Household Electricity
- 1. E5: Household Electricity Textbook Page 76
- 2. Objectives At the end of this lesson, you will be able to: Understand what is power stations and energy sources State its electrical power and its units Differentiate between power of electrical appliances and power from power stations
- 3. Look at the picture… What is this? Where is it located? What it does?
- 4. How does Singapore get its electricity? Power stations Generate electricity from oil and natural gas Transmit to homes and industries all over the country
- 5. What is POWER? 120 V 7 W W = watts
- 6. What is POWER? The larger the watts the brighter the bulb 100 W is brighter than 60 W bulb. 100 W has more power The power of an electrical appliance is the amount of electrical energy it converts to other forms of energy in one second
- 7. POWER Power is measured in watts (W) Larger unit = kilowatt (kW) 1 kW = 1000 W
- 8. Power of electrical appliances Different electrical appliances have different power ratings Do Inquiry time - pg79
- 9. Power from power stations Power stations need to generate a lot of power Measured in megawatts (MW)
- 10. How do power companies know how much electricity we consume? Electricity meters Unit for electricity meters = kilowatt-hour (kWh) Energy consumed (in kWh) = Power (in kW) X Time (in hours) Cost of electrical energy = units of electrical energy used (kWh) x Cost per unit
- 11. Calculation Exercises An electric kettle has a power rating of 2400 W. It has been used to keep water warm for 2 hrs. Calculate the cost of the electricity used if each unit costs is 17 cents.
- 12. Calculation Exercises - Answer Power of appliance = 2400 W = 2.4 kW Time in use = 2 h Energy consumed = 2.4 x 2 = 4.8 kWh Cost of electricity = 4.8 x 0.17 = $0.82
- 13. Calculation Exercises A fan has a power rating of 3600 W. It has been used to keep room cool for 720 mins. Calculate the cost of the electricity used if each unit costs is 20 cents.
- 14. Calculation Exercises - Answers Power of appliance = 3600 W = 3.6 kW Time in use = 720 mins = 12 h Energy consumed = 3.6 x 12 = 43.2 kWh Cost of electricity = 43.2 x 0.20 = $8.64
- 15. Do inquiry time and checkpoint Textbook Page 81
- 16. Objectives At the end of this lesson, you will be able to: State examples when electricity can be dangerous State the safety features in circuits and appliances State the safety precautions when using electricity
- 17. Electricity can be dangerous Main dangers: Electric shock Electrical fire
- 18. Electricity can be dangerous Frayed and damaged wires If the person touches a bare wire, current flows through the body Electric shock
- 19. Electricity can be dangerous Overloading Adapters are used to connect more than one appliance to a main socket Large current causes the wire to get hot When the current is too large, the circuit is said to be overloaded
- 20. Electricity can be dangerous Short circuits Broken or bare wire in a circuit may touch another wire in the circuit causes a short circuit Cause fire in the wires or in the appliance
- 21. Electricity can be dangerous Wet Conditions If a person touches a damaged electrical wire or appliance with wet hands, an electric current may flow through his body – electric shock
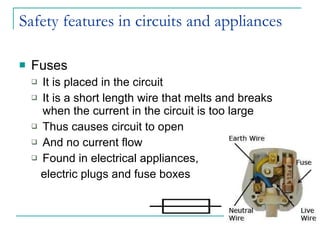
- 22. Safety features in circuits and appliances Fuses It is placed in the circuit It is a short length wire that melts and breaks when the current in the circuit is too large Thus causes circuit to open And no current flow Found in electrical appliances, electric plugs and fuse boxes
- 23. Safety features in circuits and appliances Circuit Breakers Many buildings use circuit breakers Special switch If current in a circuit becomes too large, the switch will turn off by itself
- 24. Safety features in circuits and appliances Main Switch Switches on and off the main electric supply to the whole building If there is a fire, switch off the main switch
- 25. Safety features in circuits and appliances Earth Wire Electricity flows through the live wire but not the earth wire Earth wire is for safety Earth wire connected to metal casing, most current flows to the ground through the earth wire instead So you will not get electric shock
- 26. Safety precautions when using electricity Never touch bare or broken wires Never touch appliances/switches with wet hands Never overload a circuit Never use electric appliances in wet places Do not push anything into sockets Never put nails into walls near switches, sockets and wires Do not use electrical appliances with old or frayed wires
- 27. Objectives At the end of this lesson, you will be able to: State how we can save electricity
- 28. What can we do to save electricity? Switch off lights, electrical appliances when not in used Use energy efficient lamps Set thermostat of air conditioner at a higher temperature
- 29. Do checkpoint Page 87