I2c drivers
- 1. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved Inter Integrated Circuit (I2C) Drivers
- 2. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved What to Expect ˇń I2C Overview ˇń I2C Conditions & Transactions ˇń I2C Subsystem in Linux ¨C I2C Adapter & I2C Client ˇń I2C Client Driver ˇń I2C Device Registration (Non DT and DT)
- 3. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved I2C Overview ˇń Originally developed by Phillips ˇń Suitable for small slow devices ˇń I2C is a 2-wire protocol ¨C One Serial Clock Line ¨C One Data Line ˇń Popular in Desktops & Embedded Systems ˇń Used for accessing ¨C EEPROMs ¨C RTCs ¨C ADCs ¨C ....
- 4. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved I2C Conditions ˇń Start Condition ¨C Master signals this condition to initiate the transfer on the bus ˇń Stop Condition ¨C Master signals this condition to stop the transfer ˇń ACK Condition ¨C Master or Slave signals this to acknowledge the succesful receipt of byte
- 5. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved I2C Transactions ˇń Master begins the communication by issuing the start condition. ˇń Sends a 7/10 bit slave address followed by read/write bit ˇń The addressed slave ACKs the transfer ˇń Transmitter transmits a byte of data and receiver issues ACK on successful receipt ˇń Master issues a STOP condition to conclude the transaction
- 6. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved I2C Transactions... Start Data 1 SLA + W Slave ACK Data 2 Data N Slave ACK Slave ACK Stop Master Write Slave ACK Start Addr. 1 SLA + W Slave ACK Repeat Start Data 1 Slave ACK SLA + R Stop Master ACK Data N Master NACK Master Read
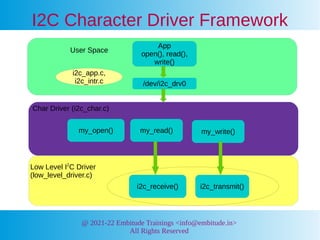
- 7. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved I2C Character Driver Framework User Space i2c_app.c, i2c_intr.c Char Driver (i2c_char.c) Low Level I2 C Driver (low_level_driver.c) App open(), read(), write() /dev/i2c_drv0 my_open() my_read() my_write() i2c_receive() i2c_transmit()
- 8. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved AM335X I2C Initialization ˇń Get the virtual address for the I2C-0 registers base address ˇń Set up the I2C speed ¨C Set the pre-scalar register to generate the I2C module internal clock from the functional clock ¨C Set the scl low time & scl high time registers ˇń Enable the events ¨C Update the ˇ®Interrupt Enable SetˇŻ register to enable various events such as XRDY, RRDY and so on
- 9. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved AM335x I2C Registers ˇń I2C_SA_REGISTER (Slave Address Register) ˇń I2C_CON_REGISTER (Configuration Register) ¨C Bits for enabling / disabling the I2C module ¨C Selecting the Fast / Standard mode of operation ¨C Selecting the Master / Slave config ¨C Sending the Start / Stop conditions on the bus ˇń I2C_DATA (RX/TX Data Register) ˇń I2C_BUF (FIFO Thresholds, DMA configuration) ˇń I2C_CNT (Bytes in I2C data payload) ˇń I2C_IRQ_STATUS_REG
- 10. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved AM335X I2C APIs ˇń #include ˇ°i2c_char.hˇ± ˇń u16 omap_i2c_read_reg(struct omap_i2c_dev *i2c_dev, int reg) ˇń void omap_i2c_write_reg(struct omap_i2c_dev *i2c_dev, int reg, u16 val) ˇń u16 wait_for_event(struct omap_i2c_dev *dev) ˇń void omap_i2c_ack_stat(struct omap_i2c_dev, u16 stat) ˇń val = omap_i2c_read_reg(dev, OMAP_I2C_BUF_REG) ˇń val |= OMAP_I2C_BUF_TXFIF ˇń omap_i2c_write_reg(dev, OMAP_I2C_BUF_REG, val)
- 11. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved Accessing EEPROM 0XAA 0x0060 EEPROM I2C Slave Address 0X50
- 12. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved Writing to EEPROM ˇń For writing at EEPROM offset 0x0060 ˇń Send the start condition ˇń Send the slave address of EEPROM (0X50), followed by direction (Read/Write) ˇń Send the EEPROM offset higher byte, followed by lower byte ˇń Send the actual data to be written ˇń Send the Stop condition ˇń START->0x50->0x00(offset high)->0x60 (offset low)- >0X99(Data)->STOP
- 13. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved Reading From EEPROM ˇń Write the EEPROM offset say 0x0060 (read offset) ¨C START->0x50->0x00(offset high)->0x60 (offset low)->STOP ˇń Read the EEPROM data ¨C Send the start condition ¨C Send the slave address of EEPROM (0X50), followed by direction (Read) ¨C Read the data ¨C Send the stop condition ¨C START->0x50->Data (RX)->Data (RX)->STOP
- 14. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved Need for Linux Device Model ˇń Maximize the code re-usability across the platforms ¨C Same device drivers on different platforms ˇń To achieve this ¨C Decouple device drivers from controller drivers ¨C Decouple hardware description from the drivers ˇń In addition to above ¨C Information about how the system is put together ˇń Effective power management ¨C Communication with user space ¨C Hotpluggable devices
- 15. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved Device Drivers in Linux Application System Call Interface Framework Driver Bus Infrastructure Hardware
- 16. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved Device model data structures ˇń struct bus_type ¨C Represents the bus such as USB, PCI, I2C etc ˇń struct device_driver ¨C Represents the driver capable of handling certain devices ˇń struct device ¨C Represents the device connected to the bus
- 17. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved Linux I2C Subsystem ˇń I2C subsystem provides ¨C API to implement I2C controller driver ¨C API to implement I2C device driver in kernel space ¨C An abstraction to implement the client drivers independent of adapter drivers
- 18. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved Linux I2C Subsystem ... User Space Kernel Space I2C Device (i2c_client) I2C Host Controller (i2c_adapter) Hardware Space /sys, /dev User Applications User Mode I2C Device Driver I2C Core i2c-dev Vertical: Character I2C Client Driver I2C Bus I2C Adapter (platform_driver) / Algo Driver (i2c_algorithm)
- 19. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved I2C Subsystem Details ˇń i2c-adapter / i2c-algo ¨C Controller-specific I2C host controller / adapter ¨C Also called as the I2C bus drivers ˇń i2c-core ¨C Hides the adapter details from the layers above ¨C By providing the generic I2C APIs ˇń i2c-dev ¨C Provides device access in user space through /sys ¨C Enables implementation of User Mode Drivers ˇń i2c-client ¨C Driver specific to an I2C device ¨C Implemented using i2c-core APIs
- 20. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved I2C Client Driver ˇń Typically a character driver vertical - /dev or /sys exposed ˇń But actually depends on the device category ˇń Registers with I2C Core (in the init function) ˇń Unregisters from I2C Core (in the cleanup function) ˇń And uses the generic function from I2C Core for data transfers ¨C int i2c_transfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)
- 21. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved I2C Client Driver init & cleanup ˇń Registering to the I2C Core using ¨C int i2c_add_driver(struct i2c_driver *) ¨C struct i2c_driver contains ˇń probe function ¨C called on device detection ˇń remove function ¨C called on device shutdown ˇń id_table ¨C Table of device identifiers ˇń Unregistering from the I2C Core using ¨C void i2c_del_driver(struct i2c_driver *) ˇń Common bare-bone of init & cleanup ¨C Just use module_i2c_driver(struct i2c_driver)
- 22. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved I2C Client Driver Registration ˇń struct i2c_driver dummy_driver = { driver = { name = ˇ°dummy_clientˇ±, owner = THIS_MODULE, }, .probe = dummy_probe, .remove = dummy_remove, .id_table = dummy_ids, } ˇń static const struct i2c_device_id dummy_ids = { { ˇ°dummy_deviceˇ±, 0}, {} } ˇń i2c_add_driver(dummy_driver)
- 23. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved I2C Adapter Driver (Un)Registeration ˇń Registering to the I2C Core using ¨C int i2c_add_numbered_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *); ¨C Registered in the platform driver probe ˇń Unregistering from the I2C Core using ¨C void i2c_del_adapter(struct i2c_driver *); ¨C In platform driver remove functions
- 24. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved I2C Client Driver Examples ˇń Path: <kernel_source>/drivers/ ¨C I2C EEPROM: AT24 ˇń misc/eeprom/at24.c ¨C I2C RTC: DS1307 ˇń rtc/rtc-ds1307.c
- 25. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved Registering the I2C Client (Non DT) ˇń On non-DT platforms, the struct i2c_board_info describes how device is connected to a board ˇń Defined with I2C_BOARD_INFO helper macro ¨C Takes as the arguments, the device name and the slave address of the device on the bus ˇń An array of such structures is registered on per bus basis using the i2c_register_board_info during the platform initialization
- 26. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved Registering the I2C Client (Non DT).. ˇń static struct i2c_board_info my_i2c_devices [] = { { I2C_BOARD_INFO (ˇ°my_deviceˇ±, 0 x1D ), . irq = 70, .platform_data = &my_data }, } ˇń i2c_register_board_info(0, my_i2c_devices, ARRAY_SIZE (my_i2c_devices))
- 27. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved Registering an I2C Client (DT) ˇń In the device tree, the I2C devices on the bus are described as children of the I2C controller node ˇń reg property gives the I2C slave address on the bus
- 28. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved Registering an I2C Client (DT) ... ˇń i2c@49607899 { compatible = "dummy_adap"; clock-frequency = <0x186a0>; #address-cells = <0x1>; #size-cells = <0x0>; my_dummy@0 { compatible = "dummy_device"; reg = <0x40>; }; }; ˇń Registered internally by i2c_core based on info from DTB ˇń i2c_new_device(struct i2c_adapter *, struct i2c_board_info *)
- 29. @ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in> All Rights Reserved What all did we learn? ˇń I2C Overview ˇń I2C Conditions & Transactions ˇń I2C Subsystem in Linux ¨C I2C Adapter & I2C Client ˇń I2C Client Driver ˇń I2C Device Registration (Non DT and DT)
























![@ 2021-22 Embitude Trainings <info@embitude.in>
All Rights Reserved
Registering the I2C Client (Non DT)..
ˇń static struct i2c_board_info my_i2c_devices [] = {
{
I2C_BOARD_INFO (ˇ°my_deviceˇ±, 0 x1D ),
. irq = 70,
.platform_data = &my_data
},
}
ˇń i2c_register_board_info(0, my_i2c_devices,
ARRAY_SIZE (my_i2c_devices))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/i2cdrivers-210702053321/85/I2c-drivers-26-320.jpg)


