HIGH DOSE PPI USE
- 1. CRITERIA FOR USE: HIGH DOSE ORAL PROTON PUMP INHIBITOR ANTONIO C. COMIA, MD
- 3. CRITERIA FOR USE: HIGH DOSE ORAL PROTON PUMP INHIBITOR (THE PROMISE OF OMEPRON 40) ANTONIO C. COMIA, MD
- 4. DOSING ISSUES ï§ STANDARD DOSE: OMEPRAZOLE 20 MG ï§ HIGH DOSE ï§ DOUBLE OR QUADRUPLE DOSE: 20 BID, 40 OD, 40 BID ï§ AS INITIAL THERAPY? ï§ IF INADEQUATE IMPROVEMENT WITH INITIAL STANDARD THERAPY?
- 5. WHEN TO GIVE HIGH DOSE PPI (OMEPRON 40) AS INITIAL THERAPY
- 6. INDICATIONS FOR HIGH DOSE PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS: DIAGNOSIS ï§Diagnostic trial (PPI test) ï§ Uncomplicated GERD: no alarm symptoms ï§ An 8-week therapeutic or empiric trial of double-dose PPI may be considered ï§ Treatment plan should be re-evaluated if there is no response after 8 weeks.
- 7. INDICATIONS FOR HIGH DOSE PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS: GERD-RELATED COUGH ï§ GERD-related chronic nonspecific cough ï§ dry and non-productive cough of âĨ 3 weeksâ duration without any other respiratory symptom, sign, or systemic illness)
- 8. CHRONIC COUGH AND GERD ï§ When GERD is the cause of chronic cough there may be no GI symptoms â silent GERD ï§ 24 hour esophageal pH monitoring provides a sensitive and specific test for the presence of GERD ï§ GERD related cough may take 2 â 3 months to resolve with therapy ï§ Definitive diagnosis of cough resulting from GERD can only be made if the cough resolves with anti-GERD therapy
- 9. CHRONIC COUGH AND GERD ï§ Accurate diagnosis and therapy of chronic cough due to GERD is difficult ï§ Therapeutic, empiric trial with PPI is reasonable initial diagnostic approach ï§ Non-response does not rule out GERD as cause of chronic cough ï§ Objective investigations for GERD are suggested (esophageal pH monitoring)
- 10. Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) ï§ Hoarseness, throat pain, dysphagia, throat clearing, dyspnea, chronic cough ï§ May not have the classic symptoms of GERD ï§ Also called silent reflux. ï§ Cause: LES dysfunction, acid reflux upwards to throat ï§ PPI TEST: useful in diagnosis and treatment ï§ Double dose, given at east 8 weeks
- 11. INDICATIONS FOR HIGH DOSE PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS AS INITIAL THERAPY ï§ Gastric Ulcers â may give Omeprazole 40 mg as initial dose, specially in high risk NSAID patients ï§ Pathologic hypersecretory conditions (e.g., Zollinger- Ellison syndrome) â up to 240 mg/day ï§ Helicobacter pylori eradication to reduce recurrence of duodenal ulcers, as part of dual or triple antibiotic-based therapy â given together with antibiotics ï§ Double-dose PPI therapy, typically for 1â2 weeks
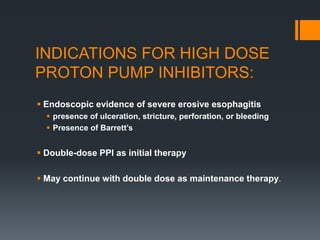
- 12. INDICATIONS FOR HIGH DOSE PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS: ï§ Endoscopic evidence of severe erosive esophagitis ï§ presence of ulceration, stricture, perforation, or bleeding ï§ Presence of Barrettâs ï§ Double-dose PPI as initial therapy ï§ May continue with double dose as maintenance therapy.
- 13. Treatment and maintenance doses for severe reflux esophagitis ï§ Relapse rates during maintenance of severe reflux esophagitis ï§ 17.5% for healing doses (high dose PPI) ï§ 29.1% for half-healing doses (standard dose PPI) ï§ Double dose (OMEPRON 40 MG) for healing and maintenance
- 14. HIGH DOSE PPI IN ULCER REBLEEDING ï§ Acid suppression with PPI use significantly reduces the risk of re-bleeding in bleeding peptic ulcers. ï§ The mechanism of action is thought to be related to clot stabilization by increasing gastric pH. ï§ Both oral and intravenous PPIs have been demonstrated to decrease hospital stay, re-bleeding rate and the need for blood transfusion in patients treated with endoscopic therapy.
- 15. INDICATIONS FOR HIGH DOSE PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS: ï§ Prevention of acute rebleeding of peptic ulcers after endoscopic hemostasis ï§ IV PPI initially for 72 hours: 80 MG LD, 8 MG PER HOUR ï§ Quadruple-dose oral PPI may be given in 2 divided doses for 5 days ï§ Standard doses should be used thereafter.
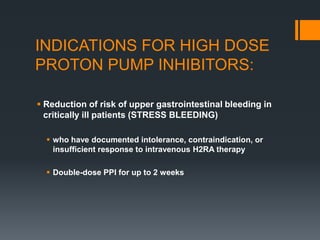
- 16. INDICATIONS FOR HIGH DOSE PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS: ï§ Reduction of risk of upper gastrointestinal bleeding in critically ill patients (STRESS BLEEDING) ï§ who have documented intolerance, contraindication, or insufficient response to intravenous H2RA therapy ï§ Double-dose PPI for up to 2 weeks
- 17. WHEN TO GIVE HIGH DOSE PPI: INADEQUATE IMPROVEMENT WITH STANDARD THERAPY
- 18. REASONS FOR LACK OF RESPONSE ï§ WRONG DIAGNOSIS â MALIGNANCY, NOT ACID- RELATED (GALLSTONES, PANCREATIC DISEASE, COLONIC) â PPI WILL NOT WORK ï§ PATIENT COMPLIANCE, TIMING OF MEDICATIONS ï§ GERD ï§ NOCTURNAL ACID BREAKTHROUGH ï§ ESOPHAGEAL AND GASTRIC MOTILITY DISORDERS ï§ LES DYSFUNCTION
- 19. REASONS FOR LACK OF RESPONSE ï§ BARRETTâS AND LPR â INADEQUATE RESPONSE ï§ PEPTIC ULCERS â CONTINUED ASPIRIN/NSAID USE ï§ RESISTANCE? TOLERANCE?
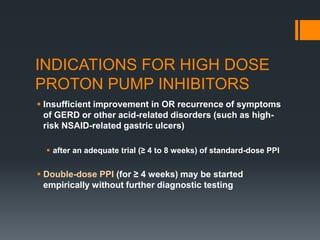
- 20. INDICATIONS FOR HIGH DOSE PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS ï§ Insufficient improvement in OR recurrence of symptoms of GERD or other acid-related disorders (such as high- risk NSAID-related gastric ulcers) ï§ after an adequate trial (âĨ 4 to 8 weeks) of standard-dose PPI ï§ Double-dose PPI (for âĨ 4 weeks) may be started empirically without further diagnostic testing
- 21. INDICATIONS FOR HIGH DOSE PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS: ï§ Insufficient improvement in or recurrence of symptoms of GERD or other acid-related disorders (such as high- risk NSAID-related gastric ulcers) after an adequate trial (âĨ 4 to 8 weeks) of double-dose PPI therapy ï§ Higher than double-dose PPI therapy may be started while awaiting further consultation and testing, and continued as maintenance therapy
- 22. INDICATIONS FOR HIGH DOSE PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS: ï§ Step-down: titrate according to symptom control. ï§ If test results suggest possible relative âresistanceâ to that particular PPI, then consider switching to another PPI at double the standard dose.
- 23. SUMMARY: Selected Indications for High-Dose PPI (OMEPRON 40) ï§ Diagnostic PPI Test for Uncomplicated GERD, and Non- cardiac Chest Pain ï§ GERD-related chronic cough ï§ Empiric diagnosis and treatment of LPR
- 24. Selected Indications for High-Dose PPI (OMEPRON 40) ï§ Treatment and maintenance of severe reflux esophagitis ï§ Prevention of rebleeding of peptic ulcers
- 26. THANK YOU!