Hyperinflation theory
- 1. Sumit Sharma 2012328 Vaibhav Goel 2012351 Varun Puri 2012355 Vats Abhishek 2012356 Vinayak Goldar
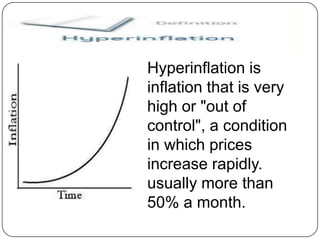
- 3. Hyperinflation is inflation that is very high or "out of control", a condition in which prices increase rapidly. usually more than 50% a month.
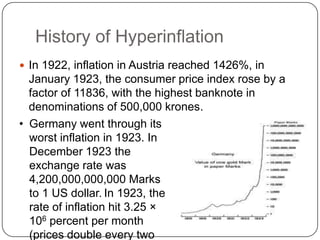
- 4. History of Hyperinflation ï In 1922, inflation in Austria reached 1426%, in January 1923, the consumer price index rose by a factor of 11836, with the highest banknote in denominations of 500,000 krones. âĒ Germany went through its worst inflation in 1923. In December 1923 the exchange rate was 4,200,000,000,000 Marks to 1 US dollar. In 1923, the rate of inflation hit 3.25 Ã 106 percent per month (prices double every two
- 5. ï Hungary went through the worst inflation ever recorded between the end of 1945 and July 1946. It is the most severe known incident of inflation recorded, peaking at 1.3 Ã 1016 percent per month (prices double every 15 hours). ï The Republic of China went through the worst inflation 1948â49. Peak Month and Rate of Inflation: Apr. 5070%
- 6. ï Hyperinflation in Zimbabwe was one of the few instances that resulted in the abandonment of the local currency. ï Hyperinflation began early in the 21st- century,in 2004, reaching 624%. ï At its Nov. 2008, peak monthly rate was 79.6 billion percent, which is equivalent to around 7Ãâ10108 percent yearly rate. At that rate, prices were doubling every 24.7
- 8. Causes ï High inflation must always be preceded by major increases in the supply of money. ï Imbalance between supply and demand for the specific currency. ï The reduction of the value of the paper money. ï Increased borrowing in order to pay of other debt.
- 9. ï The role of civil war, revolution, or deep social/political unrest is the factor in many of the hyperinflation. ï The existence of weak govt. is another important condition that triggers hyperinflation. ï Loss of confidence in the countryâs economy(the first step into hyperinflation).
- 10. Effects ï The prices of goods go higher, especially the prices of commodities. ï Creates an environment for consumption and spending, but NOT investment and saving. ï International investors will not invest in the countryâs economy (lacks FDI). ï People prefer to keep their wealth in non-monetary assets or in a relatively stable foreign currency.
- 11. Zimbabwe Paper Money Used as Toilet Paper
- 13. ï Decrease in public purchasing power. ï Currency debasement (which lowers the value of a currency, and sometimes cause a new currency to be born. ï People tend to barter instead of using money as a way of exchanging goods.
- 14. How it can be controlled There are broadly two ways of controlling hyperinflation in an economy: I).Monetary Measures The most important and commonly used method to control inflation is monetary policy of the Central Bank. Most central banks use high interest rates as the traditional way to fight or prevent inflation. Monetary measures used to control hyperinflation include: (i) bank rate policy (ii) cash reserve ratio and (iii) open market operations.
- 15. 2). Fiscal measures Fiscal measures to control hyper inflation include taxation, government expenditure and public borrowings. The government can also take some protectionist measures (such as banning the export of essential items such as pulses, cereals and oils to support the domestic consumption, encourage imports by lowering duties on import items etc.).
- 16. Prevention ï Increase the interest rate dramatically. ï Cutting government spending and debt. ï Increasing reserve rates for banks. But each of these steps might have their own side effects in the economy.