How to view the material certificate part 2
2 likes402 views
This document explains how to review a material certificate to ensure the received raw material matches requirements. It describes that a quality control engineer reviews the certificate to verify fields like the heat number, material grade, product specifications, dimensions, mechanical properties, and chemical analysis are correct. The certificate must contain these identifiers and test results to prove the material's traceability and compliance with the ordered specifications. A mill representative must also sign the certificate to certify its accuracy. The purpose is to confirm the right material is used for manufacturing to reduce risks and costs.
1 of 5
Downloaded 70 times




Recommended
Asme wps-demo



Asme wps-demoDaniel Stuparek
╠²
This document is a Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) that specifies the welding parameters and materials for a gas tungsten arc welding and shielded metal arc welding process. It lists the base metals, filler metals, welding positions, preheat and interpass temperatures, shielding gases, and electrical characteristics for two processes. Tables provide details on joint design, recorded welding parameters for each weld layer, and guidelines for heat treatment and qualified ranges according to the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code.Wis5 welding defects 02



Wis5 welding defects 02Thang Do Minh
╠²
The document discusses various welding defects that can be visually detected, including cracks, lack of solid metal, lack of fusion, lack of smoothly blended surfaces, and miscellaneous defects. It provides details on different types of each defect, their causes, and methods for prevention. It also discusses welding repairs, noting that repairs require authorization and testing to ensure defects have been fully removed before performing the repair weld.How to view the material certificate part 1



How to view the material certificate part 1Mohamed Farouk
╠²
The document discusses material certification according to EN 10204 standards. It explains that EN 10204 specifies different types of inspection documents provided by manufacturers, including Type 2.1 (declaration of compliance), 2.2 (test report with non-specific inspection), 3.1 (document from manufacturer with specific inspection and test results), and 3.2 (document prepared by manufacturer and purchaser representatives with specific inspection and test results). It provides details on the certification process, requirements for each certificate type, and how an independent third party would verify a Type 3.2 certificate for steel plates by inspecting the material, certificates, and test results to confirm compliance with standards.How to produce PQR



How to produce PQRMohamed Farouk
╠²
This document outlines the 8 steps to produce a Procedure Qualification Record (PQR) according to the ASME Section IX code. The steps are: 1) identify essential variables for the welding process, 2) add remaining essential variables from construction codes, 3) fill out the PQR format, 4) choose a qualified welder, 5) record welding parameters, 6) perform visual and mechanical tests, 7) record test results on the PQR, and 8) sign and date the completed PQR.Welders qualification



Welders qualificationLalu Rajendran
╠²
The document discusses welding qualification requirements according to ASME Section IX, including:
1. Tables outlining qualification test positions and types of welds qualified for plate and pipe groove and fillet welds in various positions.
2. Notes specifying definitions for weld positions, diameter restrictions, and that positions of welding must be shown in QW-461 and QW-461.2.
3. Requirements for number and types of examinations and test specimens required based on thickness of weld metal.
4. Limits on thickness of weld metal qualified based on thickness of test coupon and number of weld pass layers.
5. References diameter limits for groove welds inWelding defects



Welding defectsVlastimir Novakovic
╠²
The document discusses the results of a study on the impact of COVID-19 lockdowns on air pollution. Researchers analyzed data from dozens of countries and found that lockdowns led to an average decline of nearly 30% in nitrogen dioxide levels over cities. However, they also observed that this improvement was temporary and air pollution rebounded once lockdown restrictions began lifting. Overall, the study highlights how human activities are a major driver of air pollution but also that systemic changes are needed for long-term air quality improvements.RT Acceptance criteria



RT Acceptance criteriaAnand Kishor
╠²
Radiography acceptance criteria For ASME B31.3, B31.1, API 650, ASME Sec Viii , ASME Sec iXWelding defects



Welding defectsHung Le
╠²
This document provides a classification and overview of common welding defects. It divides defects into three main categories: planar defects, linear volumetric defects, and non-planar defects. Examples of each type of defect are given. The document also describes specific defect types such as cracks, inclusions, lack of fusion, porosity, overlap, undercut and provides potential causes of each.Rtfi weld defects[1]![Rtfi weld defects[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/rtfiwelddefects1-190507184037-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Rtfi weld defects[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/rtfiwelddefects1-190507184037-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Rtfi weld defects[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/rtfiwelddefects1-190507184037-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Rtfi weld defects[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/rtfiwelddefects1-190507184037-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Rtfi weld defects[1]Vishnu Chakkuzhiyil Muraleedharan
╠²
This document discusses artifacts that may appear on radiographic films. It defines several types of artifacts including burned film, chemical stains, crimp marks, lead foil scratches, light leaks, pressure marks, sand/dirt marks, scratch marks, static marks, water marks, and roller marks from automatic processing. For each artifact, it provides an example radiographic image and brief description of how the artifact is caused. The purpose is to help trainees identify and understand artifacts that could affect the interpretation of radiographic images.radiographic-interpretation.pdf



radiographic-interpretation.pdfVENKATESAN S
╠²
The document is a training manual on radiographic interpretation of welds. It contains multiple radiographic images of welds with defects labeled, asking the reader to identify the defects shown. The defects illustrated include lack of root penetration, porosity, undercutting, cracking, incomplete fusion, excess penetration, spatter, slag inclusions and others. The purpose is to help trainees learn to identify various weld defects from radiographic images.What is wps important tips regarding to wps



What is wps important tips regarding to wpsWeld Maniac
╠²
A welding procedure specification (WPS) is a document that provides parameters for welding, including joints, metals, positions, and variables. There are three types of variables: essential, non-essential, and supplementary essential. Essential variables require requalification if changed, while non-essential variables can be changed without requalification. WPS and procedure qualification records (PQR) are qualified according to material groups designated by P-numbers, with PQR tests needed to support welding between specific P-number combinations. Qualification with a given P-number tests qualifies welding within certain P-number ranges depending on materials and filler metals used.Welding Defect.ppt



Welding Defect.pptAbdul Naqiuddin
╠²
The document discusses various welding defects including cracks, surface defects, contour defects, root defects, and miscellaneous defects. It provides details on specific types of each defect such as undercut, overlap, incomplete root fusion, gas porosity, slag inclusions, and their potential causes like incorrect welding technique, contamination, or material defects. Various repair methods are also mentioned such as grinding, chipping, and arc air gouging.A QA/QC ENGINEER MUST KNOW THESE TABLE IN ASME SEC IX



A QA/QC ENGINEER MUST KNOW THESE TABLE IN ASME SEC IXWeld Maniac
╠²
This document provides information on qualifying welders and welding procedures according to the ASME Section IX code. It includes tables that specify the base metals and filler metals qualified by different welding tests. The tables indicate which base or filler metals a welder or procedure is considered qualified to weld based on the specific metals tested during qualification. Qualifying a production weld also qualifies the procedure to weld a broader range of materials according to these tables.Welder qualification



Welder qualificationkharafi national,kuwait
╠²
This document provides information on the essential variables and requirements for welder qualification according to ASME Section IX. It lists the key variables that must be specified for a welder qualification, including welding process, type, base metal, filler metal, and weld thickness limits. It also outlines the qualification requirements and limitations for weld position, diameter, progression, backing, and which filler and base metals a welder is qualified to use based on their test.Weld Defects



Weld Defectsadminn2
╠²
This document discusses various types of welding defects and imperfections including lack of fusion, porosity, slag inclusions, and solidification cracking. It describes how to identify each type, their causes, best practices for prevention, acceptance standards, and methods for detection and remediation. The key types of imperfections are classified as fabrication defects occurring during welding or service defects that form during use, and guidelines are provided for minimizing defects and producing quality welds.Visual Inspection of Welding Process



Visual Inspection of Welding ProcessGaurav Singh Rajput
╠²
The document discusses visual inspection of welds, including terminology for different types of welds and weld features. It provides checklists for welding procedures before, during, and after welding. Common welding defects such as lack of fusion, undercut, and porosity are described along with their potential causes. Visual inspection procedures and features to examine in butt and fillet welds are also outlined.CSWIP 3.2 New BOOK.pdf



CSWIP 3.2 New BOOK.pdfVENKATESAN S
╠²
The document outlines the duties and responsibilities of a Senior Welding Inspector. It discusses that the role requires strong leadership, technical, and managerial skills. Some key responsibilities include managing inspection teams, providing guidance to inspectors, making technical decisions, planning inspections, and ensuring work is completed on time and to budget. Senior Welding Inspectors must have in-depth knowledge of welding technology, quality standards, and the ability to audit work and evaluate non-destructive testing reports. Strong communication, organization, and people management skills are also important to motivate personnel and ensure high morale is maintained throughout inspection projects.Structural Steel Welding Inspection



Structural Steel Welding InspectionAsirul Hoq
╠²
This document provides generalized guidelines for structural steel welding inspection as per the AWS D1.1 Structural Welding Code for Steel. It covers standard terms, the scope of the code, limitations on its use, design of welded connections, weld joint configurations, prequalification of welding procedures, qualification requirements, fabrication, inspection, and non-destructive testing requirements. Key areas addressed include complete and partial joint penetration welds, fillet welds, prequalification criteria for common welding processes and materials, visual inspection acceptance standards, and additional non-destructive testing as required.Weldability pc



Weldability pcJithu John
╠²
This document discusses the weldability of various metal types including carbon-manganese steel, low alloy steel, quenched and tempered steel, stainless steel, nickel alloys and aluminum alloys. For carbon-manganese steel, it notes their excellent weldability and suitability for arc and other welding processes. It also discusses preheat requirements and filler metals for different welding methods. For low alloy and quenched tempered steels, it highlights their susceptibility to hydrogen cracking and need for proper joint design, preheat and control of heat input during welding. The document also briefly summarizes weldability considerations for martensitic and ferritic stainless steels.Methods of examination of joints(RT) - API 650 Tanks



Methods of examination of joints(RT) - API 650 TanksRajSamy
╠²
This document outlines standards for radiographic examination of welds on storage tanks. It discusses limits for dissimilar thickness consideration, joints that are exempt from radiographic testing, requirements for vertical and horizontal joints of different thicknesses, insert plates, length of radiographs, annular plates, examination of tank bottoms and sumps, repair and penalty guidelines, recommended techniques, weld reinforcement requirements, and documentation standards.Piping welding notes for beginners



Piping welding notes for beginnersMOHAMMAD ATIF ALI
╠²
Here are the major responsibilities of a project engineer summarized:
- Oversee all construction activities to ensure they are completed as per approved plans, schedule and budget.
- Coordinate with different project departments like safety, procurement, contracts and quality.
- Ensure materials are available on time and resolve any technical or design issues that arise.
- Lead meetings and ensure contractor action plans and schedules are understood.
- Review invoices, punch lists and change orders for approval.
- Oversee commissioning, documentation handover and project closeout.
- Monitor project progress and address any delays by expediting work or investigating causes.Welding Defects.pdf



Welding Defects.pdfUniversity of Sarajevo, Manufacturing Technology:
╠²
There are numerous welding processes including arc welding, electron beam welding,
friction welding, laser welding, and resistance welding. This article will concentrate on arc
welding, which is the most common technique used to join most steels. Factors affecting
weld quality will be discussed and how to avoid common weld defects will be presented.
Arc welding requires striking a low-voltage, high-current arc between an electrode and the
base metal. The intense heat generated with this arc melts the base metal and allows the
joining of two components. The characteristic of the metal that is being welded and the joint
type (i.e. groove, fillet, etc.) dictates the welding parameters and the procedure that needs to
be followed to obtain a sound weld joint. Welding flaws



Welding flawsJithu John
╠²
- Lamellar tearing is commonly observed discontinuity in fusion welding that occurs near the heat-affected zone in flange plates of T-butt joints. It is caused by factors like dilution and heat input during welding.
- Dilution is affected by the melted parent metal, melted filler metal, and weld width to depth ratio. Too low or too high heat input can both be detrimental.
- Solidification cracks can form due to the bead factor, which is the ratio of weld width to depth. A ratio greater than 1 or less than 1 can both result in cracks.How to Qualify a Welding Procedure



How to Qualify a Welding ProcedureAntonius Pompi Bramono
╠²
The document outlines the five step process to qualify a welding procedure according to ASME Section IX. It provides details on developing a draft procedure using 0.75" A36 steel plate welded in the flat position using GTAW and GMAW. Variables such as joint design, base metal and thickness, filler metal type and size, welding position, and electrical parameters are documented. The qualification weld was tested to verify it results in an acceptable weld with proper mechanical properties before the welding procedure specification can be used in construction.Overview fusion welding standards (lasstandaarden engels)



Overview fusion welding standards (lasstandaarden engels)Ren├® Varkevisser
╠²
This document provides an overview of European and international standards related to welding and fusion joining processes. It lists standards for welding procedure and welder qualification, non-destructive testing methods, classification of welding consumables, quality requirements, and safety and environmental standards. The overview is intended to help welding professionals find the appropriate standards for their application and welding process.Radiographic interpretation 



Radiographic interpretation kamarulariffinzainalabidin
╠²
This document provides definitions for various defects that may appear on radiographic images of welds, including:
- Excessive root penetration appears as a light irregular band within the weld image.
- Root concavity appears as dark areas along the weld center varying in density by imperfection depth.
- Incomplete filled groove appears as a dark area at the weld center with diffuse edges.
- Cracks appear as dark, fine lines that are usually diffuse or discontinuous.9488085 welding-defects



9488085 welding-defectsRony Simeon
╠²
The document discusses various types of discontinuities and defects that can occur in welding, including cracks, porosity, inclusions, insufficient penetration, and more. It defines discontinuities as interruptions in material structure that are not necessarily defects, while defects render a part unable to meet standards. Causes, preventions, and potential repairs are provided for each issue. Engineering problems can arise from design mistakes, while weld process issues relate to techniques and metallurgy.Inspection of Heat exchanger .pdf



Inspection of Heat exchanger .pdfTusharNayak32
╠²
The document discusses inspection of heat exchangers during manufacture. It outlines the key components of a heat exchanger that will be covered, including shells, channels, tube sheets, baffles, tubes, bellows, spacers, and tie rods. Minimum inspection requirements are described for each component, focusing on dimensions, workmanship, materials, and critical points often overlooked. Testing procedures for the completed heat exchanger like hydrotesting and helium leak testing are also summarized.Holo-Krome catalog



Holo-Krome catalogjerjer87
╠²
This document is a technical handbook published by Holo-Krome to provide dimensional, mechanical, and application data for their socket screw products. It outlines several limitations and considerations for using the information, including that specifications may change over time and vary slightly for non-stock products. It also notes that proper screw sizes and torque depend on specific design parameters. The handbook is organized to provide both inch and metric dimensional data followed by application data for each module.jaynt singh (CV) (5)



jaynt singh (CV) (5)Jayant Singh
╠²
This document contains a summary of Jayant Singh's professional experience and qualifications. He has over 4 years of experience working as a Quality Control Engineer at various companies in India and Oman, including L&T Heavy Engineering LLC in Oman and Bectochem Lodige Process Technology Private Limited in India. His responsibilities have included ensuring quality standards, inspecting fabrication and welding, coordinating with third party inspectors, and preparing quality control documentation. He holds a Bachelor's degree in Mechanical Engineering from Annamalai University in India.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Rtfi weld defects[1]![Rtfi weld defects[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/rtfiwelddefects1-190507184037-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Rtfi weld defects[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/rtfiwelddefects1-190507184037-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Rtfi weld defects[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/rtfiwelddefects1-190507184037-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Rtfi weld defects[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/rtfiwelddefects1-190507184037-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Rtfi weld defects[1]Vishnu Chakkuzhiyil Muraleedharan
╠²
This document discusses artifacts that may appear on radiographic films. It defines several types of artifacts including burned film, chemical stains, crimp marks, lead foil scratches, light leaks, pressure marks, sand/dirt marks, scratch marks, static marks, water marks, and roller marks from automatic processing. For each artifact, it provides an example radiographic image and brief description of how the artifact is caused. The purpose is to help trainees identify and understand artifacts that could affect the interpretation of radiographic images.radiographic-interpretation.pdf



radiographic-interpretation.pdfVENKATESAN S
╠²
The document is a training manual on radiographic interpretation of welds. It contains multiple radiographic images of welds with defects labeled, asking the reader to identify the defects shown. The defects illustrated include lack of root penetration, porosity, undercutting, cracking, incomplete fusion, excess penetration, spatter, slag inclusions and others. The purpose is to help trainees learn to identify various weld defects from radiographic images.What is wps important tips regarding to wps



What is wps important tips regarding to wpsWeld Maniac
╠²
A welding procedure specification (WPS) is a document that provides parameters for welding, including joints, metals, positions, and variables. There are three types of variables: essential, non-essential, and supplementary essential. Essential variables require requalification if changed, while non-essential variables can be changed without requalification. WPS and procedure qualification records (PQR) are qualified according to material groups designated by P-numbers, with PQR tests needed to support welding between specific P-number combinations. Qualification with a given P-number tests qualifies welding within certain P-number ranges depending on materials and filler metals used.Welding Defect.ppt



Welding Defect.pptAbdul Naqiuddin
╠²
The document discusses various welding defects including cracks, surface defects, contour defects, root defects, and miscellaneous defects. It provides details on specific types of each defect such as undercut, overlap, incomplete root fusion, gas porosity, slag inclusions, and their potential causes like incorrect welding technique, contamination, or material defects. Various repair methods are also mentioned such as grinding, chipping, and arc air gouging.A QA/QC ENGINEER MUST KNOW THESE TABLE IN ASME SEC IX



A QA/QC ENGINEER MUST KNOW THESE TABLE IN ASME SEC IXWeld Maniac
╠²
This document provides information on qualifying welders and welding procedures according to the ASME Section IX code. It includes tables that specify the base metals and filler metals qualified by different welding tests. The tables indicate which base or filler metals a welder or procedure is considered qualified to weld based on the specific metals tested during qualification. Qualifying a production weld also qualifies the procedure to weld a broader range of materials according to these tables.Welder qualification



Welder qualificationkharafi national,kuwait
╠²
This document provides information on the essential variables and requirements for welder qualification according to ASME Section IX. It lists the key variables that must be specified for a welder qualification, including welding process, type, base metal, filler metal, and weld thickness limits. It also outlines the qualification requirements and limitations for weld position, diameter, progression, backing, and which filler and base metals a welder is qualified to use based on their test.Weld Defects



Weld Defectsadminn2
╠²
This document discusses various types of welding defects and imperfections including lack of fusion, porosity, slag inclusions, and solidification cracking. It describes how to identify each type, their causes, best practices for prevention, acceptance standards, and methods for detection and remediation. The key types of imperfections are classified as fabrication defects occurring during welding or service defects that form during use, and guidelines are provided for minimizing defects and producing quality welds.Visual Inspection of Welding Process



Visual Inspection of Welding ProcessGaurav Singh Rajput
╠²
The document discusses visual inspection of welds, including terminology for different types of welds and weld features. It provides checklists for welding procedures before, during, and after welding. Common welding defects such as lack of fusion, undercut, and porosity are described along with their potential causes. Visual inspection procedures and features to examine in butt and fillet welds are also outlined.CSWIP 3.2 New BOOK.pdf



CSWIP 3.2 New BOOK.pdfVENKATESAN S
╠²
The document outlines the duties and responsibilities of a Senior Welding Inspector. It discusses that the role requires strong leadership, technical, and managerial skills. Some key responsibilities include managing inspection teams, providing guidance to inspectors, making technical decisions, planning inspections, and ensuring work is completed on time and to budget. Senior Welding Inspectors must have in-depth knowledge of welding technology, quality standards, and the ability to audit work and evaluate non-destructive testing reports. Strong communication, organization, and people management skills are also important to motivate personnel and ensure high morale is maintained throughout inspection projects.Structural Steel Welding Inspection



Structural Steel Welding InspectionAsirul Hoq
╠²
This document provides generalized guidelines for structural steel welding inspection as per the AWS D1.1 Structural Welding Code for Steel. It covers standard terms, the scope of the code, limitations on its use, design of welded connections, weld joint configurations, prequalification of welding procedures, qualification requirements, fabrication, inspection, and non-destructive testing requirements. Key areas addressed include complete and partial joint penetration welds, fillet welds, prequalification criteria for common welding processes and materials, visual inspection acceptance standards, and additional non-destructive testing as required.Weldability pc



Weldability pcJithu John
╠²
This document discusses the weldability of various metal types including carbon-manganese steel, low alloy steel, quenched and tempered steel, stainless steel, nickel alloys and aluminum alloys. For carbon-manganese steel, it notes their excellent weldability and suitability for arc and other welding processes. It also discusses preheat requirements and filler metals for different welding methods. For low alloy and quenched tempered steels, it highlights their susceptibility to hydrogen cracking and need for proper joint design, preheat and control of heat input during welding. The document also briefly summarizes weldability considerations for martensitic and ferritic stainless steels.Methods of examination of joints(RT) - API 650 Tanks



Methods of examination of joints(RT) - API 650 TanksRajSamy
╠²
This document outlines standards for radiographic examination of welds on storage tanks. It discusses limits for dissimilar thickness consideration, joints that are exempt from radiographic testing, requirements for vertical and horizontal joints of different thicknesses, insert plates, length of radiographs, annular plates, examination of tank bottoms and sumps, repair and penalty guidelines, recommended techniques, weld reinforcement requirements, and documentation standards.Piping welding notes for beginners



Piping welding notes for beginnersMOHAMMAD ATIF ALI
╠²
Here are the major responsibilities of a project engineer summarized:
- Oversee all construction activities to ensure they are completed as per approved plans, schedule and budget.
- Coordinate with different project departments like safety, procurement, contracts and quality.
- Ensure materials are available on time and resolve any technical or design issues that arise.
- Lead meetings and ensure contractor action plans and schedules are understood.
- Review invoices, punch lists and change orders for approval.
- Oversee commissioning, documentation handover and project closeout.
- Monitor project progress and address any delays by expediting work or investigating causes.Welding Defects.pdf



Welding Defects.pdfUniversity of Sarajevo, Manufacturing Technology:
╠²
There are numerous welding processes including arc welding, electron beam welding,
friction welding, laser welding, and resistance welding. This article will concentrate on arc
welding, which is the most common technique used to join most steels. Factors affecting
weld quality will be discussed and how to avoid common weld defects will be presented.
Arc welding requires striking a low-voltage, high-current arc between an electrode and the
base metal. The intense heat generated with this arc melts the base metal and allows the
joining of two components. The characteristic of the metal that is being welded and the joint
type (i.e. groove, fillet, etc.) dictates the welding parameters and the procedure that needs to
be followed to obtain a sound weld joint. Welding flaws



Welding flawsJithu John
╠²
- Lamellar tearing is commonly observed discontinuity in fusion welding that occurs near the heat-affected zone in flange plates of T-butt joints. It is caused by factors like dilution and heat input during welding.
- Dilution is affected by the melted parent metal, melted filler metal, and weld width to depth ratio. Too low or too high heat input can both be detrimental.
- Solidification cracks can form due to the bead factor, which is the ratio of weld width to depth. A ratio greater than 1 or less than 1 can both result in cracks.How to Qualify a Welding Procedure



How to Qualify a Welding ProcedureAntonius Pompi Bramono
╠²
The document outlines the five step process to qualify a welding procedure according to ASME Section IX. It provides details on developing a draft procedure using 0.75" A36 steel plate welded in the flat position using GTAW and GMAW. Variables such as joint design, base metal and thickness, filler metal type and size, welding position, and electrical parameters are documented. The qualification weld was tested to verify it results in an acceptable weld with proper mechanical properties before the welding procedure specification can be used in construction.Overview fusion welding standards (lasstandaarden engels)



Overview fusion welding standards (lasstandaarden engels)Ren├® Varkevisser
╠²
This document provides an overview of European and international standards related to welding and fusion joining processes. It lists standards for welding procedure and welder qualification, non-destructive testing methods, classification of welding consumables, quality requirements, and safety and environmental standards. The overview is intended to help welding professionals find the appropriate standards for their application and welding process.Radiographic interpretation 



Radiographic interpretation kamarulariffinzainalabidin
╠²
This document provides definitions for various defects that may appear on radiographic images of welds, including:
- Excessive root penetration appears as a light irregular band within the weld image.
- Root concavity appears as dark areas along the weld center varying in density by imperfection depth.
- Incomplete filled groove appears as a dark area at the weld center with diffuse edges.
- Cracks appear as dark, fine lines that are usually diffuse or discontinuous.9488085 welding-defects



9488085 welding-defectsRony Simeon
╠²
The document discusses various types of discontinuities and defects that can occur in welding, including cracks, porosity, inclusions, insufficient penetration, and more. It defines discontinuities as interruptions in material structure that are not necessarily defects, while defects render a part unable to meet standards. Causes, preventions, and potential repairs are provided for each issue. Engineering problems can arise from design mistakes, while weld process issues relate to techniques and metallurgy.Inspection of Heat exchanger .pdf



Inspection of Heat exchanger .pdfTusharNayak32
╠²
The document discusses inspection of heat exchangers during manufacture. It outlines the key components of a heat exchanger that will be covered, including shells, channels, tube sheets, baffles, tubes, bellows, spacers, and tie rods. Minimum inspection requirements are described for each component, focusing on dimensions, workmanship, materials, and critical points often overlooked. Testing procedures for the completed heat exchanger like hydrotesting and helium leak testing are also summarized.Similar to How to view the material certificate part 2 (20)
Holo-Krome catalog



Holo-Krome catalogjerjer87
╠²
This document is a technical handbook published by Holo-Krome to provide dimensional, mechanical, and application data for their socket screw products. It outlines several limitations and considerations for using the information, including that specifications may change over time and vary slightly for non-stock products. It also notes that proper screw sizes and torque depend on specific design parameters. The handbook is organized to provide both inch and metric dimensional data followed by application data for each module.jaynt singh (CV) (5)



jaynt singh (CV) (5)Jayant Singh
╠²
This document contains a summary of Jayant Singh's professional experience and qualifications. He has over 4 years of experience working as a Quality Control Engineer at various companies in India and Oman, including L&T Heavy Engineering LLC in Oman and Bectochem Lodige Process Technology Private Limited in India. His responsibilities have included ensuring quality standards, inspecting fabrication and welding, coordinating with third party inspectors, and preparing quality control documentation. He holds a Bachelor's degree in Mechanical Engineering from Annamalai University in India.Bolts includes docs_pdf_87



Bolts includes docs_pdf_87Pinak Nandasana
╠²
The document is a technical handbook published by Holo-Krome as a guide to dimensional, mechanical and application data for their socket screw products. It provides important limitations and notes that the data is subject to change. It is intended as a general guide and should be used in conjunction with specific design criteria and engineering principles. The handbook contains both inch and metric data organized to make finding information easy regardless of module used. T.rajakumar.cv



T.rajakumar.cvrajakumar kumar
╠²
This document provides a summary of Rajakumar Thangadurai's qualifications and work experience in non-destructive testing. It lists his personal details and contact information, then outlines over 15 years of experience performing various NDT techniques for the oil and gas, marine, construction, and power industries. It details his technical certifications in ultrasonic, magnetic particle, radiographic, and penetrant testing at levels II and III. Finally, it summarizes several recent projects in Nigeria where he served as an NDT level III inspector and ultrasonic cross checker, reviewing documentation and ensuring work was performed to specification.Jaynt singh (cv) (1)



Jaynt singh (cv) (1)Jayant Singh
╠²
Jayant Singh has over 3 years of experience in quality control engineering. He currently leads quality control for an ORPIC refinery project in Oman. Previously he worked on quality control for projects in India including an ammonia chiller, EO reactor, and units for Reliance Industries. His responsibilities include ensuring quality standards, inspecting fabrication and welding, coordinating with third party inspectors, and preparing quality documents. He has a Bachelor's degree in Mechanical Engineering from Annamalai University in India.Jaynt singh (cv) (1)



Jaynt singh (cv) (1)Jayant Singh
╠²
Jayant Singh has over 3 years of experience in quality control engineering. He currently leads quality control for an ORPIC refinery project in Oman. Previously he worked on quality control for projects in India including an ammonia chiller, EO reactor, and units for Reliance Industries. His responsibilities include ensuring quality standards, inspecting fabrication and welding, coordinating with third party inspectors, and preparing quality documents. He has a Bachelor's degree in Mechanical Engineering from Annamalai University in India.Presentation on Air Heater Inspection 



Presentation on Air Heater Inspection Summit Power International https://summitpowerinternational.com/
╠²
The document summarizes the inspection of heat exchangers conducted by engineers from the Multinational Fertilizer Company and GEA at GEA's facility in Wingles, France. Key points from the inspection include: pressure testing and dimensional checking of the heat exchangers; reviewing material certifications and weld documentation; and inspecting the packaging and crating of the units. The inspection concluded with both parties signing off on the required documentation.Shop fabrication of structural steel



Shop fabrication of structural steelAhmed Allam
╠²
The document discusses the process of shop fabrication of structural steel. It describes the key stages as receiving and inspecting raw materials, preparation such as cutting and drilling, production through welding, surface preparation and protection. Quality control is conducted throughout, including material inspections, dimension checks, identification tests and non-destructive tests. Common welding defects are also outlined along with factors that affect weld quality. Non-destructive tests like visual inspection, radiography, ultrasonic and magnetic testing are used to identify any defects before erection.Amar Resume



Amar ResumeAmar Desai
╠²
The document provides a summary of Amarkumar Pankajbhai Desai's professional experience and qualifications. It summarizes his 6 years of experience in quality assurance, inspection, and documentation for oil and gas manufacturing companies. It also lists his areas of expertise including ISO and quality system auditing, inspection, and machining. Finally, it details his work history and roles in quality assurance and inspection for several engineering companies in the oil and gas industry.Understanding AMS2750E (intermediate) v2



Understanding AMS2750E (intermediate) v2Peter Sherwin
╠²
This document provides an overview of the AMS2750E heat treatment standard. It is part of a series of guides on heat treatment control. This specific guide focuses on explaining key aspects of the AMS2750E standard for suppliers and end users, including instrumentation requirements, system accuracy tests, temperature uniformity surveys, and equipment classes. The guide also discusses how instrument suppliers can help meet the standard's requirements through services like calibrated thermocouples, instruments, field testing equipment, calibration, training and data management support.kiruba new resume



kiruba new resumekirubhakar poornam
╠²
This document provides a summary of Pooranam Kirubhakar's professional experience and qualifications. He has over 18 years of experience in quality assurance, welding inspection, and fabrication across various petroleum refineries. He holds several certifications including ASNT Level-III, AWS certified ISO 9001 Lead Auditor, and Nace Certified Level-I Coating Inspector. His experience includes roles as a QA/QC engineer, welding inspector, and RT Level-III technician for numerous projects in India, the Middle East, and Africa.8.3 Control of Nonconforming Material



8.3 Control of Nonconforming MaterialBrian McAuliffe
╠²
This document describes Cuming Corporation's procedure for controlling nonconforming material. It defines responsibilities for identifying, controlling, reporting, and disposing of nonconforming parts. Nonconforming parts are documented on a Discrepant Material Report which is reviewed by a Material Review Board to determine if the part can be used as-is, reworked, repaired, or scrapped. The procedure aims to complete disposition within 10 days and close the report within 30 days, identifying root causes when necessary. Metrics on nonconforming material reports are monitored for trends and included in management reviews.Mohamad Elyaas CV & Certf



Mohamad Elyaas CV & CertfMohamad Elyaas
╠²
This document contains the resume of Mohamad Elyaas. It summarizes his contact information, educational background, professional certifications, skills, and work experience. For his current role, he works as a Mechanical Inspector based in Saudi Arabia, where he is responsible for quality assurance and inspection tasks such as reviewing documentation, inspecting materials, monitoring fabrication and testing, identifying non-conformities, and ensuring work is done according to standards and client specifications. Previously he has over 8 years of experience in quality control and inspection roles in India.Pournaimi CV FORM R01



Pournaimi CV FORM R01hossein pournaimi
╠²
Hossein Pournaimi is seeking employment as a technical inspector. He has over 10 years of experience inspecting equipment like compressors, turbines, and vessels for quality standards. This includes experience visual inspecting, using measurement tools, reviewing documentation, and ensuring safety. He is proficient in English, holds NDT and welding certifications, and has a background in engineering.MUHAMMAD KALEEM U LLAH (2)



MUHAMMAD KALEEM U LLAH (2)Muhammad Ullah
╠²
This document provides a summary of Muhammad Kaleem Ullah's qualifications and experience. It outlines his contact information, objective, expertise in technical areas, academic qualifications including a DAE in Mechanical Engineering and B.A. in Islamic Studies. It also lists his certifications in welding, painting and NDT inspections. His over 6 years of experience includes roles as a QA/QC inspector for welding and painting for various oil, gas and petrochemical companies in Saudi Arabia and Pakistan. It details his responsibilities and skills in welding inspection, painting inspection, and implementing quality plans.Converge Short ECMP Sept 2015



Converge Short ECMP Sept 2015Jo_Vann
╠²
This document discusses electronic component management plans (ECMP) and obsolescence management in the avionics supply chain. It notes that 57% of reported counterfeit parts involve obsolete or end-of-life parts. The document outlines the 11 step ECMP process defined in IEC/TS 62239-1, including component selection, qualification, and obsolescence management. It provides an example where monitoring of manufacturer product change notices through the ECMP process allowed alternatives to be found for 40% of last-time buys. The document also discusses related standards like IEC/TS 62239-2 for COTS assemblies and third-party audit schemes through organizations like IECQ.QA- QC INSPECTOR AJITH CV - Copy



QA- QC INSPECTOR AJITH CV - CopyAjith Puthoor
╠²
Ajith Puthoor is a QA/QC inspector with over 15 years of experience in welding, piping, and painting inspection for offshore and onshore oil and gas projects. He is currently working as a QA/QC welding and painting inspector for Hyundai Heavy Industries on an offshore project in Qatar. Puthoor holds relevant certifications including CSWIP welding inspector, BGAS painting inspector, and ASNT NDT level II in radiography, ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle testing, and penetrant testing. He is responsible for inspecting materials, welds, coatings, and hydrotesting to ensure quality standards are met on pipelines and other piping infrastructure.00 saip-07



00 saip-07OsmanGone1
╠²
This document outlines inspection procedures for positive material identification (PMI) requirements at Saudi Aramco facilities. It details the responsibilities of inspectors to verify materials meet specifications using PMI analysis. Alloy items like plates, forgings, and welds must undergo PMI testing before post-weld treatments or insulation. Inspectors complete PMI reports and logs to document testing of elements like carbon, chromium, and nickel against acceptance criteria. Verified materials are color coded according to specifications to identify their composition.Pmi procedure



Pmi procedureKl├®ber Rezende
╠²
This document outlines the procedure for performing positive material identification (PMI) using x-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF). It describes the purpose, scope, references, definitions, training, safety, equipment, and procedure for PMI testing. The procedure involves surface preparation of test items, equipment calibration checks, reading frequency, identification and marking of verified materials, verification criteria, and reporting of test results. PMI is used to determine the chemical composition of metallic materials without removing samples.AJIT RESUME 14-09-2016



AJIT RESUME 14-09-2016AJIT THORAT
╠²
Ajit Thorat is an Associate Manager of Quality Assurance and Control with over 11 years of experience. He holds a Bachelor's degree in Mechanical Engineering and additional qualifications in non-destructive testing. His experience includes roles at Praj Industries, Bureau Veritas, and Alfa Laval India. He has led quality assurance for projects in oil, gas, and petrochemical industries and ensured compliance with standards like ASME, AWS, and ISO. His responsibilities include quality planning, inspection, auditing, data analysis, and customer reporting.Presentation on Air Heater Inspection 



Presentation on Air Heater Inspection Summit Power International https://summitpowerinternational.com/
╠²
Recently uploaded (20)
Air pollution is contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any ch...



Air pollution is contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any ch...dhanashree78
╠²
Air pollution is contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any chemical, physical or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere.
Household combustion devices, motor vehicles, industrial facilities and forest fires are common sources of air pollution. Pollutants of major public health concern include particulate matter, carbon monoxide, ozone, nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide. Outdoor and indoor air pollution cause respiratory and other diseases and are important sources of morbidity and mortality.
WHO data show that almost all of the global population (99%) breathe air that exceeds WHO guideline limits and contains high levels of pollutants, with low- and middle-income countries suffering from the highest exposures.
Air quality is closely linked to the earthŌĆÖs climate and ecosystems globally. Many of the drivers of air pollution (i.e. combustion of fossil fuels) are also sources of greenhouse gas emissions. Policies to reduce air pollution, therefore, offer a win-win strategy for both climate and health, lowering the burden of disease attributable to air pollution, as well as contributing to the near- and long-term mitigation of climate change.
Sachpazis: Foundation Analysis and Design: Single Piles



Sachpazis: Foundation Analysis and Design: Single PilesDr.Costas Sachpazis
╠²
Žü. ╬ÜŽÄŽāŽä╬▒Žé ╬Ż╬▒ŽćŽĆ╬¼╬Č╬ĘŽé: Foundation Analysis and Design: Single Piles
Welcome to this comprehensive presentation on "Foundation Analysis and Design," focusing on Single PilesŌĆöStatic Capacity, Lateral Loads, and Pile/Pole Buckling. This presentation will explore the fundamental concepts, equations, and practical considerations for designing and analyzing pile foundations.
We'll examine different pile types, their characteristics, load transfer mechanisms, and the complex interactions between piles and surrounding soil. Throughout this presentation, we'll highlight key equations and methodologies for calculating pile capacities under various conditions.decarbonization steel industry rev1.pptx



decarbonization steel industry rev1.pptxgonzalezolabarriaped
╠²
Webinar Decarbonization steel industrySyntax Directed Definitions Synthesized Attributes and Inherited Attributes



Syntax Directed Definitions Synthesized Attributes and Inherited AttributesGunjalSanjay
╠²
Syntax Directed Definitions
How Engineering Model Making Brings Designs to Life.pdf



How Engineering Model Making Brings Designs to Life.pdfMaadhu Creatives-Model Making Company
╠²
This PDF highlights how engineering model making helps turn designs into functional prototypes, aiding in visualization, testing, and refinement. It covers different types of models used in industries like architecture, automotive, and aerospace, emphasizing cost and time efficiency.Lessons learned when managing MySQL in the Cloud



Lessons learned when managing MySQL in the CloudIgor Donchovski
╠²
Managing MySQL in the cloud introduces a new set of challenges compared to traditional on-premises setups, from ensuring optimal performance to handling unexpected outages. In this article, we delve into covering topics such as performance tuning, cost-effective scalability, and maintaining high availability. We also explore the importance of monitoring, automation, and best practices for disaster recovery to minimize downtime.Turbocor Product and Technology Review.pdf



Turbocor Product and Technology Review.pdfTotok Sulistiyanto
╠²
High Efficiency Chiller System in HVACBest KNow Hydrogen Fuel Production in the World The cost in USD kwh for H2



Best KNow Hydrogen Fuel Production in the World The cost in USD kwh for H2Daniel Donatelli
╠²
The cost in USD/kwh for H2
Daniel Donatelli
Secure Supplies Group
Index
ŌĆó Introduction - Page 3
ŌĆó The Need for Hydrogen Fueling - Page 5
ŌĆó Pure H2 Fueling Technology - Page 7
ŌĆó Blend Gas Fueling: A Transition Strategy - Page 10
ŌĆó Performance Metrics: H2 vs. Fossil Fuels - Page 12
ŌĆó Cost Analysis and Economic Viability - Page 15
ŌĆó Innovations Driving Leadership - Page 18
ŌĆó Laminar Flame Speed Adjustment
ŌĆó Heat Management Systems
ŌĆó The Donatelli Cycle
ŌĆó Non-Carnot Cycle Applications
ŌĆó Case Studies and Real-World Applications - Page 22
ŌĆó Conclusion: Secure SuppliesŌĆÖ Leadership in Hydrogen Fueling - Page 27
How to Make an RFID Door Lock System using Arduino



How to Make an RFID Door Lock System using ArduinoCircuitDigest
╠²
Learn how to build an RFID-based door lock system using Arduino to enhance security with contactless access control.15. Smart Cities Big Data, Civic Hackers, and the Quest for a New Utopia.pdf



15. Smart Cities Big Data, Civic Hackers, and the Quest for a New Utopia.pdfNgocThang9
╠²
Smart Cities Big Data, Civic Hackers, and the Quest for a New UtopiaMulti objective genetic approach with Ranking



Multi objective genetic approach with Rankingnamisha18
╠²
Multi objective genetic approach with Ranking AI, Tariffs and Supply Chains in Knowledge Graphs



AI, Tariffs and Supply Chains in Knowledge GraphsMax De Marzi
╠²
How tarrifs, supply chains and knowledge graphs combine.How to view the material certificate part 2
- 1. How to view the material certificate By: Eng. Mohamed Farouk Bayomi JANUARY 1, 2018 MAU for inspections and audits Cairo, Egypt. 002 01114521720 Mohamedfarouk86@gmail.com CWI /API 570 /ASNT Level II
- 2. 1 | P a g e M o h a m e d F a r o u k ( ( C W I / A P I 5 7 0 / A S N T L e v e l I I ) ) How to view the material certificate? ŌĆō Part 2 Continue: PART 2 ŌĆō How to view the certificate??? We will take example for Mill certŌĆÖ, other certŌĆÖ is same procedure. 1. Mill cert: A Certified Mill Test Report (CMTR) is a quality assurance document generated by the raw material manufacturer and provided with the material to intermediate suppliers and ultimately to a finished goods manufacturer. Whether itŌĆÖs called a CMTR, Mill Test Report (MTR), Mill Certification, Metallurgical Test Report, or similar name, this document provides the end user of the raw material verification that the material received matches the requirements of their order. CMTRs are also used to maintain traceability of the material from its initial inception to its inclusion in a finished part. 2. Mill cert review process: The QC Engineer ( or equivalent deptŌĆÖ ) is responsible for review of the CMTR to ensure it meets the engineering and order requirements. Below we have summarized what QC engineers are reviewing, so that only the correct materials are issued to the shop for manufacturing. This being another way we support our promise to Reduce Project Risk and achieve the lowest total cost of ownership for our customers.
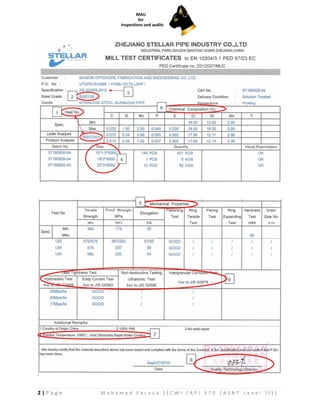
- 3. 2 | P a g e M o h a m e d F a r o u k ( ( C W I / A P I 5 7 0 / A S N T L e v e l I I ) )
- 4. 3 | P a g e M o h a m e d F a r o u k ( ( C W I / A P I 5 7 0 / A S N T L e v e l I I ) ) 3. CMTR FIELD EXPLANATION: Ō¢¬ Point 01 ŌĆō Material Heat Number Material manufacturers can identify raw material in different ways, using lot, coil or other identifying numbers, but ultimately all CMTRs will identify the material with a Heat Number. The heat number is used to maintain traceability of the material. When matching a CMTR to its raw material all accompanying paper work and in many cases markings on the raw material itself must match the heat number on the CMTR. Ō¢¬ Point 02 ŌĆō Material Grade Metal materials are produced in various grades. The CMTR identifies the grade of the material. Ō¢¬ Point 03 ŌĆō Product Specifications Met: this case is JIS standard. CMTRs certify that the raw material meets the appropriate JIS standard. The product specifications that the raw material meets are listed on the CMTR. Ō¢¬ Point 04 ŌĆō Material Dimensions The CMTR identifies the applicable dimensions of the raw material. In the case of plate material this would be the thickness, round bar the diameter, or flat bar the thickness and width. This information must match the order requirements. Ō¢¬ Point 05 & 06 ŌĆō Mechanical Properties / Chemical Analysis The product specification lists the detailed requirements that the raw material must meet to be certified to that product specification and grade. The actual measured properties of the raw material are recorded on the CMTR for the identified heat number. These properties typically consist of the Mechanical Properties, (#5), and Chemical Analysis, (#6), The values listed on the CMTR must fall within the range or limits of the product specification for the raw material to be accepted for use. Ō¢¬ Point 07 ŌĆō Heat Treatment Depending on the raw material, there may be other requirements in the product specification. For example, 300 series stainless steels require a specific heat treatment which must be recorded on the CMTR. The reviewer must identify all special processes in the product specification and confirm they are properly recorded on the CMTR. Ō¢¬ Point 08 ŌĆō Certified Mill Signature Finally the CMTR must be certified with the signature of a responsible employee of the foundry or mill producing the raw material. See above attached. Certified Mill Test Reports provide a record of traceability and properties of a raw material, ensuring that the material will perform in the way it was designed to. Deviations from product specification values can have large consequences, even causing a component failure. Summary: The Certified Mill Test Report is a tool used to ensure that received raw material matches the engineering and purchase order requirements.
- 5. 4 | P a g e M o h a m e d F a r o u k ( ( C W I / A P I 5 7 0 / A S N T L e v e l I I ) )








