HYPER-THREADING TECHNOLOGY
- 2. CONTENTS ď‚ž Introduction ď‚ž HT Architecture ď‚ž Working principle ď‚ž Advantages & Disadvantages
- 3. INTRODUCTION “HT Technology”, enables the processor to execute two threads or sets of instructions at the same time. Since hyper-threading allows two streams to be executed in parallel it is almost like having two separate processor working together.
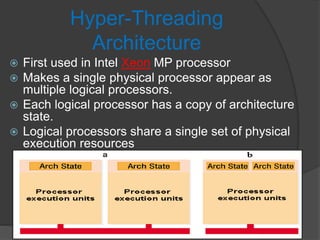
- 4. Hyper-Threading Architecture ď‚ž First used in Intel Xeon MP processor ď‚ž Makes a single physical processor appear as multiple logical processors. ď‚ž Each logical processor has a copy of architecture state. ď‚ž Logical processors share a single set of physical execution resources
- 5. ď‚ž Hyper-Threading technology is a form of simultaneous multi-threading technology (SMT), where multiple threads of software applications can be run simultaneously on one processor. ď‚ž This is achieved by duplicating the architectural state on each processor, while sharing one set of processor execution resources.
- 7. Advantages ď‚ž Extra architecture only adds about 5% to the total die area. ď‚ž No performance loss if only one thread is active. Increased performance with multiple threads ď‚ž Hyper-Threading Technology is designed to increase the ability to use a processor efficiently ď‚ž Increase thread-level parallelism
- 8. Disadvantages ď‚ž To take advantage of hyper-threading performance, serial execution can not be used. ď‚— Threads are non-deterministic and involve extra design ď‚— Threads have increased overhead ď‚ž Shared resource conflicts
- 9. Business Benefits of Hyper-Threading Technology ď‚ž Higher transaction rates for e-businesses ď‚ž Improved reaction and response times for end-users and customers. ď‚ž Increased number of users that a server system can support ď‚ž Handle increased server workloads ď‚ž Compatibility with existing server applications and operating systems
- 10. Conclusion  Intel’s Hyper-Threading Technology brings the concept of simultaneous multi-threading to the Intel Architecture  Hyper-Threading Technology shows performance gains of up to 30% on common server application benchmarks for this technology.
- 12. THANK YOU
Editor's Notes
- #5: Hyper-threading is Intel's proprietary simultaneous multithreading (SMT) implementation used to improve parallelization of computations performed on x86 microprocessors. It first appeared in February 2002 on Xeon server processors and in November 2002 on Pentium 4 desktop CPUs . Later, Intel Included this technology in Itanium, Atom, and Core 'i' Series CPUs, among others.