Hossfeld qc man2015_context_monitoring_web
This document discusses context monitoring and its potential to improve quality of experience (QoE) for HTTP adaptive streaming. It defines context as any information that helps determine a user, network, or device situation. Context influence factors include physical, temporal, social, economic, task, and technical characteristics. The document presents a case study on using context monitoring to improve QoE during video flash crowds. It describes a simulation model of an HTTP adaptive streaming system with two content delivery networks and proposes using context data on the number of users per network to improve load balancing during flash crowds. The results show context monitoring can significantly improve performance and QoE compared to approaches without this context data.

![Definition of Context and Context Influence Factors
? Context is any information that assists in determining
a situation(s) related to a user, network or device.
[A.K. Dey and G.D. Abowd. Toward a better understanding of context and
context-awareness, Technical Report Georgia Institute of Technology]
? Context refers to anything that can be used to
specify or clarify the meaning of an event.
[P. Reichl et al, Towards a comprehensive framework for QoE and user
behavior modelling, QoMEX 2015]
? Context influence factors are factors that embrace
any situational property to describe the userĪ»s
environment in terms of physical, temporal, social,
economic, task, and technical characteristics.
[U. Reiter et al, Factors influencing quality of experience. In Quality of
Experience, pp. 55-72. Springer International Publishing, 2014.]
or system.
or systemĪ«s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hossfeldqcman2015contextmonitoringweb-150514151219-lva1-app6892/85/Hossfeld-qc-man2015_context_monitoring_web-2-320.jpg)









Recommended
More Related Content
Similar to Hossfeld qc man2015_context_monitoring_web (20)
Recently uploaded (20)
Hossfeld qc man2015_context_monitoring_web
- 1. Prof. Dr. Tobias Ho?feld Chair of Modeling of Adaptive Systems (MAS) Institute for Computer Science and Business Information Systems (ICB) University of Duisburg-Essen www.mas.wiwi.uni-due.de Can context monitoring improve QoE? A case study of video flash crowds in the Internet of Services Hossfeld, Tobias; Skorin-Kapov, Lea; Haddad, Yoram; Pocta, Peter; Siris, Vasilios A.; Zgank, Andrej; Melvin, Hugh
- 2. Definition of Context and Context Influence Factors ? Context is any information that assists in determining a situation(s) related to a user, network or device. [A.K. Dey and G.D. Abowd. Toward a better understanding of context and context-awareness, Technical Report Georgia Institute of Technology] ? Context refers to anything that can be used to specify or clarify the meaning of an event. [P. Reichl et al, Towards a comprehensive framework for QoE and user behavior modelling, QoMEX 2015] ? Context influence factors are factors that embrace any situational property to describe the userĪ»s environment in terms of physical, temporal, social, economic, task, and technical characteristics. [U. Reiter et al, Factors influencing quality of experience. In Quality of Experience, pp. 55-72. Springer International Publishing, 2014.] or system. or systemĪ«s
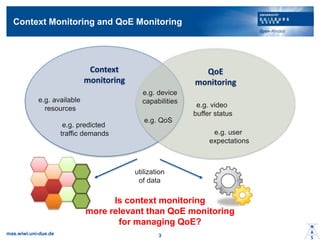
- 3. Context Monitoring and QoE Monitoring mas.wiwi.uni-due.de 3 Context monitoring QoE monitoring e.g. device capabilities e.g. video buffer status e.g. user expectations e.g. predicted traffic demands e.g. available resources e.g. QoS utilization of data Is context monitoring more relevant than QoE monitoring for managing QoE?
- 4. Context Factors ? Physical environment in which services and devices are used. ©C home, office, commuting, and other places, ©C indoors vs outdoors. ? Social environment ©C service consumption e.g. alone, with an important person, with a group of friends, or in a public place (consider gaming, watching video), ©C popularity of contents. ? Economic context ©C price for service consumption, tariff model: time, volume, flat ©C costs ? System context ©C load of system ©C system offloading possible, e.g. wifi offloading ? Usage context ©C Goal, task of service consumption, e.g. information retrieval vs. time killing ©C background vs. foreground application mas.wiwi.uni-due.de 4 Examples ? Follow the moon: temporal and economic context ? Video streaming: physical context ? Video flash crowds: social context
- 5. Agenda ? Context monitoring and QoE monitoring ? Example use case: video flash crowds ? QoE model for HTTP adaptive streaming ? Numerical results ? Open issues: realization
- 8. Content Delivery with a CDN mas.wiwi.uni-due.de 9 Core network Access network Content server Clients CDN server
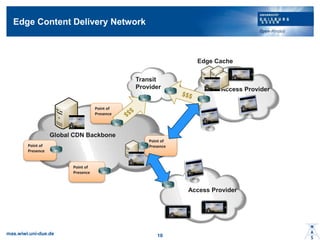
- 9. Edge Content Delivery Network mas.wiwi.uni-due.de 10 Global CDN Backbone Access Provider Access Provider Transit Provider Point of PresencePoint of Presence Point of Presence Point of Presence Edge Cache
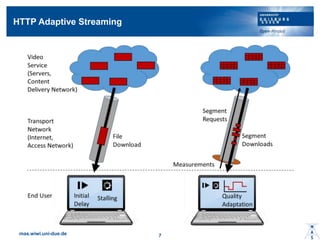
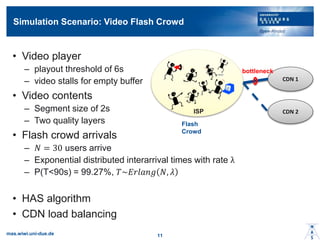
- 10. Simulation Scenario: Video Flash Crowd ? Video player ©C playout threshold of 6s ©C video stalls for empty buffer ? Video contents ©C Segment size of 2s ©C Two quality layers ? Flash crowd arrivals ©C ? = 30 users arrive ©C Exponential distributed interarrival times with rate ”╦ ©C P(T<90s) = 99.27%, ?~?????? ?, ? ? HAS algorithm ? CDN load balancing mas.wiwi.uni-due.de 11 CDN 1 CDN 2 Flash Crowd ISP bottleneck
- 11. HAS Algorithm and CDN Load Balancing ? CDN load balancing strategies 1. CDN directs the first ? users to CDN 1, subsequent users are assigned to CDN 2. Second, the CDN. 2. Context monitoring based on information about the flash crowd from a third party. Users are assigned to the CDN with the lowest number of users. ? HTTP adaptation strategy 1. Actual buffer and throughput of last segment to determine quality level of next segment 2. Additional context information on number of users and capacity per CDN 3. Non-adaptive streaming algorithm: high quality level mas.wiwi.uni-due.de 12 Bit rate Time TCP throughput Requested chunks
- 12. SIMPLE QOE MODEL FOR HTTP ADAPTIVE STREAMING
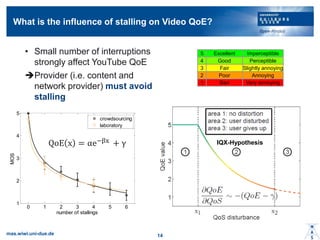
- 13. What is the influence of stalling on Video QoE? IQX-Hypothesis Excellent Good Fair Poor Bad 5 4 3 2 1 Imperceptible Perceptible Slightly annoying Annoying Very annoying ? Small number of interruptions strongly affect YouTube QoE ?Provider (i.e. content and network provider) must avoid stalling 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 number of stallings MOS crowdsourcing laboratory QoE x = ”┴e?”┬x + ”├ mas.wiwi.uni-due.de 14
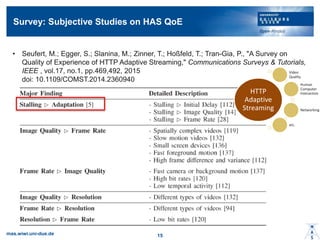
- 14. Survey: Subjective Studies on HAS QoE ? Seufert, M.; Egger, S.; Slanina, M.; Zinner, T.; Ho?feld, T.; Tran-Gia, P., "A Survey on Quality of Experience of HTTP Adaptive Streaming," Communications Surveys & Tutorials, IEEE , vol.17, no.1, pp.469,492, 2015 doi: 10.1109/COMST.2014.2360940 mas.wiwi.uni-due.de 15 HTTP Adaptive Streaming Video Quality Human Computer Interaction Networking etc.
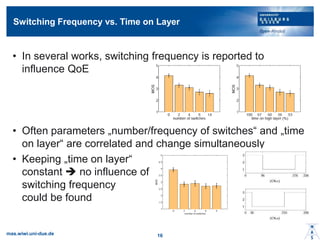
- 15. Switching Frequency vs. Time on Layer ? In several works, switching frequency is reported to influence QoE ? Often parameters ?number/frequency of switchesĪ░ and ?time on layerĪ░ are correlated and change simultaneously ? Keeping ?time on layerĪ░ constant ? no influence of switching frequency could be found mas.wiwi.uni-due.de 16
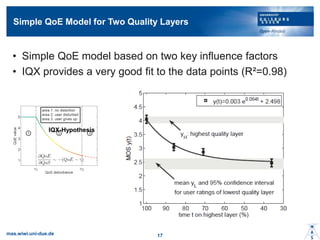
- 16. Simple QoE Model for Two Quality Layers ? Simple QoE model based on two key influence factors ? IQX provides a very good fit to the data points (R?=0.98) mas.wiwi.uni-due.de 17 IQX-Hypothesis
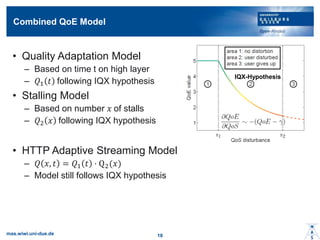
- 17. Combined QoE Model ? Quality Adaptation Model ©C Based on time t on high layer ©C ?1 ? following IQX hypothesis ? Stalling Model ©C Based on number ? of stalls ©C ?2 ? following IQX hypothesis ? HTTP Adaptive Streaming Model ©C ? ?, ? = ?1 ? ? Q2(?) ©C Model still follows IQX hypothesis mas.wiwi.uni-due.de 18 IQX-Hypothesis
- 18. NUMERICAL RESULTS: VIDEO FLASH CROWDS
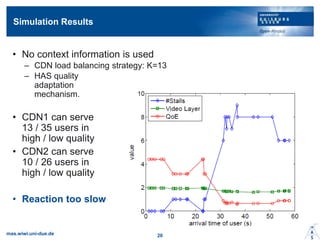
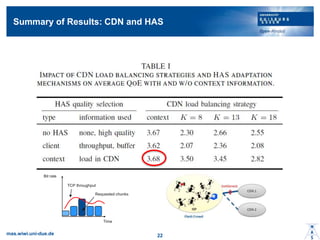
- 19. Simulation Results ? No context information is used ©C CDN load balancing strategy: K=13 ©C HAS quality adaptation mechanism. ? CDN1 can serve 13 / 35 users in high / low quality ? CDN2 can serve 10 / 26 users in high / low quality ? Reaction too slow mas.wiwi.uni-due.de 20
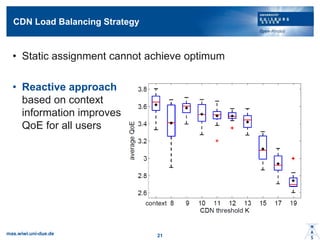
- 20. CDN Load Balancing Strategy ? Static assignment cannot achieve optimum ? Reactive approach based on context information improves QoE for all users mas.wiwi.uni-due.de 21
- 21. Summary of Results: CDN and HAS mas.wiwi.uni-due.de 22 Bit rate Time TCP throughput Requested chunks
- 22. Conclusions ? Context monitoring complements QoE monitoring ©C Utilization of additional information ©C Different types of context may be monitored ? Example of video flash crowds ©C Performance and QoE gain significantly improves ©C Technical realization needs to be developed ? Realization of context monitoring mas.wiwi.uni-due.de 23
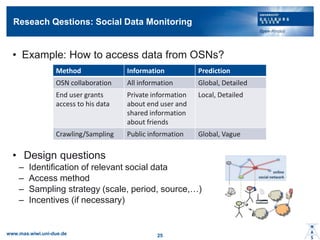
- 23. Realization of Context Monitoring using Social Data ? Accessing data from third party: Internet of Services ? Social data has to be monitored ©C Scale (single user, selected users, all users) ©C Period (every hour, once a day, ĪŁ) ©C Source (Online Social Networks OSNs, Services, Service Providers, ISPs,ĪŁ) online social network www.mas.wiwi.uni-due.de 24 http://www.smartenit.eu Content ProviderISPs CDNs $$$ $$$ $$$ $$$ Ads Data analysis ĪŁ
- 24. Reseach Qestions: Social Data Monitoring ? Example: How to access data from OSNs? ? Design questions ©C Identification of relevant social data ©C Access method ©C Sampling strategy (scale, period, source,ĪŁ) ©C Incentives (if necessary) Method Information Prediction OSN collaboration All information Global, Detailed End user grants access to his data Private information about end user and shared information about friends Local, Detailed Crawling/Sampling Public information Global, Vague www.mas.wiwi.uni-due.de 25
- 25. THANKS
