I2C
Download as PPT, PDF13 likes21,262 views
I2C is a serial communication protocol used to connect low-speed peripherals to processors and microcontrollers. It was developed by Philips in the 1980s for use in televisions. I2C uses just two bidirectional open-drain lines: serial data line (SDA) and serial clock line (SCL). Devices can operate as master or slave devices and have a 7-bit address. Communication is initiated by the master which controls the clock signal. Data is transferred in one byte packets with acknowledgement from the receiver.
1 of 26
Downloaded 1,361 times









Recommended
I2C Bus (Inter-Integrated Circuit)



I2C Bus (Inter-Integrated Circuit)Varun Mahajan
Ěý
The document discusses the I2C communication bus protocol. It describes the I2C bus concept of using two bi-directional lines (SDA and SCL) to allow devices with unique addresses to communicate as masters or slaves. The document outlines the I2C communication protocol including START/STOP conditions, byte format, acknowledgment, synchronization, arbitration, and 7-bit and 10-bit addressing schemes. Key aspects of the I2C bus such as typical transfer rates, hardware connections, and terminology are also summarized.I2C Protocol



I2C ProtocolSudhanshu Janwadkar
Ěý
This presentation discusses the details of the I2C protocol and interfacing of EEPROM with 8051 based on I2C protocol. It also discusses the other applications of I2C protocolSPI introduction(Serial Peripheral Interface)



SPI introduction(Serial Peripheral Interface)SUNODH GARLAPATI
Ěý
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is an interface bus commonly used to send data between microcontrollers and small peripherals such as shift registers, sensors, and SD cards.The I2C Interface



The I2C InterfaceCorrado Santoro
Ěý
The document describes the I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) bus interface. I2C is a digital communication protocol used to connect integrated circuits on the same circuit board. It uses just two bidirectional open-drain lines - serial data (SDA) and serial clock (SCL). Devices on the I2C bus can operate as either a master or slave. The master device initiates and controls data transfers. Slave devices respond to the master's commands. The document outlines the electrical considerations, addressing schemes, data transfer protocols, and how to implement I2C on a PIC18F25K22 microcontroller.I2C BUS PROTOCOL



I2C BUS PROTOCOLKashyap Mandaliya
Ěý
This document provides an overview of the I2C protocol. It describes that I2C was designed by Philips in the 1980s to allow communication between components on the same circuit board. It has since been migrated to NXP and expanded to support higher bus speeds and lower voltages. The document outlines the I2C architecture as a half-duplex, synchronous, multi-master bus using a serial data line and serial clock. It defines I2C nodes can function as a master or slave and transmit or receive data. Electrical characteristics, start/stop conditions, packet formats, clock stretching, arbitration and multi-byte transactions are also summarized.I2C Protocol



I2C ProtocolAnurag Tomar
Ěý
I2C is a serial protocol for two-wire interface to connect low-speed devices like microcontrollers, EEPROMs, A/D and D/A converters, I/O interfaces and other similar peripherals in embedded systems. It was invented by Philips and now it is used by almost all major IC manufacturers. Each I2C slave device needs an address – they must still be obtained from NXP (formerly Philips semiconductors).I2C



I2CSarojpatnaik5
Ěý
This document summarizes an internship final presentation on verifying an I2C protocol design using the Universal Verification Methodology. It describes the internship details, objectives of verifying the I2C protocol using UVM, testbench workflow, key aspects of the I2C protocol, the RTL design, UVM components used in the testbench architecture, simulation results showing the scoreboard passing two test cases for the master transmitter and receiver modes, and future applications of the I2C protocol.AMBA AHB 5



AMBA AHB 5SUNODH GARLAPATI
Ěý
AMBA AHB is a bus interface suitable for high-performance synthesizable designs. It defines the interface between components, such as masters, interconnects, and slaves.SPI Bus Protocol



SPI Bus ProtocolSudhanshu Janwadkar
Ěý
This presentation discusses about Serial Bus protocol SPI. It discusses the various features of the protocol, its merits and demerits and applicationI2C introduction



I2C introductionSUNODH GARLAPATI
Ěý
This document provides an overview of the I2C communication protocol. It describes that I2C is a serial communication protocol used to connect slow devices like EEPROMs and ADCs. It can operate at speeds from 100 kbps to 5 Mbps and supports both single master-multi slave and multi master-multi slave configurations. The document outlines the electrical characteristics, bus features, data frame structure, data transfer process, clock synchronization, arbitration and advantages of the I2C protocol.Serial Peripheral Interface(SPI)



Serial Peripheral Interface(SPI)Dhaval Kaneria
Ěý
The SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) is a synchronous serial communication protocol used for communication between devices. It uses a master-slave architecture with a single master device initiating data transfer. Key features include using separate clock and data lines, operating in full duplex mode, and allowing multiple slave devices through individual chip selects. It provides a lower pin count solution than parallel buses at the cost of slower communication speeds.I2C-Bus Design and Verification Specs



I2C-Bus Design and Verification SpecsMostafa Khamis
Ěý
Philips Semiconductors (now NXP Semiconductors) developed a simple bidirectional 2-wire bus for efficient inter-IC control. This bus is called the Inter-IC or I2C-bus which is a 8-bit oriented serial bus. Only two bus lines are required:
a serial data line (SDA)
a serial clock line (SCL).I2 c



I2 csean chen
Ěý
The document discusses the I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) protocol, which is a serial communication standard used to connect low-speed peripherals to embedded systems and other devices. It describes the basic I2C protocol including data transfer methods, components, and modes. It also provides code examples from an iBoot project that implement I2C read and write functionality using registers, state machines, and GPIO interfaces.AXI Protocol.pptx



AXI Protocol.pptxYazan Yousef
Ěý
A presentation about the AXI protocol includes all the signal description and explanation referred to the AXI specification Axi protocol



Axi protocolAzad Mishra
Ěý
The document discusses Advanced eXtensible Interface (AXI), which is a third generation interface specification that is targeted at high performance systems. AXI uses separate address/control and data phases to improve performance. It supports burst transactions where only the start address is issued and multiple outstanding addresses can be in flight simultaneously. AXI consists of five channels to separate read and write operations. Simulation results showed that AXI provides higher throughput than older AMBA interfaces, though older interfaces may have lower latency in some cases. AXI's standardization and flexibility make it useful for integrating IP cores.Ambha axi



Ambha axiHARINATH REDDY
Ěý
Advanced eXtensible InterfaceĚý(AXI), part of theĚýARM Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture (AMBA3) (AXI3) and 4 (AXI4) specifications.Slow peripheral interfaces (i2 c spi uart)



Slow peripheral interfaces (i2 c spi uart)PREMAL GAJJAR
Ěý
The Serial Peripheral Interface or SPI bus is a synchronous serial data link, a de facto standard, named by Motorola, that operates in full duplex mode. It is used for short distance, single master communication, for example in embedded systems, sensors, and SD cards.Uart



UartAditee Apurvaa
Ěý
The document discusses UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) communication. It describes how UARTs allow for asynchronous serial communication between devices using only 2 wires by converting parallel data to serial and vice versa. The UART communication process involves a transmitting UART adding start, stop and optionally parity bits to data before transmitting it serially bit-by-bit to a receiving UART which reconstructs the parallel data. It also discusses the TTL and RS-232 physical layer standards for UART.AMBA 5 COHERENT HUB INTERFACE.pptx



AMBA 5 COHERENT HUB INTERFACE.pptxSairam Chebrolu
Ěý
CHI is an evolution of the ACE protocol and part of the AMBA architecture. It was designed to improve performance and scalability for applications in mobile, networking, automotive and data center systems. CHI uses a layered architecture with protocol, network and link layers. It supports coherency across processor clusters and memory with topologies like ring, mesh and crossbar. Key nodes include request nodes, home nodes and subordinate nodes. The system address map routes transactions between nodes using unique node IDs. APB protocol v1.0



APB protocol v1.0Azad Mishra
Ěý
The document describes conventions and signals used in the AMBA 3 APB protocol specification version 1.0. It summarizes write and read transfer procedures, including optional wait states using the PREADY signal. Error responses are also described. The operating states of the APB include IDLE, SETUP, and ACCESS states. PREADY controls exiting the ACCESS state.I2c protocol - Inter–Integrated Circuit Communication Protocol



I2c protocol - Inter–Integrated Circuit Communication ProtocolAnkur Soni
Ěý
This document provides an overview of the I2C communication protocol. It describes how I2C uses only two wires (SDA and SCL) to allow data transmission between an I2C master and multiple I2C slave devices. The document explains the I2C message structure, including the start condition, address frame, read/write bit, data frames, ACK/NACK bits, and stop condition. It also discusses the advantages of I2C, such as supporting multiple masters/slaves and error checking, and disadvantages like slower speeds compared to SPI. Real-life uses of I2C include connections to OLED displays, sensors, and other peripherals.SPI Protocol in LPC2148



SPI Protocol in LPC2148Dnyanesh P. Joshi
Ěý
The document discusses the SPI protocol used in the LPC2148 microcontroller. It describes the SPI communication modes of master and slave. It explains the various SPI registers used for configuration - SPCCR for clock settings, SPCR for control settings like CPHA and CPOL, SPDR for data transfer, and SPSR for status. It provides steps for initialization and data transfer in both master and slave modes. The document also discusses factors like clock frequency, data length, and interrupt handling related to SPI communication using LPC2148.Session 8,9 PCI Express



Session 8,9 PCI ExpressSubhash Iyer
Ěý
The document provides an overview of the PCI Express system architecture. It discusses the architectural perspective of PCI Express including how it maintains backwards compatibility with PCI/PCI-X while improving performance through serial point-to-point connectivity and packet-based transactions. It also covers the PCI Express transaction model and types, including memory, I/O, configuration and message transactions, as well as posted and non-posted transaction types.Pcie basic



Pcie basicSaifuddin Kaijar
Ěý
PCIe is a standard expansion card interface introduced in 2004 to replace PCI and PCI-X. It uses serial instead of parallel communication and is scalable, allowing for higher maximum system bandwidth. The presentation discusses the history of expansion card standards leading to PCIe, including ISA, EISA, VESA, PCI, and PCI-X. It also covers key aspects of PCIe such as the root complex, endpoints, switches, lanes, bus:device.function notation, enumeration, and address spaces such as configuration space.Apb



ApbAzad Mishra
Ěý
The document describes the AMBA 3 APB protocol. It has an unpipelined design to reduce complexity and power consumption. Transfers take at least two cycles with the first being a setup phase and second an access phase controlled by the PENABLE signal. Slaves can extend transfers using the PREADY signal. Errors are indicated by PSLVERR. The protocol defines read and write transfers with or without wait states.axi protocol



axi protocolAzad Mishra
Ěý
The AXI protocol specification describes an advanced bus architecture with burst-based transactions using separate address/control and data phases over independent channels. It supports features like out-of-order transaction completion, exclusive access for atomic operations, cache coherency, and a low power interface. The AXI protocol is commonly used in System-on-Chip designs for high performance embedded processors and peripherals.PCI express



PCI expresssarangaprabod
Ěý
PCI Express is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard that was created to replace older standards like PCI, PCI-X, and AGP. It provides dedicated bandwidth to devices through the use of lanes and is commonly used as the interface for graphics cards, hard drives, and other peripherals. PCIe has gone through several generations that have increased its maximum bandwidth. It uses a layered protocol architecture and is designed for compatibility while providing scalable bandwidth and other advantages over older standards.SPI Protocol



SPI ProtocolAnurag Tomar
Ěý
The document describes the Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) protocol which allows for full duplex synchronous serial communication between a master and slave device using 4 pins - MOSI, MISO, SCK, and an optional SS pin. It details the SPI registers for control, status, and data and provides examples of SPI communication with peripherals like digital pots and shift registers. Common issues like conflicts with programming interfaces and ensuring proper chip select signaling are also covered.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
SPI Bus Protocol



SPI Bus ProtocolSudhanshu Janwadkar
Ěý
This presentation discusses about Serial Bus protocol SPI. It discusses the various features of the protocol, its merits and demerits and applicationI2C introduction



I2C introductionSUNODH GARLAPATI
Ěý
This document provides an overview of the I2C communication protocol. It describes that I2C is a serial communication protocol used to connect slow devices like EEPROMs and ADCs. It can operate at speeds from 100 kbps to 5 Mbps and supports both single master-multi slave and multi master-multi slave configurations. The document outlines the electrical characteristics, bus features, data frame structure, data transfer process, clock synchronization, arbitration and advantages of the I2C protocol.Serial Peripheral Interface(SPI)



Serial Peripheral Interface(SPI)Dhaval Kaneria
Ěý
The SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) is a synchronous serial communication protocol used for communication between devices. It uses a master-slave architecture with a single master device initiating data transfer. Key features include using separate clock and data lines, operating in full duplex mode, and allowing multiple slave devices through individual chip selects. It provides a lower pin count solution than parallel buses at the cost of slower communication speeds.I2C-Bus Design and Verification Specs



I2C-Bus Design and Verification SpecsMostafa Khamis
Ěý
Philips Semiconductors (now NXP Semiconductors) developed a simple bidirectional 2-wire bus for efficient inter-IC control. This bus is called the Inter-IC or I2C-bus which is a 8-bit oriented serial bus. Only two bus lines are required:
a serial data line (SDA)
a serial clock line (SCL).I2 c



I2 csean chen
Ěý
The document discusses the I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) protocol, which is a serial communication standard used to connect low-speed peripherals to embedded systems and other devices. It describes the basic I2C protocol including data transfer methods, components, and modes. It also provides code examples from an iBoot project that implement I2C read and write functionality using registers, state machines, and GPIO interfaces.AXI Protocol.pptx



AXI Protocol.pptxYazan Yousef
Ěý
A presentation about the AXI protocol includes all the signal description and explanation referred to the AXI specification Axi protocol



Axi protocolAzad Mishra
Ěý
The document discusses Advanced eXtensible Interface (AXI), which is a third generation interface specification that is targeted at high performance systems. AXI uses separate address/control and data phases to improve performance. It supports burst transactions where only the start address is issued and multiple outstanding addresses can be in flight simultaneously. AXI consists of five channels to separate read and write operations. Simulation results showed that AXI provides higher throughput than older AMBA interfaces, though older interfaces may have lower latency in some cases. AXI's standardization and flexibility make it useful for integrating IP cores.Ambha axi



Ambha axiHARINATH REDDY
Ěý
Advanced eXtensible InterfaceĚý(AXI), part of theĚýARM Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture (AMBA3) (AXI3) and 4 (AXI4) specifications.Slow peripheral interfaces (i2 c spi uart)



Slow peripheral interfaces (i2 c spi uart)PREMAL GAJJAR
Ěý
The Serial Peripheral Interface or SPI bus is a synchronous serial data link, a de facto standard, named by Motorola, that operates in full duplex mode. It is used for short distance, single master communication, for example in embedded systems, sensors, and SD cards.Uart



UartAditee Apurvaa
Ěý
The document discusses UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) communication. It describes how UARTs allow for asynchronous serial communication between devices using only 2 wires by converting parallel data to serial and vice versa. The UART communication process involves a transmitting UART adding start, stop and optionally parity bits to data before transmitting it serially bit-by-bit to a receiving UART which reconstructs the parallel data. It also discusses the TTL and RS-232 physical layer standards for UART.AMBA 5 COHERENT HUB INTERFACE.pptx



AMBA 5 COHERENT HUB INTERFACE.pptxSairam Chebrolu
Ěý
CHI is an evolution of the ACE protocol and part of the AMBA architecture. It was designed to improve performance and scalability for applications in mobile, networking, automotive and data center systems. CHI uses a layered architecture with protocol, network and link layers. It supports coherency across processor clusters and memory with topologies like ring, mesh and crossbar. Key nodes include request nodes, home nodes and subordinate nodes. The system address map routes transactions between nodes using unique node IDs. APB protocol v1.0



APB protocol v1.0Azad Mishra
Ěý
The document describes conventions and signals used in the AMBA 3 APB protocol specification version 1.0. It summarizes write and read transfer procedures, including optional wait states using the PREADY signal. Error responses are also described. The operating states of the APB include IDLE, SETUP, and ACCESS states. PREADY controls exiting the ACCESS state.I2c protocol - Inter–Integrated Circuit Communication Protocol



I2c protocol - Inter–Integrated Circuit Communication ProtocolAnkur Soni
Ěý
This document provides an overview of the I2C communication protocol. It describes how I2C uses only two wires (SDA and SCL) to allow data transmission between an I2C master and multiple I2C slave devices. The document explains the I2C message structure, including the start condition, address frame, read/write bit, data frames, ACK/NACK bits, and stop condition. It also discusses the advantages of I2C, such as supporting multiple masters/slaves and error checking, and disadvantages like slower speeds compared to SPI. Real-life uses of I2C include connections to OLED displays, sensors, and other peripherals.SPI Protocol in LPC2148



SPI Protocol in LPC2148Dnyanesh P. Joshi
Ěý
The document discusses the SPI protocol used in the LPC2148 microcontroller. It describes the SPI communication modes of master and slave. It explains the various SPI registers used for configuration - SPCCR for clock settings, SPCR for control settings like CPHA and CPOL, SPDR for data transfer, and SPSR for status. It provides steps for initialization and data transfer in both master and slave modes. The document also discusses factors like clock frequency, data length, and interrupt handling related to SPI communication using LPC2148.Session 8,9 PCI Express



Session 8,9 PCI ExpressSubhash Iyer
Ěý
The document provides an overview of the PCI Express system architecture. It discusses the architectural perspective of PCI Express including how it maintains backwards compatibility with PCI/PCI-X while improving performance through serial point-to-point connectivity and packet-based transactions. It also covers the PCI Express transaction model and types, including memory, I/O, configuration and message transactions, as well as posted and non-posted transaction types.Pcie basic



Pcie basicSaifuddin Kaijar
Ěý
PCIe is a standard expansion card interface introduced in 2004 to replace PCI and PCI-X. It uses serial instead of parallel communication and is scalable, allowing for higher maximum system bandwidth. The presentation discusses the history of expansion card standards leading to PCIe, including ISA, EISA, VESA, PCI, and PCI-X. It also covers key aspects of PCIe such as the root complex, endpoints, switches, lanes, bus:device.function notation, enumeration, and address spaces such as configuration space.Apb



ApbAzad Mishra
Ěý
The document describes the AMBA 3 APB protocol. It has an unpipelined design to reduce complexity and power consumption. Transfers take at least two cycles with the first being a setup phase and second an access phase controlled by the PENABLE signal. Slaves can extend transfers using the PREADY signal. Errors are indicated by PSLVERR. The protocol defines read and write transfers with or without wait states.axi protocol



axi protocolAzad Mishra
Ěý
The AXI protocol specification describes an advanced bus architecture with burst-based transactions using separate address/control and data phases over independent channels. It supports features like out-of-order transaction completion, exclusive access for atomic operations, cache coherency, and a low power interface. The AXI protocol is commonly used in System-on-Chip designs for high performance embedded processors and peripherals.PCI express



PCI expresssarangaprabod
Ěý
PCI Express is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard that was created to replace older standards like PCI, PCI-X, and AGP. It provides dedicated bandwidth to devices through the use of lanes and is commonly used as the interface for graphics cards, hard drives, and other peripherals. PCIe has gone through several generations that have increased its maximum bandwidth. It uses a layered protocol architecture and is designed for compatibility while providing scalable bandwidth and other advantages over older standards.SPI Protocol



SPI ProtocolAnurag Tomar
Ěý
The document describes the Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) protocol which allows for full duplex synchronous serial communication between a master and slave device using 4 pins - MOSI, MISO, SCK, and an optional SS pin. It details the SPI registers for control, status, and data and provides examples of SPI communication with peripherals like digital pots and shift registers. Common issues like conflicts with programming interfaces and ensuring proper chip select signaling are also covered.Similar to I2C (20)
communication interfaces-Embedded real time systems



communication interfaces-Embedded real time systemsRaghunath reddy
Ěý
Internal communication interfaces
1.I2C
2.SPI
3.UART
4.I-Wire
External communication interfaces
1.RS232 /RS 422 AND RS485
2.USB (UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS)
3.INFRARED
4.Bluetooth
5.Wi-Fi
6.IEEE 1394 Fire wire
7. Ethernet
I2C And SPI Part-23



I2C And SPI Part-23Techvilla
Ěý
I²C (Inter-Integrated Circuit), pronounced I-squared-C, is a multi-master, multi-slave, single-ended, serial computer bus invented by Philips Semiconductor (now NXP Semiconductors). It is typically used for attaching lower-speed peripheral ICs to processors and microcontrollers. Alternatively I²C is spelled I2C (pronounced I-two-C) or IIC (pronounced I-I-C).
Since October 10, 2006, no licensing fees are required to implement the I²C protocol. However, fees are still required to obtain I²C slave addresses allocated by NXP.[1]
Several competitors, such as Siemens AG (later Infineon Technologies AG, now Intel mobile communications), NEC, Texas Instruments, STMicroelectronics (formerly SGS-Thomson), Motorola (later Freescale), and Intersil, have introduced compatible I²C products to the market since the mid-1990s.
SMBus, defined by Intel in 1995, is a subset of I²C that defines the protocols more strictly. One purpose of SMBus is to promote robustness and interoperability. Accordingly, modern I²C systems incorporate policies and rules from SMBus, sometimes supporting both I²C and SMBus, requiring only minimal reconfiguration.
The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) bus is a synchronous serial communication interface specification used for short distance communication, primarily in embedded systems. The interface was developed by Motorola and has become a de facto standard. Typical applications include sensors, Secure Digital cards, and liquid crystal displays.
SPI devices communicate in full duplex mode using a master-slave architecture with a single master. The master device originates the frame for reading and writing. Multiple slave devices are supported through selection with individual slave select (SS) lines.
Sometimes SPI is called a four-wire serial bus, contrasting with three-, two-, and one-wire serial buses. The SPI may be accurately described as a synchronous serial interface,[1] but it is different from the Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI) protocol, which is also a four-wire synchronous serial communication protocol, but employs differential signaling and provides only a single simplex communication channel.Peripherals and interfacing



Peripherals and interfacingRAMPRAKASHT1
Ěý
This document provides an overview of peripherals and interfacing using various communication protocols. It discusses the I2C bus protocol for accessing peripheral chips. It covers the operation of the I2C bus including start/stop bits and acknowledgement. It then summarizes the use of various peripherals that interface using I2C including EEPROM, analog to digital converters, LCDs, and sensors. It also covers serial communication protocols like UART and interfacing for devices like keyboards.Part-2: Mastering microcontroller with embedded driver development



Part-2: Mastering microcontroller with embedded driver developmentFastBit Embedded Brain Academy
Ěý
Join this video course on udemy . Click here :
https://www.udemy.com/course/mastering-microcontroller-with-peripheral-driver-development/?couponCode=SLIDESHARE
In this course, the code is developed such a way that, It can be ported to any MCU you have at your hand.
If you need any help in porting these codes to different MCUs you can always reach out to me!
The course is strictly not bound to any 1 type of MCU. So, if you already have any Development board which runs with ARM-Cortex M3/M4 processor,
then I recommend you to continue using it.
But if you don’t have any Development board, then check out the below Development boards.
An Implementation of I2C Slave Interface using Verilog HDL



An Implementation of I2C Slave Interface using Verilog HDLIJMER
Ěý
This document describes the implementation of an I2C slave interface using Verilog HDL. It introduces the I2C protocol which uses only two bidirectional lines (SDA and SCL) for communication. The document discusses the I2C protocol specifications including start/stop conditions, addressing, read/write operations, and acknowledgements. It then provides details on designing an I2C slave module in Verilog that responds to commands from an I2C master and allows synchronization through clock stretching. The module is simulated in ModelSim and synthesized in Xilinx. Simulation waveforms demonstrate successful read and write operations to the slave device.COM_BASIC.pptx



COM_BASIC.pptxBhagvatShukla
Ěý
This document provides information on various communication protocols. It discusses I2C communication protocol in detail, including how I2C works, multiple slave configuration, steps of I2C transmission, and advantages and disadvantages of I2C. It also briefly covers USB, UART/USART, RS-232, RS-422, and RS-485 protocols.I2C PRESENTATION.PPT



I2C PRESENTATION.PPTvenkatesh405785
Ěý
I2C is a serial communication protocol used to connect integrated circuits. It was developed by Philips in the 1980s and uses just two bidirectional lines - serial data line (SDA) and serial clock line (SCL). I2C has endured because it provides reliable communication using software-controlled collision detection at transfer rates up to 3.4 Mbps. Data is transferred between a master device that initiates the transaction and slave devices with unique addresses in sequences of 8-bit bytes with acknowledgement.I2C



I2CLITS IT Ltd,LASRC.SPACE,SAWDAGOR BD,FREELANCE BD,iREV,BD LAW ACADEMY,SMART AVI,HEA,HFSAC LTD.
Ěý
The document summarizes how the I2C bus works. It describes that the I2C bus uses only 2 wires (SDA and SCL) to allow a microcontroller to communicate with multiple slave devices like sensors, EEPROMs, and ADCs. It provides details on the open-drain configuration that allows bidirectional communication, START and STOP conditions that begin and end transmissions, ACK/NACK responses from slaves, and how the master can write to or read from registers in slave devices to transfer data.project 3 full report



project 3 full reportShubham Shivhare
Ěý
This document describes a project on using the I2C protocol for serial communication between an AT89C251 microcontroller and an AT24C04 EEPROM chip. It includes an introduction to the project, descriptions of the microcontroller and I2C protocol, and code for programming the microcontroller to save and read data from the EEPROM using I2C addresses and communication procedures.An hemmanur



An hemmanurSangeetha Marikkannan
Ěý
The document discusses Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C), a serial communication protocol used to connect integrated circuits. It describes I2C's history, structure, communication process, addressing scheme, and provides a sample code for reading analog to digital converter values from a chip via I2C.Assembler4



Assembler4Omar Sanchez
Ěý
Firmware is a program that provides low-level control for a device's specific hardware. It performs control, monitoring and data manipulation functions. Firmware is stored in non-volatile memory like EPROM or flash memory. Common reasons for updating firmware include fixing bugs or adding new features. Firmware may be the only program that runs on an embedded system and provides all of its functions.ijseas20150367



ijseas20150367Chinmay Modi
Ěý
1) The document describes the design and implementation of an IP (Inter-Integrated Circuit) 2PC protocol. 2) IP2PC protocol allows multiple devices to communicate over a serial data bus without data or address loss and enables faster devices to communicate with slower ones. 3) The design of an IP2PC protocol controller in Verilog is presented along with its simulation on an FPGA platform to allow communication between multiple masters and slaves.Implementation of I2C Master Bus Protocol on FPGA



Implementation of I2C Master Bus Protocol on FPGAIJERA Editor
Ěý
The focus of this paper is on I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) protocol interface between Master Bus protocol and
slave. Here we are interfacing between micro-controller and DS1307. I2C bus protocol sends 8 bit data from
micro-controller to DS1307. This module was designed in VHDL and simulated and synthesized using Xilinx
ISE Design Suite 14.2. I2C and optimized for area and power. This concept is widely applicable from any high
speed device or low speed device to any low speed device or high speed device. This module acts as a slave for
the DS1307 at the same time acts like a master for the micro-controller device which can be considered as a
slave. . It can be used to interface low speed peripherals like motherboard, embedded system, mobile phones,
set top boxes, DVD, PDA’s or other electronic devices.I2C protocol and DS1307 RTC interfacing



I2C protocol and DS1307 RTC interfacingBhargav Kakadiya
Ěý
The summary provides an overview of the key points about interfacing with the DS1307 real-time clock (RTC) chip using the I2C protocol:
1) The document discusses the I2C protocol signals and components used to interface with the DS1307 RTC, which stores time and date data.
2) It describes initializing the I2C bus, addressing the DS1307 slave device, and transmitting/receiving data to read from and write to the RTC registers.
3) The DS1307 has registers to store seconds, minutes, hours, date, and other time/date fields in BCD format and can output a square wave time signal on its SQW pin at different frequencies.Raspberry Pi - Lecture 3 Embedded Communication Protocols



Raspberry Pi - Lecture 3 Embedded Communication ProtocolsMohamed Abdallah
Ěý
The document discusses various embedded communication protocols. It begins by defining communication in embedded systems and examples of common protocols including UART, I2C, SPI, CAN and LIN. It then explains key concepts such as bit rate, baud rate, serial vs parallel communication and synchronous vs asynchronous communication. The document proceeds to provide detailed explanations of the UART, I2C and SPI protocols, including their frame formats, data validity rules, arbitration mechanisms and usage examples. It concludes by noting some key characteristics of each protocol.I2c buses



I2c busesNaveen Dubey
Ěý
This document provides an overview of the Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) bus. It describes the key features and evolution of I2C buses, including their simplicity, flexibility, addressing schemes, and ability to support multiple masters. The document also details the I2C bus architecture, protocol for data communication including start/stop conditions and bit transfers, and how the Microchip Master Synchronous Serial Port module is used to implement I2C functionality.Microcontroller part 9_v1



Microcontroller part 9_v1Keroles karam khalil
Ěý
This document provides an in-depth overview of the I2C communication protocol. It begins by defining I2C, its characteristics such as being a multi-master multi-slave synchronous serial communication standard. It then covers I2C electrical characteristics, start/stop conditions, addressing, data transfer process including acknowledgements, and arbitration. The document uses diagrams and examples to illustrate I2C communication including reading and writing data between a master and slave device.I2C
- 1. Mr.Tejas Dave Chovatiya Ravi Jitendra Edle Sachin Nigam Prepared by:- Guide by:- “ I2C Bus Protocol Implementation” THAKUR INSTITUTE OF CAREER ADVANCEMENT
- 2. Shorthand for an “Inter-integrated circuit” bus Developed by Philips Semiconductor for TV sets in the 1980’s I 2 C devices include EEPROMs, thermal sensors, and real-time clocks Used as a control interface to signal processing devices that have separate data interfaces, e.g. RF tuners, video decoders and encoders, and audio processors. I 2 C bus has three speeds: Slow (under 100 Kbps) Fast (400 Kbps) High-speed (3.4 Mbps) – I 2 C v.2.0 Limited to about 10 feet for moderate speeds What is I2C?
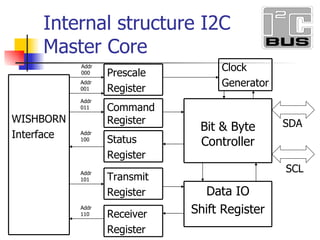
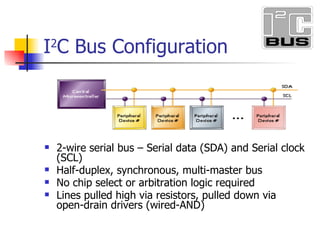
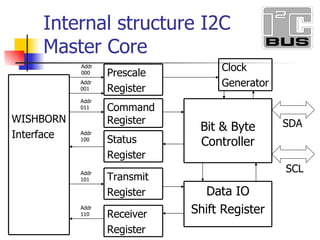
- 3. Addr 000 Addr 001 Addr 011 Addr 100 Addr 101 Addr 110 SDA SCL Internal structure I2C Master Core WISHBORN Interface Prescale Register Command Register Transmit Register Status Register Receiver Register Data IO Shift Register Bit & Byte Controller Clock Generator
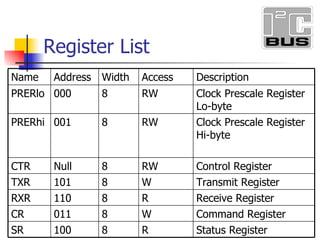
- 5. Register List Status Register R 8 100 SR Command Register W 8 011 CR Receive Register R 8 110 RXR Transmit Register W 8 101 TXR Control Register RW 8 Null CTR Clock Prescale Register Hi-byte RW 8 001 PRERhi Clock Prescale Register Lo-byte RW 8 000 PRERlo Description Access Width Address Name
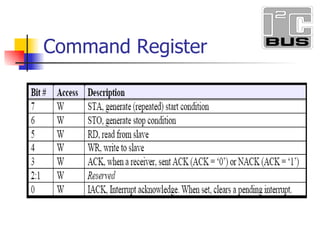
- 6. Control register
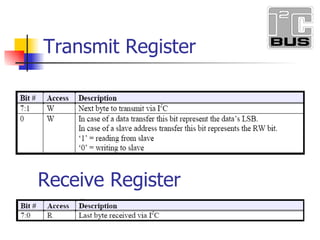
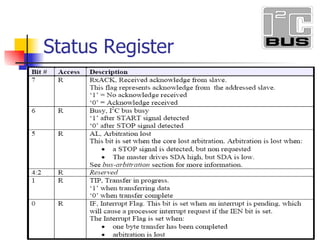
- 7. Transmit Register Receive Register
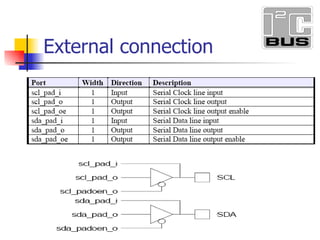
- 10. I 2 C Bus Configuration 2-wire serial bus – Serial data (SDA) and Serial clock (SCL) Half-duplex, synchronous, multi-master bus No chip select or arbitration logic required Lines pulled high via resistors, pulled down via open-drain drivers (wired-AND)
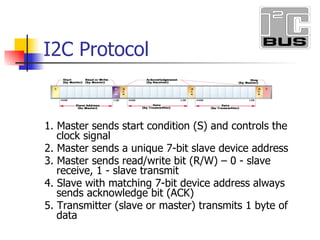
- 11. I2C Protocol 1. Master sends start condition (S) and controls the clock signal 2. Master sends a unique 7-bit slave device address 3. Master sends read/write bit (R/W) – 0 - slave receive, 1 - slave transmit 4. Slave with matching 7-bit device address always sends acknowledge bit (ACK) 5. Transmitter (slave or master) transmits 1 byte of data
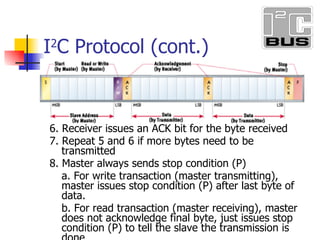
- 12. I 2 C Protocol (cont.) 6. Receiver issues an ACK bit for the byte received 7. Repeat 5 and 6 if more bytes need to be transmitted 8. Master always sends stop condition (P) a. For write transaction (master transmitting), master issues stop condition (P) after last byte of data. b. For read transaction (master receiving), master does not acknowledge final byte, just issues stop condition (P) to tell the slave the transmission is done
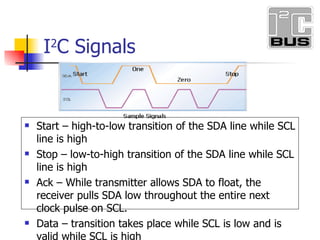
- 13. Start – high-to-low transition of the SDA line while SCL line is high Stop – low-to-high transition of the SDA line while SCL line is high Ack – While transmitter allows SDA to float, the receiver pulls SDA low throughout the entire next clock pulse on SCL. Data – transition takes place while SCL is low and is valid while SCL is high I 2 C Signals
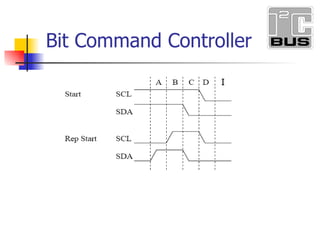
- 14. Bit Command Controller I
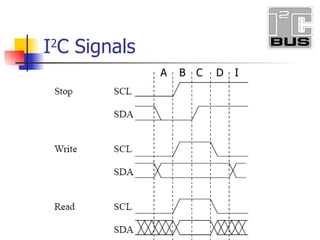
- 15. A B I 2 C Signals C D I
- 16. Write 1 byte of data to a slave Generate start command Write slave address+write bit Receive acknowledge from slave Write data Receive acknowledge from slave Generate stop command
- 17. Read 1 byte of data to a slave Generate start command Write slave address+write bit Receive acknowledge from slave Write data Receive acknowledge from slave Generate stop command
- 18. Receive acknowledge from slave Generate repeated start signal Write slave address + read bit Receive acknowledge from slave Read byte from slave Write no acknowledge to slave,indicationg end of transfer Generate stop signal
- 19. I 2 C Features “ Clock stretching” – when the receiver needs more time to process a bit, it can pull SCL low to keep it from going high a bit longer. This technique is called clock stretching . On SDL low, the transmitter can send its next data value, but this value will not be interpreted as a valid data symbol by the receiver until after the slave is ready to release SCL to go high. “ General call” broadcast – addresses every device on the bus 10-bit extended addressing for new designs. 7-bit addresses all exhausted
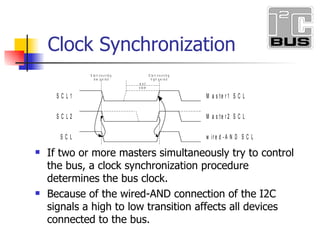
- 20. Clock Synchronization If two or more masters simultaneously try to control the bus, a clock synchronization procedure determines the bus clock. Because of the wired-AND connection of the I2C signals a high to low transition affects all devices connected to the bus.
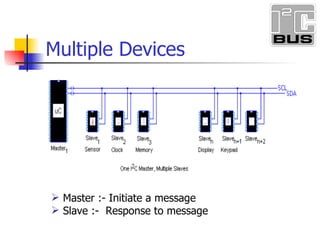
- 21. Master :- Initiate a message Slave :- Response to message Multiple Devices
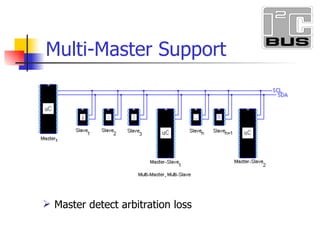
- 22. Master detect arbitration loss Multi-Master Support
- 23. Reduce IC Pins, Cost and Area Reduce PCB Size And Cost Advantages Of I2C
- 24. Addr 000 Addr 001 Addr 011 Addr 100 Addr 101 Addr 110 SDA SCL Internal structure I2C Master Core WISHBORN Interface Prescale Register Command Register Transmit Register Status Register Receiver Register Data IO Shift Register Bit & Byte Controller Clock Generator
- 25. References I 2 C: http://www-us2.semiconductors.philips.com/acrobat/various/ I2C_BUS_SPECIFICATION_1995.pdf http://www.esacademy.com/faq/i2c/index.htm http://www.embedded.com/story/OEG20020528S0057
- 26. Thank you


