HMD_PCR-RFLP_KIBGE_KCHI.pptx
- 1. Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) Dr. Abdul Hameed,PhD Chief Scientific Officer Institute of Biomedical and Genetic Engineering (IBGE), 24-Mauve Area, G-9/1, Islamabad, Pakistan ahameed0786@hotmail.com
- 2. RFLP ŌĆō Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism ’é¦ Variation in the DNA sequence of a genome detected by cutting DNA into pieces with restriction enzymes. ’é¦ Important tool in genome mapping, localization of genetic disease genes, determination of risk for a disease, genetic fingerprinting and paternity testing etc.
- 4. Restriction Endonucleases Also called restriction enzymes 1962: ŌĆ£molecular scissorsŌĆØ discovered in bacteria 3,000 enzymes have been identified, around 200 have unique properties, many are purified and available commercially
- 5. Restriction Endonucleases Named for bacterial genus, species, strain, and type Example: EcoR1 Genus: Escherichia Species: coli Strain: R Order discovered: 1
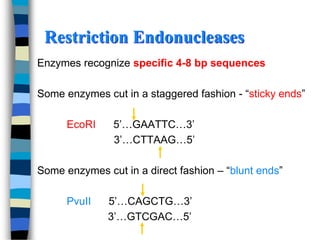
- 6. Restriction Endonucleases Enzymes recognize specific 4-8 bp sequences Some enzymes cut in a staggered fashion - ŌĆ£sticky endsŌĆØ EcoRI 5ŌĆÖŌĆ”GAATTCŌĆ”3ŌĆÖ 3ŌĆÖŌĆ”CTTAAGŌĆ”5ŌĆÖ Some enzymes cut in a direct fashion ŌĆō ŌĆ£blunt endsŌĆØ PvuII 5ŌĆÖŌĆ”CAGCTGŌĆ”3ŌĆÖ 3ŌĆÖŌĆ”GTCGACŌĆ”5ŌĆÖ
- 7. Uses for Restriction Enzymes RFLP analysis (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism) DNA sequencing DNA storage ŌĆō libraries Transformation Large scale analysis ŌĆō gene chips
- 8. Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism Analysis 1. DNA digestion with restriction enzyme(s) 2. Separation of Digested DNA on gel electrophoresis ŌĆó Smear - Many DNA fragments with slight differences in length 3. Denaturing the double-stranded DNA to make it single-stranded by treating the gel chemically 4. Southern blotting (Transfer of single stranded DNA on to a positively charged nylon membrane
- 9. RFLP Analysis 4. Southern blotting: i. Transfer DNA from gel to nylon membrane ii. Expose nylon membrane to solution with radioactive complementary nucleotide probes that hybridize to specifically chosen DNA sequences on nylon membrane iii. Place nylon membrane against X-ray film, where hybridized radioactive probes cause exposure of X-ray film, producing an autoradiogram http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/staff/dave/roanoke/genetics980211.html
- 10. Genotyping a biallelic RFLP marker in a family. ŌĆó PCR amplification ŌĆó Digestion with restriction enzyme ŌĆó Separation of digested DNA fragments by agarose gel electrophoresis ŌĆó Staining the gel with ethidium Bromide (Fluoresce under UV-illumination only when bound to DNA
- 11. NPHS2 Mutation Identified By DNA Sequencing
- 12. NPHS2 Gene: NORMAL Exon 5 Sequence ’ü« cataggaaaggagcccaagaatcaagcctgtcatccaaacttttttctgcctagATCGTGACCAAAGA CATGTTTATAATGGAGATAGATGCCATTTGCTACTACCGAATGGAAAATGCC TCTCTTCTCCTAAGCAGTCTTGCTCATGTATCTAAAGCTGTGCAATTCCTTG TGCAAACCACTATGAAGCGTCTCCTAGCACATCGATCCCTCACTGAAATTCT TCTAGAGAGGAAGAGCATCGCCCAAGATGCAAAGgtacttagataaacataatggcca atatgctgaaa NPHS2 Gene: MUTANT exon 5 Sequence (9bp Del) ’ü« cataggaaaggagcccaagaatcaagcctgtcatccaaacttttttctgcctagATCGTGACCAAAGA CATGTTTATAATGGAGATAGATGCCATTTGCTACTACCGAATGGAAAATGCC TCTCTTCTCCTAAGCAGTCTTGCTCATGTATCTAAAGCTGTGCAATTCCTTG TGCAAACCACTATGAAGCGTCTCCTAGCACATCGATCCCTCACTGAAATTCT GAAGAGCATCGCCCAAGATGCAAAGgtacttagataaacataatggccaatatgctgaaa PCR-RFLP (NPHS2 Exon 5)
- 14. NPHS2, Ex.5 Restriction Maps
- 15. PCR-RFLP Steps ’ü« PCR Amplification (NPHS2 Gene Ex.5) ’ü« Digestion with R.E (XbaI) ’ü« Agarose Gel Electrophoresis ’ü« Gel Staining with Ethidium Bromide ’ü« Gel Photograph Under UV-illumination
- 16. Figure 2: Molecular basis of nephrotic syndrome. (A) Pedigree of NPHS family shows consanguineous family with three male patients (filled boxes). (B) RFLP analysis of PCR fragment amplified from exon 5 of the NPHS2 gene utilizing Xba I restriction enzyme. The 293bp PCR product of exon 5 for all family members was digested with Xba I restriction enzyme. Fragments were resolved on 2.0% agarose gel. Individuals with a single fragment of 284bp were identified as homozygous mutant since they did not contain the restriction site for XbaI. Those with two fragments (225bp and 68 bp) were heterozygous normal/carriers for the mutation. M: DNA size standard, UC: Undigested control PCR product.
- 18. Choosing the Restriction Enzyme for your SNP http://watcut.uwaterloo.ca/template.php
- 19. Paste FASTA sequence here
- 20. SNP in the sequence [g/a] Click
- 21. Click
- 22. Restriction Database (rebase) ’ü« http://rebase.neb.com/rebase/rebase.ht ml


















![SNP in the sequence
[g/a]
Click](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hmdpcr-rflpkibgekchi-220928183530-10f00592/85/HMD_PCR-RFLP_KIBGE_KCHI-pptx-20-320.jpg)



