Iati open aid presentation march 13 2013
- 1. Open Aid Partnership Innovations Labs World Bank Institute IATI Steering Committee Paris, March 13, 2013
- 2. OAP Objectives 1. Improve Aid Transparency: increase transparency on aid flows and public service delivery 2. Enhance Results: Better target, monitor, and coordinate aid flows within countries 3. Establish Feedback Loop: Empower citizens and CSOs to provide direct feedback on project outcomes Increase Aid Transparency and Citizen Engagement for Better Results
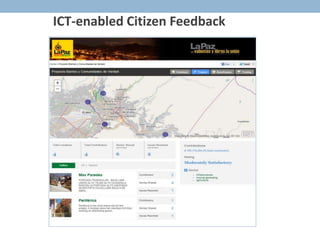
- 3. Key Components of Partnership ŌĆó Open Aid Map a common platform to show locations of donor programs ŌĆó Country Platforms for open aid flows and public expenditures ŌĆó Capacity Development to empower CSOs and citizens to effectively use and generate data ŌĆó Citizen Feedback Loops to promote citizen engagement in the delivery of public services ŌĆó Impact Evaluations to assess the impact of open aid on development outcomes
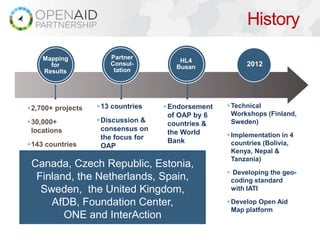
- 4. History Mapping Partner HL4 for Consul- Busan 2012 Results tation ’é¦2,700+ projects ’é¦ 13 countries ’é¦ Endorsement ’é¦ Technical of OAP by 6 Workshops (Finland, ’é¦30,000+ ’é¦ Discussion & countries & Sweden) locations consensus on the World the focus for ’é¦ Implementation in 4 Bank ’é¦143 countries OAP countries (Bolivia, Kenya, Nepal & Tanzania) Canada, Czech Republic, Estonia, ’é¦ Developing the geo- Finland, the Netherlands, Spain, coding standard Sweden, the United Kingdom, with IATI AfDB, Foundation Center, ’é¦ Develop Open Aid Map platform ONE and InterAction
- 5. Mapping for Results Regions Countries Sectors Projects maps.worldbank.org
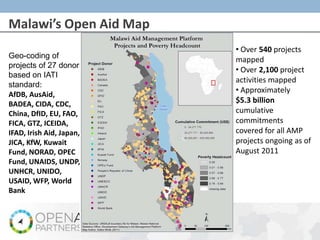
- 6. MalawiŌĆÖs Open Aid Map ŌĆó Over 540 projects Geo-coding of mapped projects of 27 donors Open Geo-coding Aid Map ŌĆó Over 2,100 project based on IATI activities mapped standard: ŌĆó Approximately AfDB, AusAid, BADEA, CIDA, CDC, $5.3 billion China, DfID, EU, FAO, cumulative FICA, GTZ, ICEIDA, commitments IFAD, Irish Aid, Japan, covered for all AMP JICA, KfW, Kuwait projects ongoing as of Fund, NORAD, OPEC August 2011 Fund, UNAIDS, UNDP, UNHCR, UNIDO, USAID, WFP, World 2.0 Bank
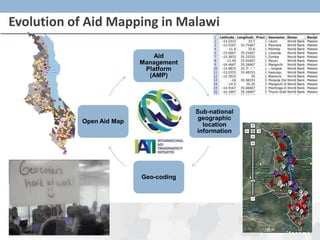
- 7. Evolution of Aid Mapping in Malawi Aid Management AMP Platform AMP 2.0 (AMP) Sub-national geographic Open Aid Map location information Geo-coding
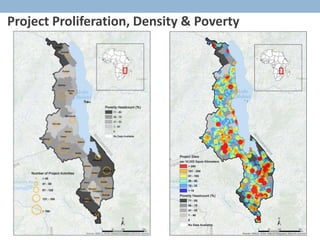
- 8. Project Proliferation, Density & Poverty Open AMP Geo-coding Aid Map AMP 2.0
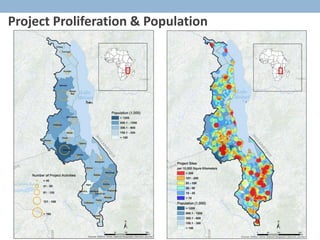
- 9. Project Proliferation & Population Open AMP Geo-coding Aid Map AMP 2.0
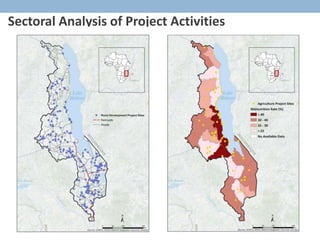
- 10. Sectoral Analysis of Project Activities Open AMP Geo-coding Aid Map AMP 2.0
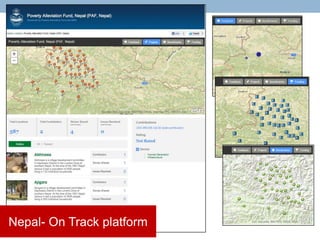
- 12. Nepal- On Track platform
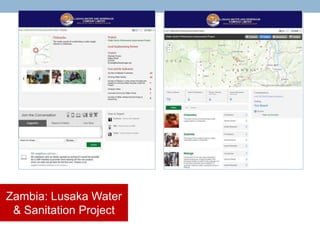
- 13. Zambia: Lusaka Water & Sanitation Project
- 14. Initiatives Next Steps 1. Broader endorsement by donors and other partners 2. Build upon existing IATI standards with geo-standards 3. Leverage as communications tools to promote transparency agenda Partners
- 15. EXTRA ║▌║▌▀Żs
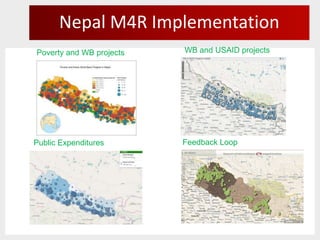
- 16. Nepal M4R Implementation Poverty and WB projects WB and USAID projects Public Expenditures Feedback Loop
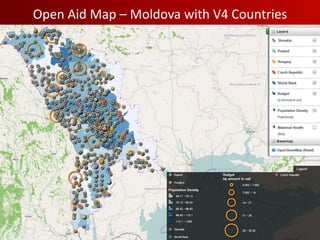
- 17. Open Aid Map ŌĆō Moldova with V4 Countries
Editor's Notes
- 1. It is important to understand the distribution of aid flows within a country in order to better target aid, however research on the distribution of aid has almost exclusively been conducted at the cross-country level. This is in large part due to the lack of data available on sub-national locations. By providing this information, this would enable decision-makers to know how to more effectively allocate development resources at the sub-national level. This will enable better targeting of aid efforts once underserved regions are more easily identified. 2. Understanding the precise location of development activities allows governments, donors and citizens to monitor progress and outcomes, and would encourage those at the local level to provide feedback on development projects in their area. 3. Enabling donors to see where other donor projects are located allows them to avoid duplicating efforts in the same region and increases the efficiency of development resources. 4. The volume of information provided by donors can make it difficult to make sense of the data. Being able to visualize the locations of all development activities on a map can enhance understanding of patterns in aid allocation. Making this information easier to understand will increase accessibility and use of the data among a wide group of stakeholders. 5. The IATI encourages development organizations to make information the ŌĆ£Who, Where, and HowŌĆØ of development projects publicly available and easy to use and understand. Crucial to this is the Where- geographical information on where organizations are operating within countries. This information allows governments, citizens and donors to gain a more comprehensive picture of donor activities within countries, thus enabling better decision-making.