IA.pptx a presentation about impact assessment
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes1 view
fasdsa
1 of 23
Download to read offline





















Recommended
Environmental Impact Assessement13164243.ppt



Environmental Impact Assessement13164243.pptabdi beder
Ěý
Environmental Impact Assessement13164243.pptENVS502_UnitIII.pptx environmental planning and management



ENVS502_UnitIII.pptx environmental planning and managementparisakarim560
Ěý
Increasing demographic pressures
Technological advancement and development (modernisation)
Increasing pollution and resource depletion
Environment/natural resources viewed as common-pool resources.
Intensification of agriculture (to meet human population requirements) and industry
Coastal Road Project



Coastal Road ProjectEkonnect Knowledge Foundation
Ěý
Developing Projects in an Environmental and Social Management Framework - A presentation by Dr. Prasad ModakEnvironmental Impact Assessment



Environmental Impact AssessmentBahadur Prasad
Ěý
This document presents an environmental impact assessment report prepared by six students for a project referred to as MEL422. It summarizes the key aspects and steps of an environmental impact assessment process, including identifying and predicting environmental effects, considering social and health impacts, and preventing, mitigating and offsetting significant adverse effects. The report then outlines the various stages of an environmental impact assessment, from screening and scoping to impact analysis, mitigation, reporting and environmental management planning. It provides examples and checklists to guide the environmental impact assessment process.Environmental impact assessment (eia) By Mr Allah Dad Khan Visiting Professor...



Environmental impact assessment (eia) By Mr Allah Dad Khan Visiting Professor...Mr.Allah Dad Khan
Ěý
Environmental impact assessment (eia) By Mr Allah Dad Khan Visiting Professor The University Of Agriculture PeshawarEnvironmental impact assessment



Environmental impact assessmentNanyang Technological University, Singapore
Ěý
The document discusses environmental impact assessments (EIAs). It defines EIAs as processes that identify, predict, and evaluate the physical, chemical, biological, social, and other impacts of proposed projects prior to major decisions. The document outlines the key stages of EIAs, including screening, scoping, preliminary assessments, mitigation, environmental management plans, public participation, and impact assessment methods. It emphasizes that EIAs are tools used to reduce negative environmental impacts and promote sustainable development.EIA 02_EIA Process-2017 for Civil Engineering.pptx



EIA 02_EIA Process-2017 for Civil Engineering.pptxMdAbdulJabbar10
Ěý
Environmental Impact Assessment Related FileNALINI ( topic for M. Sc Ag. Agroforestry assigment EIA and ERA.pptx)



NALINI ( topic for M. Sc Ag. Agroforestry assigment EIA and ERA.pptx)HNaliniNirala
Ěý
The document discusses environmental impact assessment and risk assessment. It provides:
1) An overview of the environmental impact assessment process, which involves screening projects, scoping potential impacts, collecting baseline data, predicting and mitigating impacts, public hearings, decision making, and monitoring.
2) Some shortcomings of the current environmental impact assessment process in India, such as certain projects being exempted, lack of expertise in assessment teams, and issues with public hearings and quality of assessment reports.
3) An overview of environmental risk assessment, which involves identifying hazards, evaluating risks, implementing precautions, and regularly reviewing assessments.Environmental Impact Assessment and Environmental Audit- Unit III



Environmental Impact Assessment and Environmental Audit- Unit IIIGAURAV. H .TANDON
Ěý
This document provides an overview of environmental impact assessments and environmental audits. It defines environmental impact assessment as the systematic identification and evaluation of potential impacts of proposed projects on the natural environment. The key steps of an EIA include organizing an interdisciplinary team, performing an assessment of the site and potential impacts, writing an environmental impact statement, and reviewing the EIS. Environmental audits evaluate an organization's environmental performance and position and identify ways to improve environmental management systems. The document outlines the basic components and steps in conducting environmental audits.20170912_ESIA Training for environmental engineering



20170912_ESIA Training for environmental engineeringPriyankaKotoky1
Ěý
It is also for protection of environmentEnvironmental impact assessment (EIA)



Environmental impact assessment (EIA)School of planning and architecture
Ěý
The document provides an overview of environmental impact assessment (EIA). It defines EIA as assessing the effects of proposed projects on the environment. EIA identifies alternatives and aims to balance economic and environmental costs and benefits. It integrates environmental concerns early in project planning. EIA started as a mandatory regulatory process in the US in 1969 and is now required in over 100 countries. The key stages of EIA are screening, scoping, baseline data collection, impact analysis, mitigation planning, public hearings, decision making, and monitoring. EIA aims to be fair, provide credible information for decisions, and ensure sustainability.EIA Methods



EIA MethodsSOUBAM INDRAKUMAR SINGH
Ěý
This document discusses various methodologies used in environmental impact assessments (EIAs). It outlines key characteristics an EIA methodology should have, such as being appropriate to the task and free from bias. Common impact identification methods are described, including checklists, matrices, networks and overlays. The stages of impact prediction, evaluation and identification are explained. The document also discusses techniques for impact prediction, evaluation of significance, and designing environmental protection measures. Overall it provides an overview of conceptual approaches and analytical tools used in EIAs.EIA



EIAKirui Ben
Ěý
This document discusses various methodologies used in environmental impact assessments (EIAs). It outlines key characteristics an EIA methodology should have, such as being appropriate to the task and free from bias. Common impact identification methods are described, including checklists, matrices, networks and overlays. The stages of impact prediction, evaluation and identification are explained. The document also discusses techniques for impact prediction, evaluation of significance, and designing environmental protection measures. Overall it provides an overview of conceptual approaches and analytical tools used in EIAs.Project Management Training.pptx



Project Management Training.pptxMohameAbullahi
Ěý
The document provides an overview of project management training that covers the project management life cycle. It discusses key areas such as:
- Defining a project and project management.
- Understanding the project management process which includes initiating, planning, executing, monitoring and evaluation, and closing.
- Identifying the knowledge areas involved in project management like integration, scope, time, cost, quality, and risk management.
- Explaining the importance of developing a project charter and stakeholder analysis during the initiating process.
- Detailing the components of a project charter and what a stakeholder analysis involves.
- Outlining the planning, execution, monitoring and evaluation, and closing processes within the project lifeEcw 579 week 13



Ecw 579 week 13Adilah Anuar
Ěý
The document discusses environmental impact assessments (EIA) in Malaysia. It describes the purpose and legal requirements of EIAs, which were introduced in 1987 to identify and mitigate environmental impacts of development projects. The key aspects of the EIA process in Malaysia are:
1) Projects are screened to determine if an EIA is required based on their potential environmental impacts.
2) The scoping process identifies which issues and impacts the EIA will address.
3) EIAs involve assessing alternatives, environmental baselines, impacts, and mitigation measures.
4) Completed EIA reports are submitted for review and must include opportunities for public consultation.Re sakss presentation on project management mburu 2



Re sakss presentation on project management mburu 2African Regional Strategic Analysis and Knowledge Support System (ReSAKSS)
Ěý
The document discusses project management and impact evaluation. It defines a project, outlines the project cycle which includes identification, preparation, appraisal, implementation, monitoring and evaluation. It discusses why projects fail and types of projects. Logical framework analysis and cost-benefit analysis are presented as tools for project planning, implementation and evaluation. Impact evaluation aims to determine if a project achieved its intended effects by estimating what would have occurred without the project.Clark.pdf



Clark.pdfGajendran Chelliah
Ěý
This document summarizes a presentation on project-level environmental impact assessments for deep-sea mining. It defines EIAs and their objectives, outlines the EIA process as part of a larger regulatory context, and discusses key issues to consider in EIAs for deep-sea mining including: the structure and content of EIA reports, the role of risk assessment, challenges around baseline data given the data-poor nature of deep-sea environments, and lessons learned from New Zealand's experience conducting EIAs for offshore mining projects.Asu history and theory lecture 3a-programming 14-10-2017



Asu history and theory lecture 3a-programming 14-10-2017Galala University
Ěý
This document provides an overview of a lecture on architectural programming. It discusses programming as the first step of the project lifecycle where the goals and requirements are defined through research. This establishes the criteria to guide the design solution. The lecture notes then outline the programming framework, including preparing for programming through analyzing and synthesizing information at different scales. It also discusses common characteristics of programming formats such as defining goals and gathering/analyzing data. The goals of programming are to separate the definition of criteria from design and understand implications on costs.Asu history and theory lecture 3a-programming 14-10-2017



Asu history and theory lecture 3a-programming 14-10-2017Galala University
Ěý
This document provides an overview of a lecture on architectural programming. It discusses programming as the first step of the project lifecycle where the goals and requirements are defined through research. This establishes the criteria to guide the design solution. The lecture covers the programming framework including preparing for programming, analyzing and synthesizing information, and considering design factors like human, environmental, cultural and technical issues. Architectural programming is presented as the process of gathering, analyzing and documenting relevant information to define the problem to be solved by design.SEA.pptx



SEA.pptxQuasid
Ěý
The document discusses strategic environmental assessment (SEA) as a tool for assessing the environmental impacts of policies, plans, and programs. It provides examples of SEAs from India and other countries. The key points made in the document are:
1) SEA facilitates mainstreaming environmental and social considerations into key policy documents and helps assess cumulative effects of projects on sustainability.
2) SEA is a global tool that is being increasingly used and formalized in development practices to address landscape-level impacts.
3) SEA contributes to integrated policymaking, enhanced stakeholder participation, and consideration of issues like resource efficiency and disaster vulnerability in planning.Unit 3 point 1 Environmental Sustainability



Unit 3 point 1 Environmental Sustainabilityashishjaswal
Ěý
The document discusses various types of impact assessments used to evaluate proposed projects and policies. It defines environmental impact assessment (EIA) as identifying future environmental consequences of actions. The objectives of EIA are to identify, predict, and evaluate economic, environmental and social impacts, and provide information for decision making. It also discusses life cycle analysis (LCA) which evaluates sustainability impacts across a product's entire life cycle. Social impact assessment (SIA) is defined as researching and managing social changes from policies and projects. It seeks to identify who benefits and is negatively impacted. The document outlines the methodologies and processes for each type of assessment.Environmental Impact Assessment



Environmental Impact AssessmentPrithvi Ghag
Ěý
This document discusses environmental impact assessment (EIA). It defines EIA as a study that predicts how a proposed project may affect the environment. EIAs identify the best project option by comparing alternatives and weighing economic and environmental costs and benefits. The EIA process involves scoping a project to identify key issues, conducting an impact assessment, obtaining public input, and using the results to inform decision-making about projects that could significantly affect the environment.Architectural design 3 10-4-2011 notes



Architectural design 3 10-4-2011 notesGalala University
Ěý
The document provides notes from an architectural design studio class discussing a community center project. It covers key stages of the design process including understanding the program and site analysis, developing a concept, and applying sustainability strategies. The program is translated into a bubble diagram showing relationships between functions. Site analysis considers physical characteristics like climate and topography as well as surrounding context. Developing a concept brings the program and site together in a holistic idea. Sustainability will be assessed using the QSAS rating system.environmentalimpactassessmenteia-210826024951.pdf



environmentalimpactassessmenteia-210826024951.pdfssusereef268
Ěý
The document provides information on environmental impact assessments (EIAs) and environmental management plans (EMPs). It defines EIAs as processes that identify, predict, evaluate, and mitigate biophysical, social, and other effects of development proposals prior to major decisions. The objectives of EIAs are to consider environmental factors in decision-making, identify potential impacts, and promote sustainable development through impact minimization. Methods used in EIAs include life cycle analyses for products, specific assessment protocols for GMOs, and fuzzy logic for hard-to-quantify impacts. EMPs are action plans that indicate which mitigation measures from EIA reports will be implemented to manage environmental impacts from projects. They ensure impacts are monitored and responsibilityEnvironmental impact assessment (eia)



Environmental impact assessment (eia)SANDEEP PATRE
Ěý
This document discusses environmental impact assessments (EIAs) and management plans. It defines EIAs as processes that identify, predict, evaluate and mitigate biophysical, social and other effects of development proposals before major decisions. The objectives of EIAs are to consider environmental factors in decision-making, identify potential impacts, minimize adverse impacts, and promote sustainable development through public participation and environmental management plans. Common EIA methods discussed include product life cycle analysis, assessments of genetically modified organisms, and fuzzy logic to measure hard to quantify impacts. The document also outlines types of EIAs like strategic, regional and sectoral EIAs, and describes the typical steps involved in conducting an EIA.Genetics Basic concepts Presentation in colorful ilustrative style.pptx



Genetics Basic concepts Presentation in colorful ilustrative style.pptxTONGCUAISAIAHJEREMIA
Ěý
Pedigreee analysis sampleMore Related Content
Similar to IA.pptx a presentation about impact assessment (20)
NALINI ( topic for M. Sc Ag. Agroforestry assigment EIA and ERA.pptx)



NALINI ( topic for M. Sc Ag. Agroforestry assigment EIA and ERA.pptx)HNaliniNirala
Ěý
The document discusses environmental impact assessment and risk assessment. It provides:
1) An overview of the environmental impact assessment process, which involves screening projects, scoping potential impacts, collecting baseline data, predicting and mitigating impacts, public hearings, decision making, and monitoring.
2) Some shortcomings of the current environmental impact assessment process in India, such as certain projects being exempted, lack of expertise in assessment teams, and issues with public hearings and quality of assessment reports.
3) An overview of environmental risk assessment, which involves identifying hazards, evaluating risks, implementing precautions, and regularly reviewing assessments.Environmental Impact Assessment and Environmental Audit- Unit III



Environmental Impact Assessment and Environmental Audit- Unit IIIGAURAV. H .TANDON
Ěý
This document provides an overview of environmental impact assessments and environmental audits. It defines environmental impact assessment as the systematic identification and evaluation of potential impacts of proposed projects on the natural environment. The key steps of an EIA include organizing an interdisciplinary team, performing an assessment of the site and potential impacts, writing an environmental impact statement, and reviewing the EIS. Environmental audits evaluate an organization's environmental performance and position and identify ways to improve environmental management systems. The document outlines the basic components and steps in conducting environmental audits.20170912_ESIA Training for environmental engineering



20170912_ESIA Training for environmental engineeringPriyankaKotoky1
Ěý
It is also for protection of environmentEnvironmental impact assessment (EIA)



Environmental impact assessment (EIA)School of planning and architecture
Ěý
The document provides an overview of environmental impact assessment (EIA). It defines EIA as assessing the effects of proposed projects on the environment. EIA identifies alternatives and aims to balance economic and environmental costs and benefits. It integrates environmental concerns early in project planning. EIA started as a mandatory regulatory process in the US in 1969 and is now required in over 100 countries. The key stages of EIA are screening, scoping, baseline data collection, impact analysis, mitigation planning, public hearings, decision making, and monitoring. EIA aims to be fair, provide credible information for decisions, and ensure sustainability.EIA Methods



EIA MethodsSOUBAM INDRAKUMAR SINGH
Ěý
This document discusses various methodologies used in environmental impact assessments (EIAs). It outlines key characteristics an EIA methodology should have, such as being appropriate to the task and free from bias. Common impact identification methods are described, including checklists, matrices, networks and overlays. The stages of impact prediction, evaluation and identification are explained. The document also discusses techniques for impact prediction, evaluation of significance, and designing environmental protection measures. Overall it provides an overview of conceptual approaches and analytical tools used in EIAs.EIA



EIAKirui Ben
Ěý
This document discusses various methodologies used in environmental impact assessments (EIAs). It outlines key characteristics an EIA methodology should have, such as being appropriate to the task and free from bias. Common impact identification methods are described, including checklists, matrices, networks and overlays. The stages of impact prediction, evaluation and identification are explained. The document also discusses techniques for impact prediction, evaluation of significance, and designing environmental protection measures. Overall it provides an overview of conceptual approaches and analytical tools used in EIAs.Project Management Training.pptx



Project Management Training.pptxMohameAbullahi
Ěý
The document provides an overview of project management training that covers the project management life cycle. It discusses key areas such as:
- Defining a project and project management.
- Understanding the project management process which includes initiating, planning, executing, monitoring and evaluation, and closing.
- Identifying the knowledge areas involved in project management like integration, scope, time, cost, quality, and risk management.
- Explaining the importance of developing a project charter and stakeholder analysis during the initiating process.
- Detailing the components of a project charter and what a stakeholder analysis involves.
- Outlining the planning, execution, monitoring and evaluation, and closing processes within the project lifeEcw 579 week 13



Ecw 579 week 13Adilah Anuar
Ěý
The document discusses environmental impact assessments (EIA) in Malaysia. It describes the purpose and legal requirements of EIAs, which were introduced in 1987 to identify and mitigate environmental impacts of development projects. The key aspects of the EIA process in Malaysia are:
1) Projects are screened to determine if an EIA is required based on their potential environmental impacts.
2) The scoping process identifies which issues and impacts the EIA will address.
3) EIAs involve assessing alternatives, environmental baselines, impacts, and mitigation measures.
4) Completed EIA reports are submitted for review and must include opportunities for public consultation.Re sakss presentation on project management mburu 2



Re sakss presentation on project management mburu 2African Regional Strategic Analysis and Knowledge Support System (ReSAKSS)
Ěý
The document discusses project management and impact evaluation. It defines a project, outlines the project cycle which includes identification, preparation, appraisal, implementation, monitoring and evaluation. It discusses why projects fail and types of projects. Logical framework analysis and cost-benefit analysis are presented as tools for project planning, implementation and evaluation. Impact evaluation aims to determine if a project achieved its intended effects by estimating what would have occurred without the project.Clark.pdf



Clark.pdfGajendran Chelliah
Ěý
This document summarizes a presentation on project-level environmental impact assessments for deep-sea mining. It defines EIAs and their objectives, outlines the EIA process as part of a larger regulatory context, and discusses key issues to consider in EIAs for deep-sea mining including: the structure and content of EIA reports, the role of risk assessment, challenges around baseline data given the data-poor nature of deep-sea environments, and lessons learned from New Zealand's experience conducting EIAs for offshore mining projects.Asu history and theory lecture 3a-programming 14-10-2017



Asu history and theory lecture 3a-programming 14-10-2017Galala University
Ěý
This document provides an overview of a lecture on architectural programming. It discusses programming as the first step of the project lifecycle where the goals and requirements are defined through research. This establishes the criteria to guide the design solution. The lecture notes then outline the programming framework, including preparing for programming through analyzing and synthesizing information at different scales. It also discusses common characteristics of programming formats such as defining goals and gathering/analyzing data. The goals of programming are to separate the definition of criteria from design and understand implications on costs.Asu history and theory lecture 3a-programming 14-10-2017



Asu history and theory lecture 3a-programming 14-10-2017Galala University
Ěý
This document provides an overview of a lecture on architectural programming. It discusses programming as the first step of the project lifecycle where the goals and requirements are defined through research. This establishes the criteria to guide the design solution. The lecture covers the programming framework including preparing for programming, analyzing and synthesizing information, and considering design factors like human, environmental, cultural and technical issues. Architectural programming is presented as the process of gathering, analyzing and documenting relevant information to define the problem to be solved by design.SEA.pptx



SEA.pptxQuasid
Ěý
The document discusses strategic environmental assessment (SEA) as a tool for assessing the environmental impacts of policies, plans, and programs. It provides examples of SEAs from India and other countries. The key points made in the document are:
1) SEA facilitates mainstreaming environmental and social considerations into key policy documents and helps assess cumulative effects of projects on sustainability.
2) SEA is a global tool that is being increasingly used and formalized in development practices to address landscape-level impacts.
3) SEA contributes to integrated policymaking, enhanced stakeholder participation, and consideration of issues like resource efficiency and disaster vulnerability in planning.Unit 3 point 1 Environmental Sustainability



Unit 3 point 1 Environmental Sustainabilityashishjaswal
Ěý
The document discusses various types of impact assessments used to evaluate proposed projects and policies. It defines environmental impact assessment (EIA) as identifying future environmental consequences of actions. The objectives of EIA are to identify, predict, and evaluate economic, environmental and social impacts, and provide information for decision making. It also discusses life cycle analysis (LCA) which evaluates sustainability impacts across a product's entire life cycle. Social impact assessment (SIA) is defined as researching and managing social changes from policies and projects. It seeks to identify who benefits and is negatively impacted. The document outlines the methodologies and processes for each type of assessment.Environmental Impact Assessment



Environmental Impact AssessmentPrithvi Ghag
Ěý
This document discusses environmental impact assessment (EIA). It defines EIA as a study that predicts how a proposed project may affect the environment. EIAs identify the best project option by comparing alternatives and weighing economic and environmental costs and benefits. The EIA process involves scoping a project to identify key issues, conducting an impact assessment, obtaining public input, and using the results to inform decision-making about projects that could significantly affect the environment.Architectural design 3 10-4-2011 notes



Architectural design 3 10-4-2011 notesGalala University
Ěý
The document provides notes from an architectural design studio class discussing a community center project. It covers key stages of the design process including understanding the program and site analysis, developing a concept, and applying sustainability strategies. The program is translated into a bubble diagram showing relationships between functions. Site analysis considers physical characteristics like climate and topography as well as surrounding context. Developing a concept brings the program and site together in a holistic idea. Sustainability will be assessed using the QSAS rating system.environmentalimpactassessmenteia-210826024951.pdf



environmentalimpactassessmenteia-210826024951.pdfssusereef268
Ěý
The document provides information on environmental impact assessments (EIAs) and environmental management plans (EMPs). It defines EIAs as processes that identify, predict, evaluate, and mitigate biophysical, social, and other effects of development proposals prior to major decisions. The objectives of EIAs are to consider environmental factors in decision-making, identify potential impacts, and promote sustainable development through impact minimization. Methods used in EIAs include life cycle analyses for products, specific assessment protocols for GMOs, and fuzzy logic for hard-to-quantify impacts. EMPs are action plans that indicate which mitigation measures from EIA reports will be implemented to manage environmental impacts from projects. They ensure impacts are monitored and responsibilityEnvironmental impact assessment (eia)



Environmental impact assessment (eia)SANDEEP PATRE
Ěý
This document discusses environmental impact assessments (EIAs) and management plans. It defines EIAs as processes that identify, predict, evaluate and mitigate biophysical, social and other effects of development proposals before major decisions. The objectives of EIAs are to consider environmental factors in decision-making, identify potential impacts, minimize adverse impacts, and promote sustainable development through public participation and environmental management plans. Common EIA methods discussed include product life cycle analysis, assessments of genetically modified organisms, and fuzzy logic to measure hard to quantify impacts. The document also outlines types of EIAs like strategic, regional and sectoral EIAs, and describes the typical steps involved in conducting an EIA.Re sakss presentation on project management mburu 2



Re sakss presentation on project management mburu 2African Regional Strategic Analysis and Knowledge Support System (ReSAKSS)
Ěý
More from TONGCUAISAIAHJEREMIA (6)
Genetics Basic concepts Presentation in colorful ilustrative style.pptx



Genetics Basic concepts Presentation in colorful ilustrative style.pptxTONGCUAISAIAHJEREMIA
Ěý
Pedigreee analysis sampleICE BREAKER Of the world games united bansa



ICE BREAKER Of the world games united bansaTONGCUAISAIAHJEREMIA
Ěý
The document appears to contain a list of words with some letters intentionally altered or misspelled in order to test literacy and understanding. The words include variations of "analyze", "critique", "systematic", and "literacy" with letters changed or removed to make them difficult to decipher but related to the original word.ISAIAH GWAPO EARTHSCI



ISAIAH GWAPO EARTHSCITONGCUAISAIAHJEREMIA
Ěý
Iya ini ni Manay Mir. Isa ka maayo nga tinuga sang CHMSU. Mabout gd siya nga bata. She is the one that got near.MIR ISA KA MAAYO NGA TINUGA Audio-FINAL.pdf



MIR ISA KA MAAYO NGA TINUGA Audio-FINAL.pdfTONGCUAISAIAHJEREMIA
Ěý
Audio media can make unique contributions to teaching and learning by transmitting sounds through waves that are heard through equipment. There are several advantages to using audio in teaching, such as being inexpensive, readily available, and allowing for repetition of content. However, audio also has limitations like having a fixed sequence and not allowing the teacher to monitor student attention. Audio can be integrated into teaching in several ways, such as through teacher-prepared tapes, prerecorded tapes, or student-prepared tapes. Selecting appropriate audio materials and utilizing them effectively in the classroom requires previewing, preparing, and engaging learners during playback.EDMUND LOVES CHARLENE SO MUCH AYIEEE EDTECH1 MIDTERM INDIVIDUAL PROJECT.pdf



EDMUND LOVES CHARLENE SO MUCH AYIEEE EDTECH1 MIDTERM INDIVIDUAL PROJECT.pdfTONGCUAISAIAHJEREMIA
Ěý
1) Carbohydrates can be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides, or polysaccharides depending on their structure. Monosaccharides like glucose are simple sugars, disaccharides contain two monosaccharide units, and polysaccharides are long chains of monosaccharide units.
2) Carbohydrates undergo hydrolysis, which uses water to break bonds, or dehydration synthesis, which condenses molecules and removes a water molecule.
3) Carbohydrates serve important functions in the body including energy storage, structure, and as components of other biomolecules. They are broken down and used for energy but also play structural and protective roles.Recently uploaded (20)
Information Technology for class X CBSE skill Subject



Information Technology for class X CBSE skill SubjectVEENAKSHI PATHAK
Ěý
These questions are based on cbse booklet for 10th class information technology subject code 402. these questions are sufficient for exam for first lesion. This subject give benefit to students and good marks. if any student weak in one main subject it can replace with these marks.A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...



A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...Beena E S
Ěý
A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by Aaron ShepardMate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptx



Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptxLiny Jenifer
Ěý
A powerpoint presentation on the short story Mate by Kate Greenville. This presentation provides information on Kate Greenville, a character list, plot summary and critical analysis of the short story.The Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .



The Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .saanidhyapatel09
Ěý
This PowerPoint presentation provides an insightful overview of the Constitution, covering its key principles, features, and significance. It explains the fundamental rights, duties, structure of government, and the importance of constitutional law in governance. Ideal for students, educators, and anyone interested in understanding the foundation of a nation’s legal framework.
Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil Sir



Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil SirGUJARATCOMMERCECOLLE
Ěý
Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil SirChapter 3. Social Responsibility and Ethics in Strategic Management.pptx



Chapter 3. Social Responsibility and Ethics in Strategic Management.pptxRommel Regala
Ěý
This course provides students with a comprehensive understanding of strategic management principles, frameworks, and applications in business. It explores strategic planning, environmental analysis, corporate governance, business ethics, and sustainability. The course integrates Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to enhance global and ethical perspectives in decision-making.How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18



How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18Celine George
Ěý
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to modify existing web pages in Odoo 18. Web pages in Odoo 18 can also gather user data through user-friendly forms, encourage interaction through engaging features. FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptx



FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptxDanmarieMuli1
Ěý
Sinulog Festival of Cebu City, and Thingyan Festival of Myanmar.Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣs



Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣsCeline George
Ěý
In this slide we’ll discuss on the useful environment methods in Odoo 18. In Odoo 18, environment methods play a crucial role in simplifying model interactions and enhancing data processing within the ORM framework.Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptx



Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
Ěý
This ppt is useful for not only for B.Ed., M.Ed., M.A. (Education) or any other PG level students or Ph.D. scholars but also for the school, college and university teachers who are interested to prepare an e-content with AI for their students and others.N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity Briefing



N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity BriefingMebane Rash
Ěý
The number of languages spoken in NC public schools.Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Finals of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdf



EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfLiz Walsh-Trevino
Ěý
EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfHow to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣs



How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣsCeline George
Ěý
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18. In Odoo, Init Hooks are essential functions specified as strings in the __init__ file of a module.Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptx



Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
Ěý
This ppt has been made for the students pursuing PG in social science and humanities like M.Ed., M.A. (Education), Ph.D. Scholars. It will be also beneficial for the teachers and other faculty members interested in research and teaching research concepts.Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...



Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...pinkdvil200
Ěý
Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
IA.pptx a presentation about impact assessment
- 2. Definitio ns • Impact – having a strong effect on someone or something • Assessment – refers to analyzing and evaluating impacts on someone or something
- 3. Definitio ns • Analysis – objective task of identifying actions and of taking measurements of baseline conditions that are likely to occur as a result of the action • Evaluation - subjective or normative task which depends on the application of human values; involves determining the significance of the effects on the affected parties
- 4. Impact Assessment • a structured process for considering the implications, for people and their environment, of proposed actions while there is still an opportunity to modify (or even, if appropriate, to abandon) the proposals • applied to all levels of decision-making, from policies to specific projects
- 5. Example of Impact Assessment • Environmental Impact Assessment • a.k.a. Ecological Impact Assessment • a wide range of predictive tasks within environmental planning • focuses on prediction and evaluation of the effects of human activities on the structure and functions of “normal” ecosystem components
- 6. Environmental Impact Assessment • assess the impacts of human activities on nature: the ecosystem and its resources • conducted by government agency (DENR) and experts from both private and public sectors (project proponent and/or external agency)
- 7. Rationale of EIA • to have an opportunity to identify costly and undesirable effects • to modify projects in the design stage
- 8. Phases of EIA • Phase 1: Defining Study Goals • Phase 2: Identifying Potential Impacts • Phase 3: Measuring Baseline Conditions and Predicting Significant Impacts • Phase 4: Evaluating Significance of Findings • Phase 5: Considering Alternatives to the Proposed Action • Phase 6: Communication of Findings and Recommendations
- 9. IA Template
- 10. IA Project Template • Long size • 1.5 spacing • Font style Times New Roman 12 • Strictly NO Borders
- 11. Template EIA • Cover Page • Introduction • Presentation of Collected Data • Analysis, Evaluation and Findings • Recommendations • Reaction/Reflection • References • Appendix
- 12. Cover Page • Title of Chosen Project/Activity - e.g. “An Impact Assessment on SM Supermart” • Members (alphabetical order) • Course, Yr., & Section • Academic Year
- 13. Part 1 Introduction • Background of Project/Activity - history, owner, nature of project, purpose, objective • Location Profile - location, landscape • Project Rationale - why chose that project/activity in your IA?
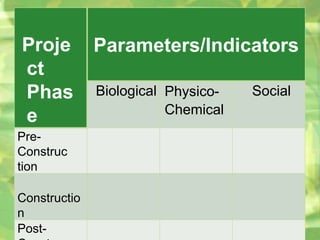
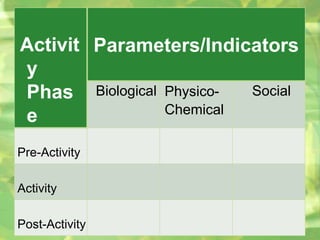
- 14. Part 2 Presentation of Data • Parameters VS Project Phase A. Project/Activity Phase - Pre-Construction, Construction, Post- Construction - Pre-Activity, Activity, Post-Activit B. Parameters/Indicators - Biological (biota) - Physico-Chemical (air, water, land, structures) - Social (community) - Others (economic, religious, political, etc.)
- 17. Part 3 Analysis, Evaluation & Findings • Measuring Baseline Conditions - a description of condition based on data • Predicting Impacts - identification and description of identified impacts • Evaluating Significance of Findings - measure the value of identified impacts • Summary of Findings - list of what was discovered
- 18. Part 4 Recommendations • list of suggestions on how to improve project or mitigate (if present) problems identified - alternative actions or solutions
- 19. Part 5 Reaction/Reflection • individual post-IA output describing your learnings, realizations, insights, comments or challenges encountered in the conduct of the impact assessment
- 20. Part 6 References - list of sources used during conduct of impact assessment
- 21. Part 7 Appendix - evidences of the conduct of IA (with captions) like actual or target site, interview
- 22. Criteria on Grading • Overall Format – 20% • Overall Presentation of IA – 20% • Presentation of Data, Analysis, Evaluation, Findings & Recommendations – 50% • Punctuality – 10%
- 23. Thank You!!







