IB PYP Intro for teachers
- 1. Primary Years Programme (PYP) Introduction
- 2. What is PYP? ŌĆó An International, trans-disciplinary program designed to foster the development of the whole child, not just in the classroom but through other means of learning. ŌĆó PYP focuses on the total growth of the developing child, encompassing social, physical, emotional and cultural needs in addition to academic welfare. ŌĆó PYP combines best research and practice from a range of national systems with a wealth of knowledge and experience from international schools to create a relevant and engaging educational framework for all children.
- 3. IB Primary Years Programme ŌĆó Provides an opportunity for learners to construct meaning, principally through concept-driven inquiry. ŌĆó Traditional academic subjects are part of the PYP but it emphasizes the interrelatedness of knowledge and skills through a trans-disciplinary programme of inquiry. ŌĆó The PYP focuses on the heart as well as the mind and addresses social, physical, emotional and cultural needs as well as academic ones.
- 4. The PYP aims to develop in students: ŌĆó Sensitivity to the experiences of others through the curriculum ŌĆó The characteristics listed in the student profile ŌĆó The attitudes that are an explicit element of the programme ŌĆó The expectation of socially responsible action as a result of the learning experience.
- 5. What is trans-disciplinary inquiry? ŌĆó Focus on big ideas/issues/CONCEPTS ŌĆó Essential KNOWLEDGE, SKILLS, ATTITUDES are necessary and must be taught ŌĆó Focus on taking socially responsible ACTION ŌĆó Emphasis: inquiry, problem solving, critical thinking ŌĆó Integrates where appropriate key learning areas
- 6. Internationalism: The PYP Perspective ŌĆó The PYP says that a school should be proud to send out into the world a person we could call an internationalist. ŌĆó A PYP school regardless of location, size or constitution strives towards developing an international person. What is an international person? ŌĆó From PYP perspective it is a person with attributes and dispositions described in the student profile.
- 7. What is the PYP learner profile? The goal of the Primary Years Program is to create internationally minded students. IBO believes that students should be: ŌĆó Principled ŌĆó Caring ŌĆó Open-minded ŌĆó Well-balanced ŌĆó Reflective ŌĆó Inquirers ŌĆó Thinkers ŌĆó Communicators ŌĆó Risk-takers ŌĆó Knowledgeable
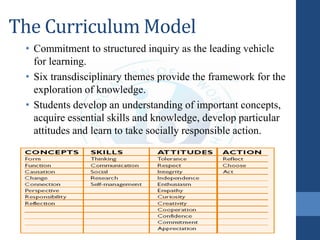
- 8. What do we want to learn? The Written Curriculum ŌĆó The PYP strives for balance between search for understanding, acquisition of knowledge and skills, the development of positive attitudes and positive action. ŌĆó There are 5 essential elements of the curriculum: ’é¦ Concepts ’é¦ Knowledge ’é¦ Skills ’é¦ Attitudes ’é¦ Action
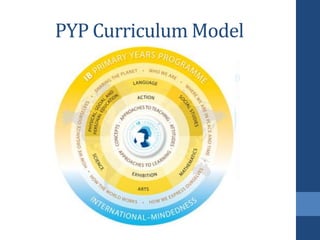
- 10. The Curriculum Model ŌĆó Commitment to structured inquiry as the leading vehicle for learning. ŌĆó Six transdisciplinary themes provide the framework for the exploration of knowledge. ŌĆó Students develop an understanding of important concepts, acquire essential skills and knowledge, develop particular attitudes and learn to take socially responsible action.
- 11. ORGANIZING THEMES- TheIB-PYPcurriculumisbuiltaroundsixorganizingthemes. Who we are - An exploration of the nature of the self; our beliefs and values; personal, physical, mental, social, and spiritual health; of our families, friends, communities, and cultures; our rights and responsibilities; of what it means to be human.
- 12. Where we are in place and time An exploration of our orientation in place and time; our personal histories; history and geography from local and global perspectives; of our homes and journeys; of the discoveries, explorations and migrations of human kind; of the contributions of individuals and civilizations .
- 13. How we express ourselves An exploration of the ways in which we discover and express our nature, ideas, feelings, beliefs and values through language and the arts.
- 14. How the world works An exploration of the physical and material world; natural and human- made phenomena; of the world of science and technology.
- 15. How we organize ourselves An exploration of human systems and communities; of the world of work, its nature and its value; of employment and unemployment and their impact on us and the world around us.
- 16. Sharing the planet An exploration of our rights and responsibilities as we strive to share finite resources with other people and with other living things; of communities and of the relationships within and between them.
- 17. The process of inquiry Students learn to ask questions. They are encouraged to develop their own questions related to the materials being studied. Through questioning, students learn there are a broad range of "right" answers for a given question and they begin to appreciate the enormous, complex world in which they live.
- 18. KEY QUESTIONS The IB - PYP's fundamental concepts are articulated as key questions and they drive the inquiry process. Each question is comprehensive and integrates many ideas. The key questions students should ask are: ŌĆó FORM - What is it like? ŌĆó FUNCTION - How does it work? ŌĆó CAUSATION - Why is it like it is? ŌĆó CHANGE - How is it changing? ŌĆó CONNECTION - How is it connected to other things? ŌĆó PERSPECTIVE - What are the points of view? ŌĆó RESPONSIBILITY - What is our responsibility? ŌĆó REFLECTION - How do we know?
- 19. Attitudes In addition to the concepts, content and skills that are imbedded in the curriculum, students are taught and they practise the attitudes outlined by IBO. These attitudes are descriptive of a person who is a responsible citizen of his/her local and world wide community.
- 20. Students should demonstrate the following: ŌĆó Appreciation - Appreciating the wonder and beauty of the world and its people ŌĆó Commitment - Being committed to their learning, persevering, and showing self discipline and responsibility ŌĆó Confidence - Feeling confident in their ability as learners, having the courage to take risks, applying what they have learned and making appropriate decisions ŌĆó Cooperation - Cooperating, collaborating, and leading or following as the situation demands ŌĆó Creativity - Being creative and imaginative in their thinking and in their approach to problems and dilemmas
- 21. Students should demonstrate the following: ŌĆó Curiosity - Being curious about the nature of learning and of the world, its people and cultures ŌĆó Empathy - Imaginatively projecting themselves into another's situation, in order to understand his/her thoughts, reasoning and emotions ŌĆó Enthusiasm - Enjoying learning ŌĆó Independence - Thinking and acting independently, making their own judgments based on reasoned principles and being able to defend their judgments ŌĆó Integrity - Having integrity and a firm sense of fairness and honesty ŌĆó Respect - Respecting themselves, others, and the world around them ŌĆó Tolerance - Feeling sensitivity towards differences and diversity in the world and being responsive to the needs of others