Human Blood Glucose Nursing Lectue Notes by Masud Rana RN,MSN
- 1. Masud Rana
- 2. ’üĮ Glucose is monosaccharide found in fruits and also derived from breakdown of carbohydrates in the diet and the conversion of glycogen by liver. ’üĮ Glucose is the bodyŌĆÖs main source of cellular energy, brain.
- 3. ’üĮ It is the maintenance of blood glucose level within the normal range. ’üĮ Blood glucose level must be maintained within the narrow limits of 70-100 mg/dl. ’üĮ Blood sugar level are regulated by negative feedback in order to keep the body in homeostsis.
- 4. ’üĮ Normal blood glucose level (fasting): 70-110 mg/dl ’üĮ Post-prandial blood glucose level: 120-140 mg/dl ’üĮ Above and below the level considered as abnormal ’üĮ Hyperglycemia- levels above the normal range ’üĮ Hypoglycemia- levels below the normal range
- 5. Glucose are derived from three sources 1. Intestinal absorption of dietary carbohydrate 2. Glycogenolysis in liver and kidney ŌĆó Liver stores 25-138grams of glycogen, a 3 to 8 hours supply 3. Gluconeogenesis- the formation of glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors e.g. lactate, pyruvate, amino acids (alanine & glutamine)
- 7. ’üĮ Glycogenesis is the process of formation of glycogen from glucose molecules. ’üĮ Glucogenolysis process by which glycogen, stored in the liver and muscle cell, is broken down into glucose ’üĮ Gluconeogenesis is the metabolic pathway which leads to generation of glucose from non- carbohydrate substrates like proteins, lipids etc. ’üĮ Glycolysis is the process in which glucose is broken down to produce energy ’üĮ Lipogenesis- conversion of glucose into fat
- 9. ’üĮ There are two categories of endocrine influences: 1. Hormone which decrease the blood glucose level- Insulin 2. Hormones which increase the blood glucose levels: Glucagon, Epinephrine, Thyroxin, Growth Hormone, Cortisol and Glucocorticoids.
- 11. ’üĮ Fasting Plasma Glucose (FBS/FPG)- A FBS is taken after at least eight hours of fasting ’üĮ Random Plasma Glucose (RBS/RPG)- Test is done any time of the day without regard to time since last meal ’üĮ Post-Prandial Blood Glucose (PPBS)- The test done about 2hr after a good meal.
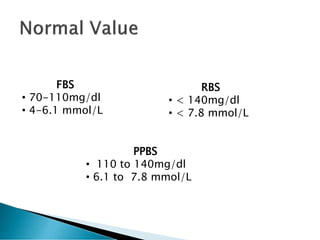
- 12. FBS ŌĆó 70-110mg/dl ŌĆó 4-6.1 mmol/L RBS ŌĆó < 140mg/dl ŌĆó < 7.8 mmol/L PPBS ŌĆó 110 to 140mg/dl ŌĆó 6.1 to 7.8 mmol/L
- 13. ’üĮ Fasting blood sugar (FBS) ’üĮ 2-hour postprandial blood sugar ((2hrPPBS) ’üĮ Random blood sugar (RBS) ’üĮ Oral glucose telarance test (OGTT) ’üĮ Hemoglobin A1c, or glyselated hemoglobin (HbA1C)
- 15. ’üĮ In diabetes mellitus, the level of FBS is 126mg/dl ’üĮ The patient is considered critically hypoglycemic if serum/plasma glucose is <45mg/dl ’üĮ Renal threshold for glucose is 160-180mg/dl ’üĮ When the blood glucose exceed the renal threshold for glucose and presences in urine referred to glycosuria ’üĮ CSF glucose 60-90 mg/dl. Urine glucose: Nill
- 16. ŌŚ”mg/dL * 0.0555 = mmol/L ŌŚ” mmol/L * 18 = mg/dl ŌŚ” mg/dl/18 = mmol/L