Treatment focuses on removing ammonia via medications like sodium phenylacetate-sodium benzoate, supplying essential precursors like arginine, and preventing protein intake and catabolism. VigMetabolic 5 5-2013



Metabolic 5 5-2013Azad Haleem
Ěý
This document summarizes various inborn errors of metabolism, including:
- Disorders of amino acid metabolism such as phenylketonuria (PKU), tyrosinemia, maple syrup urine disease (MSUD), homocystinuria, and nonketotic hyperglycinemia.
- Urea cycle defects which result in abnormal nitrogen metabolism and elevated ammonia levels.
- Disorders of organic acid metabolism including propionic acidemia, methylmalonic acidemia, isovaleric acidemia, and glutaric aciduria type 1.
- A disorder of fatty acid metabolism, medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (MCAD), is also mentioned.20110722 - Czaja - LFTs.ppt



20110722 - Czaja - LFTs.pptHassanWajid4
Ěý
Liver function tests can evaluate for liver injury and dysfunction. Elevated levels of aminotransferases AST and ALT indicate hepatocyte injury, while elevated alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin suggest cholestasis or bile flow obstruction. Tests of synthetic function include albumin and coagulation factors. Specific diseases are identified by viral hepatitis serologies, iron studies, ceruloplasmin, and antimitochondrial antibodies. Abnormal tests must be interpreted in context of the clinical picture and potential non-hepatic causes. Liver biopsy may be needed to determine etiology and severity of injury when tests are inconclusive.APPROACH TO ABNORMAL LFT



APPROACH TO ABNORMAL LFTNavas Shareef
Ěý
SYSTEMATIC APPROACH TO LIVER FUNCTION TEST
BY Dr. Navas Shareef. P.P (MBBS)
THIS PRESENTATION IS MADE IN A SIMPLIFIED FORM SO THAT EVERYONE COULD UNDERSTAND ABOUT A LIVER FUNCTION TEST EASILYHepatic encephalopathy



Hepatic encephalopathyBikash Praharaj
Ěý
This document provides an overview of hepatic encephalopathy. It defines hepatic encephalopathy as a complex metabolic disorder seen in patients with liver dysfunction, characterized by disturbances in consciousness and behavior. It discusses the pathogenesis, including the ammonia and false neurotransmitter hypotheses. Precipitating factors and clinical manifestations ranging from mild cognitive changes to coma are described. Diagnosis involves ruling out other causes and elevated ammonia levels. Treatment focuses on reducing ammonia through dietary changes, lactulose, antibiotics, and other supportive measures. Prognosis depends on the severity and underlying liver disease.Antigout pharmacology. Medicine use in gout



Antigout pharmacology. Medicine use in goutPawan Maharjan
Ěý
This document discusses drug use in the treatment of gout. It begins by describing gout as a disorder of purine metabolism that causes high uric acid levels and the precipitation of urate crystals in joints. It then covers the types and pathogenesis of gout. The main drug classes used for treatment are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, and corticosteroids for acute attacks. For chronic management, uricosuric agents like probenecid increase uric acid excretion, while allopurinol and febuxostat inhibit uric acid synthesis by blocking xanthine oxidase. The document provides details on the mechanisms of action, pharmacokineticsAlcoholic liver disease



Alcoholic liver diseaseKiran Bikkad
Ěý
Chronic excessive alcohol consumption can lead to a spectrum of alcoholic liver disease including fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and cirrhosis. Fatty liver is most common, while only 10-20% of alcoholics develop hepatitis. Hepatitis is characterized by hepatocyte injury, ballooning, and inflammation. Cirrhosis results in fibrosis and nodular regeneration of liver architecture. Complications include ascites, variceal bleeding, and hepatic encephalopathy. Treatment of alcoholic liver disease involves abstaining from alcohol and managing complications. Corticosteroids may benefit severe hepatitis. Liver transplantation is an option for end-stage disease if abstinence is maintained.INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE-UC,CD DRUGS.pptx



INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE-UC,CD DRUGS.pptxasmitapandey5196
Ěý
This document discusses inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. It covers the etiology, pathogenesis, clinical features, and pharmacotherapy of IBD. Regarding treatment, it describes the use of 5-aminosalicylic acids, corticosteroids, immunomodulators, antibiotics/probiotics, biological therapies targeting TNF-α, and newer non-TNF-α inhibitors to induce and maintain remission of IBD. Adverse effects of the different drug classes are also outlined.Acute liver failure in children



Acute liver failure in childrenRamsha Baig
Ěý
Acute hepatic failure in children is defined as biochemical evidence of acute liver injury within 8 weeks with coagulopathy and encephalopathy or prolonged prothrombin time not due to preexisting liver disease. It can be caused by infections, drugs, metabolic disorders, toxins, autoimmune conditions, and ischemia. Presentations include jaundice, fever, vomiting, and altered mental status. Treatment involves supportive care, treating the underlying cause, managing complications, and temporary liver support such as bioartificial liver devices or transplantation. Prognosis depends on the cause, with viral hepatitis having a better prognosis than drug-induced failure.Hepatic Failure & Hepato Renal Syndrome.pptx



Hepatic Failure & Hepato Renal Syndrome.pptxdrhardikastik1
Ěý
Hepatic failure and hepatorenal syndrome are characterized by liver dysfunction and associated kidney impairment. Portal hypertension and toxins that normally metabolized by the liver can accumulate in the brain, causing encephalopathy. Hepatorenal syndrome is classified as type 1 with rapid renal decline or type 2 with slower progression. It involves circulatory changes and activation of vasoactive systems. Treatment focuses on correcting precipitating factors, volume expansion, medications to constrict renal vasculature, and liver transplantation which is the definitive treatment. Dialysis may be used as a bridge to transplantation.A review of liver anatomy and physiology for anesthesiologists



A review of liver anatomy and physiology for anesthesiologistsArun Shetty
Ěý
The document provides an overview of liver anatomy and physiology. It discusses the liver's macroscopic and microscopic structure, including its lobes, vascular and biliary systems. Key functions of the liver are metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and drugs. The liver's role in hematopoiesis, bilirubin metabolism, and production of clotting factors is also summarized. Phases of drug biotransformation and factors affecting it are briefly explained. Common liver function tests and their clinical significance are reviewed to assess hepatic abnormalities.Dyselectrolytemias



DyselectrolytemiasDr Sunit Lokwani
Ěý
Covers topics of hypo/hyperkalemia, hypo/hypercalcemia and hypo/hypernatremia in an oncology setting.Liver function tests interpretation bilirubin metabolism



Liver function tests interpretation bilirubin metabolismDrMAnwar2
Ěý
liver function tests for PGs and under graduatesRecent advances in renal ...



Recent advances in renal ...kalpanatiwari17
Ěý
This document summarizes recent advances in renal pharmacology presented by Dr. Kalpana Tiwari. It begins by classifying kidney disease as either acute or chronic, then describes stages and treatments for acute kidney injury including optimization of hemodynamics, elimination of nephrotoxins, and initiation of renal replacement therapy if needed. Chronic kidney disease is defined and stages outlined. New pharmacological treatments discussed include ferric citrate, ferric carboxymaltose, belatacept, tolvaptan, etelcalcetide, and ravulizumab-cwvz. The mechanisms of action and side effects of these drugs are summarized.Recently uploaded (20)
ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ěý
ASP.NET Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatNUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdf



NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdfDolisha Warbi
Ěý
NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION, Introduction, definition, types - macronutrient and micronutrient, food pyramid, meal planning, nutritional assessment of individual, family and community by using appropriate method, nutrition education, nutritional rehabilitation, nutritional deficiency disorder, law/policies regarding nutrition in India, food hygiene, food fortification, food handling and storage, food preservation, food preparation, food purchase, food consumption, food borne diseases, food poisoningAdministrative bodies( D and C Act, 1940



Administrative bodies( D and C Act, 1940P.N.DESHMUKH
Ěý
These presentation include information about administrative bodies such as D.T.A.B
CDL AND DCC, etc.Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
Ěý
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxBISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAH



BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHcoacharyasetiyaki
Ěý
BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHHow to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Proforma Invoice in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
Ěý
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.Interim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptx



Interim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptxsirjeromemanansala
Ěý
This is the latest issuance on PMES as replacement of RPMS. Kindly message me to gain full access of the presentation. Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdf



Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdfAjaz Hussain
Ěý
The intersection of AI and pharmaceutical formulation science highlights significant blind spots—systemic gaps in pharmaceutical development, regulatory oversight, quality assurance, and the ethical use of AI—that could jeopardize patient safety and undermine public trust. To move forward effectively, we must address these normalized blind spots, which may arise from outdated assumptions, errors, gaps in previous knowledge, and biases in language or regulatory inertia. This is essential to ensure that AI and formulation science are developed as tools for patient-centered and ethical healthcare.RRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper (MMV Exam MCQ)



RRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper (MMV Exam MCQ)SONU HEETSON
Ěý
RRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper. MMV MCQ PDF Free Download for Railway Assistant Loco Pilot Exam.AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...



AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria
Ěý
AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publication, UGC-MMTTC, MANUU, 25/02/2025, Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria, University of Delhi, vinodpr111@gmail.comHannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...



Hannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...EduSkills OECD
Ěý
Hannah Borhan, Research Assistant, OECD Education and Skills Directorate and Pietro Gagliardi, Policy Analyst, OECD Public Governance Directorate present at the OECD webinar 'From classroom to community engagement: Promoting active citizenship among young people" on 25 February 2025. You can find the recording of the webinar on the website https://oecdedutoday.com/webinars/
Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ěý
Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatAzure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHat



Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ěý
Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHatHelping Autistic Girls Shine Webinar şÝşÝߣs



Helping Autistic Girls Shine Webinar şÝşÝߣsPooky Knightsmith
Ěý
For more information about my speaking and training work, visit: https://www.pookyknightsmith.com/speaking/AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...



AI and Academic Writing, Short Term Course in Academic Writing and Publicatio...Prof. (Dr.) Vinod Kumar Kanvaria
Ěý
Hepatic encephalopathy
- 2. Definition • It is a state of disordered CNS function, resulting from failure of liver to detoxify toxic agents because of hepatic insufficiency and porto-systemic shunt. • It represents a reversible decrease in neurologic function. • It occurs most often in patients with cirrhosis but also occur in acute hepatic failure.
- 3. Pathogenesis • Ammonia formed by protein breakdown in GIT • Liver liver dysfunction (abnormal) NH3 Passes BBB Hepatic encephalopathy. • Other factors: • Increase sensitivity to glutamine & GABA (inhibitory neurotransmitter) • Increase circulating levels of endogenous benzodiazepines.
- 4. Pathogenesis (acute & chronic ) The basic cause is same in both forms but the mechanism is somewhat different Diminished detoxification of toxic intestinal nitrogenous compounds Increased in blood NH3 etc Toxic effect on brain Appearance of abnormal amines in systemic circulation Interference with neurotransmission
- 5. Endotoxins • Ammonia. • Mercaptans (degradation of methionine in the gut) • Phenols. • Free fatty acids. • Gamma amino butyric acid(GABA) • Octopamine.
- 6. Causes • Chronic parenchymal liver disease: • Chronic hepatitis. • Cirrhosis. • Fulminating hepatic failure: • Acute viral hepatitis. • Drugs. • Toxins e.g. Wilson’s Disease, CCL4. • Surgical Portal-systemic anastomoses, - portacaval shunts, or Transjugular intrahepatic portal-systemic shunting [TIPS]).
- 7. Precipitating Agents • (A) Increase Nitrogen Load (a) Constipation. (b) Gastro intestinal bleeding. (c) Excess dietary intake of protein & fatty acids. (d) Azotemia.
- 8. Precipitating Agents • (B) Infections & Trauma (Surgery) • (C) Electrolyte & Metabolic imbalance • Hypokalemia. • Alkalosis. • Hypoxia. • Hyponatremic.
- 9. Precipitating Agents • (D) Drugs • Diuretics. • Narcotics, Tranquilizers, Sedatives.
- 10. Clinical Features • A Disturbance in consciousness • Disturbances in sleep rhythm. • Impaired memory/ apraxia. • Mental confusion. • Apathy. • Drowsiness / Somnolence. • Coma.
- 11. • B. Changes Personality • Childish behavior. • May be aggressive out burst. • Euphoric. • Foetor hepaticus – Foul–smelling breath associated with liver disease due to mercaptans.
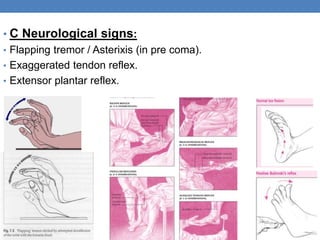
- 12. • C Neurological signs: • Flapping tremor / Asterixis (in pre coma). • Exaggerated tendon reflex. • Extensor plantar reflex.
- 13. Clinical Staging
- 16. Investigation • Diagnosis is usually made clinically • Routine Investigations - CBC, LFTS, Electolytes, Urea, Creatinine, Prothrombin time, Albumin , A/G ratio. • Elevation of blood ammonia. • EEG (Electroencephalogram) • CSF & CT Scan – Normal.
- 17. Differential Diagnosis • Subdural Haematoma. • Drug or Alcohol intoxication. • Wernicke’s encephalopathy. • Hypoglycaemia.
- 18. Management • Supportive Treatment. • Specific Treatment aims at: • Decreasing ammonia production in colon • Elimination or treatment of precipitating factors.
- 20. TREATMENT • Hospitalize the patient. • Maintain ABC. • Identify and remove the precipitating factors. • Iv fluid dextrose ,saline. • Stop Diuretic Therapy. • Correct any electrolyte imbalance. • Ryle tube feeding & bladder catheterization. • Reduce the ammonia (NH3) Load. • Diet – Restriction of protein diet. High glucose diet. • Treat Constipation by Laxatives.
- 21. Lactulose • Lactulose 15-30ml X 3 – 4 times a day- result aims at 2-4 stools/day. • Rectal use is indicated when patient is unable to take orally. • 300ml of lactulose in 700ml of saline or sorbitol as a retention enema for 30 – 60 min. • May be repeated 4 – 6 hours.
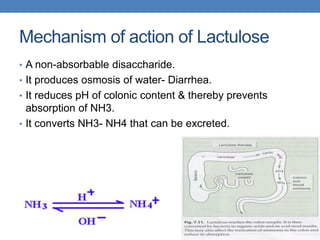
- 22. Mechanism of action of Lactulose • A non-absorbable disaccharide. • It produces osmosis of water- Diarrhea. • It reduces pH of colonic content & thereby prevents absorption of NH3. • It converts NH3- NH4 that can be excreted.
- 23. Treat the GIT & other Infections Antibiotics: • Rifaximin • Broad spectrum antibiotic, recently approved in humans for HE. • Negligible systemic absorption. • Shown to decrease hospitalizations and length of stay as compared to lactulose in humans. • DOSE: 550 mg orally B.I.D
- 24. • Metronidazole : 250mg orally T.D.S • Neomycin : 0.5 – 1 g orally 6 or 12 hours for 7 days. • Side effects: Ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity. • Vancomycin : 1 g orally B.I.D
- 25. DIET • With held dietary protein during acute episode if patient cannot eat. • Oral intake should be 60 – 80 g/day as tolerated. • Vagetable protein is better tolerated than meat protein. • G.I.T bleeding should be controlled • 120ml of magnesium citrate by mouth or NG tube every 3 – 4 hours until stool free of blood.
- 26. Stimulation of metabolic ammonia metabolism: • Sodium benzoate • 5 g orally twice a day. • L-ornithine-L-aspartate • 9 g orally thrice a day. • L-acyl-carnitine aspartate • 4 g orally daily. • Zinc sulphate • 600mg/day in divided doses.
- 27. Correct amino acid metabolic imbalance • Infusion or oral administration of BCAA (branched-chain amino acid) • Its use is unnecessary except in patient who are intolerant of standard protein supplements. GABA/BZ complex antagonist: • Flumazenil ( particularly if patient has been given banzodiazepines ) • Opiods & sedatives should be avoided.
- 28. Acarbose • α – glucosidase inhibitor. • Under study. • Other Therapies: • Prebiotics & probiotics. • Extracorporeal albumin dialysis ( MARS) • Liver transplant.
- 29. PROGNOSIS • Acute hepatic encephalopathy may be treatable. • Chronic forms of the disorder often keep getting worse or continue to come back. • Both forms may result in irreversible coma and death. • Approximately 80% (8 out of 10 patients) die if they go into a coma. • Recovery & the risk of the condition returning vary from patient to patient
- 30. REFERENCES • Davidson’s Principles & Practice of Medicine- 21st edition. • Harrison’s Principles of internal Medicine-10th & 17th edition. • Current Medical Diagnosis & Treatment – 2014 edition.








