1 of 25























Recommended
Building Summary



Building Summaryaileencv
Ěý
The 9-story building structure passed the initial nonlinear static analysis but failed the life safety standards on the first story beam. In the linear dynamic analysis, the columns of the first three stories and beams of the 7th and 8th stories failed. To fix this, the columns were redesigned with larger dimensions and reinforcement, while the beams at the top were redesigned with less reinforcement. These changes increased the column stiffness and reduced top beam stiffness, allowing the building to pass the linear dynamic analysis.555 timer-digital-clock



555 timer-digital-clockGaditek
Ěý
This document discusses the 555 timer integrated circuit and its use in building a digital clock circuit. It provides details on the 555 timer pins and its three operating modes: astable, monostable, and bistable. It then describes a digital clock circuit built using a 555 timer chip that displays time on 7-segment displays and can be set using buttons. Links are provided for additional information on 555 timer clocks.Melissa Lorenzo Resume



Melissa Lorenzo ResumeMelissa Lorenzo - Business Systems Analyst
Ěý
Melissa Lorenzo is an experienced ERP consultant with expertise in business process analysis, requirements gathering, and solutions implementation. She has successfully led multiple large-scale ERP projects on time and within budget. Her experience includes implementing financial systems for NetSuite and SAP at various organizations. She is skilled in streamlining processes, eliminating inefficiencies, and ensuring compliance.Oral Cancer Screening 



Oral Cancer Screening Ghasaq Bakkal
Ěý
Ghasaq Al-Bakkal, DMD, is a family dentist at Belmont Dental Clinic, for which more information can be found at BelmontDentalClinic.ca. Dr. Ghasaq Al-Bakkal also focuses on preventive dentistry, including oral cancer screening.
Electron microscope



Electron microscopeshabeel pn
Ěý
The document summarizes the key differences between light microscopes and electron microscopes. Light microscopes have a resolving power of about half the wavelength of visible light, limiting magnification to around 1500x. Electron microscopes use short wavelength electrons, allowing much higher resolving power and magnification over 500,000x. There are two main types: transmission electron microscopes (TEM) that pass electrons through thin samples, and scanning electron microscopes (SEM) that detect electrons reflected from surfaces to generate 3D images. TEMs require harsh chemical fixation of cells that can introduce artifacts.Digital clock



Digital clockasifnoman240
Ěý
The presentation introduces digital clocks, including their history, components, implementation, uses, and future plans. It discusses how the first digital watches were invented in the 1880s and the first digital alarm clock was patented in 1956. The presentation implements a digital clock circuit in Multisim using ICs like 74LS47, 74LS90, 74HC32, and other components like function generators, push buttons, and 7-segment displays. Digital clocks are now commonly used in devices like cars, radios, TVs, and computers to display time accurately and easily readably compared to analog clocks. Future plans include adding time setting, on/off, date, and alarm functions.

Accès à l'emploi des jeunes diplômés : les résultats de l'étudeLinkedIn
Ěý
Cette étude porte sur les critères que les jeunes diplômés français présument être importants aux yeux des recruteurs pour décrocher leur premier emploi. Ces résultats sont mis en perspective avec les réponses des recruteurs français sur les critères qu’ils privilégient dans les faits.
Types of meals



Types of mealsBhupender Dighliya
Ěý
The document discusses various types of meals including breakfast, brunch, lunch, high tea, dinner and supper. It provides details on traditional breakfast foods and meals from different cultures like continental, English, American and Indian breakfast. Breakfast is usually the first meal of the day while dinner is the largest meal. Lunch is eaten midday and high tea is had in the late afternoon or evening. Elevenses refers to a morning snack taken around 11am.Structural Health Monitoring Example



Structural Health Monitoring Exampleaileencv
Ěý
Paper on Structural Health Monitoring of the Jindo Bridges in South Korea. Also a research focus of mine.Research Focus



Research Focusaileencv
Ěý
My final paper for Signal Processing and Smart Structures Technology Class. It also is the focus of my graduate research.Structural Health Monitoring Presentation



Structural Health Monitoring Presentationaileencv
Ěý
Structural health monitoring uses sensors and data collection techniques to monitor structures for damage or changes over time. This improves safety, reliability and reduces costs. The document discusses using P3HT, a conductive polymer, for sensors as it displays electro-chemical sensing abilities. SHM involves identifying critical damage types, data acquisition from sensors, signal processing, and statistical modeling to correlate responses to damage types.Advanced Composites Final Paper



Advanced Composites Final Paperaileencv
Ěý
The final write-up for Advanced Fiber Reinforced Composites Class. The paper was to design a memo to a fictional client, clearly stating the design results and process for the pressure vessel.Composites Final Presentation



Composites Final Presentationaileencv
Ěý
Final Project presentation for Advanced Fiber Reinforced Composites Class. The project was to design a pressure vessel, minimizing cost and materials.Design of 9 story frame



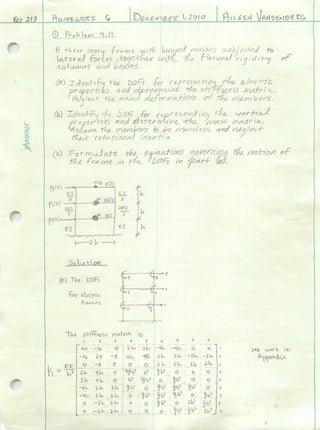
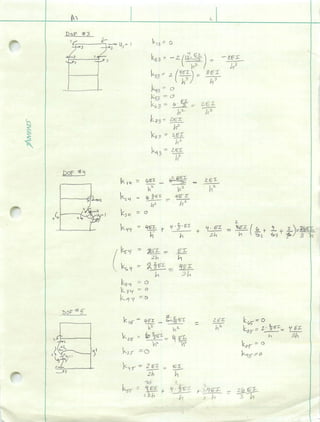
Design of 9 story frameaileencv
Ěý
This document summarizes the final project for a 9-story building located in California designed to seismic standards. It includes pushover curves analyzing the building's response to lateral loads, linear dynamic analysis per FEMA-356, and a sensitivity study exploring the effects of increased mass, reduced member stiffness, and scaled ground motions. The analysis required reinforcing the first story columns more but less for 7th story beams. The design proved highly sensitive to changes and will require closer inspection.Subspace Identification



Subspace Identificationaileencv
Ěý
This document discusses sub-space system identification. It begins with an introduction to state space representation and the difference between deterministic and stochastic systems. It then outlines the procedure for sub-space identification, which involves generating block Hankel matrices and extracting system parameters. As a case study, it examines using sub-space identification to calibrate a finite element model of a 17th century bridge by determining its natural frequencies and mode shapes from ambient vibration data. This led to an updated model with better accuracy in predicting the bridge's earthquake response.Fiber Optics Presentation



Fiber Optics Presentationaileencv
Ěý
Fiber optic sensors have four potential functions in structural health monitoring: monitoring external manufacturing process parameters, serving as embedded sensors for non-destructive evaluation, functioning as a data-link network to support other SHM systems, and complementing performance monitoring and control systems. Fiber optic sensors have advantages over conventional electronic sensors in that they are made of silica-based materials, enable multiplexing, and have a lower cost. They can provide distributed sensing along structures like buildings to monitor temperature. Fiber Bragg grating sensors embedded in concrete have been used to measure strain on the Confederation Bridge in Canada.More Related Content
More from aileencv (8)
Structural Health Monitoring Example



Structural Health Monitoring Exampleaileencv
Ěý
Paper on Structural Health Monitoring of the Jindo Bridges in South Korea. Also a research focus of mine.Research Focus



Research Focusaileencv
Ěý
My final paper for Signal Processing and Smart Structures Technology Class. It also is the focus of my graduate research.Structural Health Monitoring Presentation



Structural Health Monitoring Presentationaileencv
Ěý
Structural health monitoring uses sensors and data collection techniques to monitor structures for damage or changes over time. This improves safety, reliability and reduces costs. The document discusses using P3HT, a conductive polymer, for sensors as it displays electro-chemical sensing abilities. SHM involves identifying critical damage types, data acquisition from sensors, signal processing, and statistical modeling to correlate responses to damage types.Advanced Composites Final Paper



Advanced Composites Final Paperaileencv
Ěý
The final write-up for Advanced Fiber Reinforced Composites Class. The paper was to design a memo to a fictional client, clearly stating the design results and process for the pressure vessel.Composites Final Presentation



Composites Final Presentationaileencv
Ěý
Final Project presentation for Advanced Fiber Reinforced Composites Class. The project was to design a pressure vessel, minimizing cost and materials.Design of 9 story frame



Design of 9 story frameaileencv
Ěý
This document summarizes the final project for a 9-story building located in California designed to seismic standards. It includes pushover curves analyzing the building's response to lateral loads, linear dynamic analysis per FEMA-356, and a sensitivity study exploring the effects of increased mass, reduced member stiffness, and scaled ground motions. The analysis required reinforcing the first story columns more but less for 7th story beams. The design proved highly sensitive to changes and will require closer inspection.Subspace Identification



Subspace Identificationaileencv
Ěý
This document discusses sub-space system identification. It begins with an introduction to state space representation and the difference between deterministic and stochastic systems. It then outlines the procedure for sub-space identification, which involves generating block Hankel matrices and extracting system parameters. As a case study, it examines using sub-space identification to calibrate a finite element model of a 17th century bridge by determining its natural frequencies and mode shapes from ambient vibration data. This led to an updated model with better accuracy in predicting the bridge's earthquake response.Fiber Optics Presentation



Fiber Optics Presentationaileencv
Ěý
Fiber optic sensors have four potential functions in structural health monitoring: monitoring external manufacturing process parameters, serving as embedded sensors for non-destructive evaluation, functioning as a data-link network to support other SHM systems, and complementing performance monitoring and control systems. Fiber optic sensors have advantages over conventional electronic sensors in that they are made of silica-based materials, enable multiplexing, and have a lower cost. They can provide distributed sensing along structures like buildings to monitor temperature. Fiber Bragg grating sensors embedded in concrete have been used to measure strain on the Confederation Bridge in Canada.