human evolution
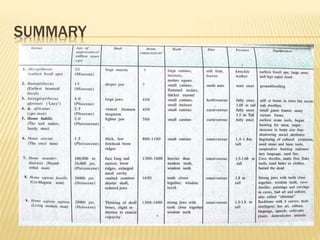
- 3. WHAT IS HUMAN EVOLUTION ï Human evolution is the evolutionary process that leads to the emergence of anatomically modern humans. Human evolution is the lengthy process of change by which people originated from apelike ancestors. Scientific evidence shows that the physical and behavioural traits shared by all people originated from apelike ancestors and evolved over a period of approximately six million years. ï Humans are primates. Physical and genetic similarities show that the modern human species, Homo sapiens, has a very close relationship to another group of primate species, the apes. Humans and the great apes (large apes) of Africa -- chimpanzees (including bonobos, or so-called âpygmy chimpanzeesâ) and gorillas -- share a common ancestor that lived between 8 and 6 million years ago.. ï Mainly focus on the genus âHOMOâ
- 4. HISTORY OF HUMAN EVOLUTION ï T.H. HUXLEY (1863) made first attempt to manâs origin in his book âManâs Place In Natureâ and visualized apes the closest human relatives. ï Later in 1871, Charles Darwin advocated his idea about manâs ancestry in his book âThe Descent With Manâ and propounded origin of man from apes First fossils of human ancestors were described by Eugene Dobois in 1880âs. ï This includes skull cap, lower law jaw fragments and Thigh bones from East Indies. Most pre human fossils were discovered and studied from 1920 onwards. ï The main contributors for the study of human evolution were Raymond Dart (1920s), Davidson Black (1934), L.S.B Leakey and Mary Leakey and their son Richard.
- 6. GREAT APES DRYOPETHECUS ï They lived during the MIOCENE Epoch ï Roughly 10-5 Mya ï They resembled more like monkeys ï They were branchiators ï They were found in eastern Africa RAMAPETHECUS ï They were also present in the MIOCENE Epoch ï They were present roughly 12.5 Mya ï Resembles more like Apes ï They dwelled on both trees and land ï Their fossils were found in the shivalik hills
- 7. AUSTRALOPITHECUS ï It is a extinct genus which evolved in the eastern Africa around 4 Mya and then started spreading throughout the continent ï Many species of the australopithicus evolved eg: A afrenesis, A africanus , A anamensis, A garhi, A sedbia ï They played the most significant role in human evolution as the genus âhomoâ is derived from australopithecus from some time after 2.8 mya ï One of the Australopith species went onto become the first homo genus in africa some 2.5 mya ï Their brain capacity was roughly ~ 490-600cc ï They were largely frugivorous
- 8. AUSTRALOPITHECUS ï Ape-man. ï Connecting link between man and ape. ï Australopithecus africanus is a common fossil.
- 9. HUMAN CHARACTERS OF AUSTRALOPITHECUS ï Erect posture with 4 ft height. ï Bipedal locomotion. ï Basin-like pelvic girdle. ï Dentition like man. ï Hands used for non-locomontory functions.
- 10. HOMO HABILIS They were present during the Pleistocene epoch and lived during 2.8 to 1.5 Mya âĒ It is the least similar to modern humans of all species in the genus âhomoâ âĒ It was short in stature(4ft 3inch) and had long disproportional arms âĒ Its brain capacity was ~ 550- 687cc âĒ There feeding habits varied from fruits, leafs and occasionally eating small lizards âĒ Homo habilis is thought to have mastered the Lower Palaeolithic Olduwan tool set which used stone flakes. H. habilis used these stones to butcher animals and to skin the animals .
- 11. HOMO ERECTUS ï First true man. ï Primitive man. ï Connecting link between ape man and modern man. ï Also called java man. ï Lived in java and Peking.
- 12. HOMO SAPIENS ï Homo sapiens have lighter skeletons than those humans who came before them ï Large brains: approximately 1300 cubic centimetres ï Thin walled, high vaulted skull with a forehead almost perpendicular to the ground ï The main differences between homo sapiens sapiens, and homo sapiens is that we have more brains and brawn
- 13. SUMMARY
- 14. REFERENCE LIST ï Roberto. S, (2015) Human evolution. Available from slideshare at /robertosaezm/human-evolution-notes-from- the-field?qid=6f168658-bbdd-4f7f-9178- 0e179b506157&v=&b=&from_search=2 ï Radhakrishanan. A ,(2019) human evolution. Available from slideshare at /AkashRadhakrishnan4/human-evolution- 97604514?qid=723a4e6f-5514-4126-9577- 90aa66f0817b&v=&b=&from_search=8 ï Dilkarsh. A ,(2017) Evolution of man. Available from slideshare at /DilkashAmbreen1/evolution-of-man- 73224474?qid=6ab89fd8-8360-484e-a00f- 403d2a8fe008&v=&b=&from_search=3 ï Tail . P , (2011) Homo sapiens . Available from slideshare at /Phoenixtail/homo-sapiens-6782246 ï Tinks . I , (2015) Evolution of man. Available from slideshare at ï /ivy_thinks/evolution-of-man-47698969