Human Genetics_Karyotype Procedure.pptx
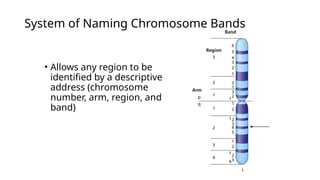
- 3. ŌĆó Allows any region to be identified by a descriptive address (chromosome number, arm, region, and band) System of Naming Chromosome Bands
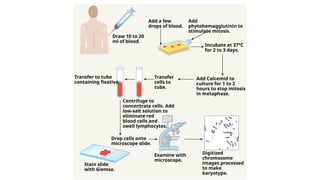
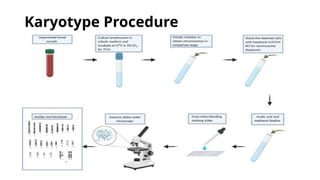
- 4. Add a few drops of blood. Add phytohemagglutinin to stimulate mitosis. Draw 10 to 20 ml of blood. Incubate at 37┬░C for 2 to 3 days. Transfer to tube containing fixative. Transfer cells to tube. Add Colcemid to culture for 1 to 2 hours to stop mitosis in metaphase. Centrifuge to concentrate cells. Add low-salt solution to eliminate red blood cells and swell lymphocytes. Drop cells onto microscope slide. Examine with microscope. Digitized chromosome images processed to make karyotype. Stain slide with Giemsa.
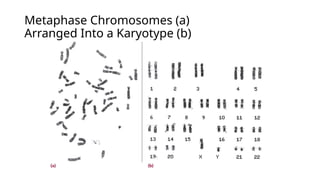
- 5. Metaphase Chromosomes (a) Arranged Into a Karyotype (b)
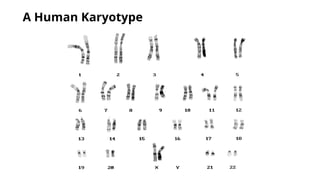
- 6. Constructing and Analyzing Karyotypes ŌĆó Different stains and dyes produce banding patterns specific to each chromosome ŌĆó Karyotypes reveal variations in chromosomal structure and number ŌĆó 1959: Discovery that Down syndrome is caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21 ŌĆó Chromosome banding and other techniques can identify small changes in chromosomal structure
- 7. Information Obtained from a Karyotype ŌĆó Number of chromosomes ŌĆó Sex chromosome content ŌĆó Presence or absence of individual chromosomes ŌĆó Nature and extent of large structural abnormalities