IBM GPFS
Download as pptx, pdf3 likes1,965 views
GPFS (General Parallel File System) is a high-performance clustered file system developed by IBM that can be deployed in shared disk or shared-nothing distributed parallel modes. It was created to address the growing imbalance between increasing CPU, memory, and network speeds, and the relatively slower growth of disk drive speeds. GPFS provides high scalability, availability, and advanced data management features like snapshots and replication. It is used extensively by large companies and supercomputers due to its ability to handle large volumes of data and high input/output workloads in distributed, parallel environments.
1 of 9
Downloaded 44 times


![Existing Solutions Inability
? DAS, NAS, SAN [alone]
? Many data centers have become victims of
ˇ°filer-sprawlˇ±
? Data administration and management
(such as migration, backups, archiving)
costs to skyrocket!
? I/O performance & application workflow](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4272d31a-c8c5-4c2b-8e77-68eb62b9d2fa-150903104546-lva1-app6891/85/IBM-GPFS-5-320.jpg)




Ad
Recommended
Ibm spectrum scale fundamentals workshop for americas part 1 components archi...
Ibm spectrum scale fundamentals workshop for americas part 1 components archi...xKinAnx
?
The document provides instructions for installing and configuring Spectrum Scale 4.1. Key steps include: installing Spectrum Scale software on nodes; creating a cluster using mmcrcluster and designating primary/secondary servers; verifying the cluster status with mmlscluster; creating Network Shared Disks (NSDs); and creating a file system. The document also covers licensing, system requirements, and IBM and client responsibilities for installation and maintenance.DAS RAID NAS SAN
DAS RAID NAS SANGhassen Smida
?
This document provides an overview of various data storage technologies including RAID, DAS, NAS, and SAN. It discusses RAID levels like RAID 0, 1, 5 which provide data striping and redundancy. Direct attached storage (DAS) connects directly to servers but cannot be shared, while network attached storage (NAS) uses file sharing protocols over IP networks. Storage area networks (SAN) use dedicated storage networks like Fibre Channel and iSCSI to provide block-level access to consolidated storage. The key is choosing the right solution based on capacity, performance, scalability, availability, data protection needs, and budget.VMware HCI solutions - 2020-01-16
VMware HCI solutions - 2020-01-16David Pasek
?
The document outlines VMware's Vsan and Dell EMC VxRail solutions tailored for SMB and midmarket customers, detailing specific configurations and pricing for hyper-converged infrastructure. It provides various pre-designed solutions with indicative pricing, focusing on different use cases such as Remote Office/Branch Office (ROBO) and environments accommodating up to 50 or more virtual machines. Additionally, it includes conceptual infrastructure designs, licensing details, and technical specifications for each solution type.Lecture5 virtualization
Lecture5 virtualizationhktripathy
?
Virtualization allows multiple operating systems and applications to run on a single hardware device by dividing the resources virtually. It provides isolation, encapsulation, and interposition. There are two types of hypervisors - Type 1 runs directly on hardware and Type 2 runs on an operating system. Virtualization can be applied to servers, desktops, applications, networks, and storage to improve utilization, security, and manageability.Oracle ACFS High Availability NFS Services (HANFS) Part-I
Oracle ACFS High Availability NFS Services (HANFS) Part-IAnju Garg
?
To satisfy increasing demands for data storage from big data and IoT, Oracle DBAs will need to handle massive amounts of normal file system storage. While some organizations have adopted open stack storage, others are evaluating options like NAS, NFS or other file systems. Oracle Database 12c R1 introduces ACFS as a high availability NFS file system (HANFS) that allows files on ACFS clusters to be accessed outside the cluster using highly available NFS exports, providing continuous access even if the exporting node fails.Ibm spectrum scale fundamentals workshop for americas part 8 spectrumscale ba...
Ibm spectrum scale fundamentals workshop for americas part 8 spectrumscale ba...xKinAnx
?
The document provides an overview of key concepts covered in a GPFS 4.1 system administration course, including backups using mmbackup, SOBAR integration, snapshots, quotas, clones, and extended attributes. The document includes examples of commands and procedures for administering these GPFS functions.Gpfs introandsetup
Gpfs introandsetupasihan
?
This document provides an overview of installing and configuring a 3 node GPFS cluster. It discusses using 8 shared LUNs across the 3 servers to simulate having disks from 2 different V7000 storage arrays for redundancy. The disks will be divided into 2 failure groups, with hdisk1-4 in one failure group representing one simulated array, and hdisk5-8 in the other failure group representing the other simulated array. This is to ensure redundancy in case of failure of an entire storage array.Ibm spectrum scale fundamentals workshop for americas part 5 ess gnr-usecases...
Ibm spectrum scale fundamentals workshop for americas part 5 ess gnr-usecases...xKinAnx
?
This document provides an overview of Spectrum Scale 4.1 system administration. It describes the Elastic Storage Server options and components, Spectrum Scale native RAID (GNR), and tips for best practices. GNR implements sophisticated data placement and error correction algorithms using software RAID to provide high reliability and performance without additional hardware. It features auto-rebalancing, low rebuild overhead through declustering, and end-to-end data checksumming.Room 3 - 1 - Nguy?n Xu?n Tr??ng L?m - Zero touch on-premise storage infrastru...
Room 3 - 1 - Nguy?n Xu?n Tr??ng L?m - Zero touch on-premise storage infrastru...Vietnam Open Infrastructure User Group
?
This document discusses Zero touch on-premise storage infrastructure with OpenStack Cinder. It describes Viettel's IT infrastructure with mixed storage resources and the challenges of managing it. The solution presented uses OpenStack Cinder and additional tools to automate the management and provisioning of block storage for bare metal servers and OpenStack instances. This removes manual configuration steps and improves performance by pre-zoning storage connections. The goal is to make volume management simpler and allow adding new storage resources without additional configuration through the unified management solution.Ceph Day Beijing - Ceph All-Flash Array Design Based on NUMA Architecture
Ceph Day Beijing - Ceph All-Flash Array Design Based on NUMA ArchitectureDanielle Womboldt
?
This document discusses an all-flash Ceph array design from QCT based on NUMA architecture. It provides an agenda that covers all-flash Ceph and use cases, QCT's all-flash Ceph solution for IOPS, an overview of QCT's lab environment and detailed architecture, and the importance of NUMA. It also includes sections on why all-flash storage is used, different all-flash Ceph use cases, QCT's IOPS-optimized all-flash Ceph solution, benefits of using NVMe storage, QCT's lab test environment, Ceph tuning recommendations, and benefits of using multi-partitioned NVMe SSDs for Ceph OSDs.Storage Technology Overview
Storage Technology Overviewnomathjobs
?
The document provides an overview of storage technology options including network attached storage (NAS), storage area networks (SANs), and discusses specific NAS and SAN products. It highlights the key features of an iSCSI SAN brick platform including software for snapshots, replication, and continuous data protection. Appliance strategies and partnerships are also summarized.Ibm spectrum scale fundamentals workshop for americas part 4 spectrum scale_r...
Ibm spectrum scale fundamentals workshop for americas part 4 spectrum scale_r...xKinAnx
?
This document provides information about replication and stretch clusters in IBM Spectrum Scale. It defines replication as synchronously copying file system data across failure groups for redundancy. While replication improves availability, it reduces performance and increases storage usage. Stretch clusters combine two or more clusters to create a single large cluster, typically using replication between sites. Replication policies and failure group configuration are important to ensure effective data duplication.Logical Data Fabric: Architectural Components
Logical Data Fabric: Architectural ComponentsDenodo
?
The document outlines the concept of a logical data fabric, emphasizing its ability to efficiently consolidate diverse data sources for analytics and insights automation. It highlights the key components and functionalities, such as data integration, virtualization, governance, and performance optimization supported by major analysts like Gartner and Forrester. Denodo's logical data fabric aims to enhance data management by delivering trusted data rapidly to various consumers.ZFS
ZFSmewandalmeida
?
The document discusses key features of the ZFS file system including its use of pooled storage, data integrity through checksumming, snapshots and clones, scalability, and dynamic striping. Some advantages of ZFS over traditional file systems are more efficient storage utilization through pooled devices, self-healing capabilities, and faster administration through instant snapshots and clones. Challenges of ZFS include limited adoption, higher CPU and power usage than some traditional file systems, and lack of built-in encryption.VMware NSX 101: What, Why & How
VMware NSX 101: What, Why & HowAniekan Akpaffiong
?
The document outlines a seminar presentation on VMware NSX, focused on its benefits, components, and use cases in software-defined networking. It explores NSX's capabilities such as advanced security features, dynamic provisioning of networks, and the virtualization of network services, including routing and micro-segmentation. Additionally, the document covers NSX architecture, deployment considerations, and the essential concepts of software-defined data centers.IBM Spectrum Scale for File and Object Storage
IBM Spectrum Scale for File and Object StorageTony Pearson
?
This document discusses IBM Spectrum Scale, which provides universal access to files and objects across data centers. It can scale to support up to 18 quintillion files per file system and 256 file systems per cluster. IBM Spectrum Scale provides high performance, proven reliability, and flexible access to data through various file and object protocols. It can be deployed as software on various systems, as pre-built systems, or as cloud services. The document outlines the various capabilities and uses of IBM Spectrum Scale, such as file management policies, caching, encryption, protocol servers, integration with Hadoop and backup/disaster recovery.Virtualization & cloud computing
Virtualization & cloud computingSoumyajit Basu
?
Virtualization allows multiple operating systems to run on a single machine by creating virtual versions of hardware resources. There are three main types of virtualization: partial, full, and para. A hypervisor manages virtual machines and allocates resources to guest operating systems. Cloud computing delivers computing as an on-demand utility over the internet by sharing resources. It provides software, platforms and infrastructure as services across public, private, hybrid and community clouds. Big data refers to massive volumes of structured and unstructured data that is difficult to process using traditional techniques and requires specialized infrastructure.Apache Hudi: The Path Forward
Apache Hudi: The Path ForwardAlluxio, Inc.
?
Apache Hudi is a serverless transactional layer designed for data lakes that supports both streaming and batch pipelines, enabling efficient data processing. It features components for table metadata management, indexing, and concurrency control, while ensuring scalability on Hadoop-compatible storage systems. The platform has an active community contributing to ongoing improvements and new features such as indexing, schema evolution, and integration with various data processing engines.Storage Basics
Storage BasicsMurali Rajesh
?
Storage systems include disks, disk shelves, controllers, and switches. Servers connect to storage using host bus adapters (HBAs) and software initiators to access disks over Fibre Channel (FCP) or iSCSI. NetApp uses its DataOntap operating system to manage disks aggregated into RAID groups and provisioned into volumes that provide file-level access over protocols like NFS, CIFS, iSCSI, and FC. Volumes contain file systems and can be accessed by servers over dedicated block storage devices called LUNs.Snowflake Datawarehouse Architecturing
Snowflake Datawarehouse ArchitecturingIshan Bhawantha Hewanayake
?
Snowflake is a SaaS data warehousing platform that operates on cloud infrastructure (AWS, Azure, GCP) without requiring hardware or software management from the user. Its architecture separates storage and compute, allowing for scalable and cost-efficient processing, while features like micro-partitioning and various data connectors enhance performance. Key use cases include data loading through bulk or continuous methods, and it offers a simplified approach compared to traditional databases.IBM Spectrum Scale Authentication for File Access - Deep Dive
IBM Spectrum Scale Authentication for File Access - Deep DiveShradha Nayak Thakare
?
This document discusses authentication and ID mapping in IBM Spectrum Scale. It provides an overview of authentication basics, UNIX and Windows authentication, and ID mapping. It then describes authentication and ID mapping in IBM Spectrum Scale, including supported authentication methods, ID mapping methods, and configuration prerequisites. Active Directory authentication with automatic, RFC2307, and LDAP ID mapping is explained in more detail.Modern Data Warehousing with the Microsoft Analytics Platform System
Modern Data Warehousing with the Microsoft Analytics Platform SystemJames Serra
?
The Microsoft Analytics Platform System (APS) is a turnkey appliance that provides a modern data warehouse with the ability to handle both relational and non-relational data. It uses a massively parallel processing (MPP) architecture with multiple CPUs running queries in parallel. The APS includes an integrated Hadoop distribution called HDInsight that allows users to query Hadoop data using T-SQL with PolyBase. This provides a single query interface and allows users to leverage existing SQL skills. The APS appliance is pre-configured with software and hardware optimized to deliver high performance at scale for data warehousing workloads.The Data Center Network Evolution
The Data Center Network EvolutionCisco Canada
?
The document discusses the evolution of data center networks, focusing on Software Defined Networking (SDN) and Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI). It emphasizes the decoupling of control and data planes, the use of overlay networks like VXLAN, and the integration of centralized management for enhanced automation and programmability. Furthermore, it highlights the inclusion of open standards and extensibility in network architecture to support both physical and virtual environments.Network virtualization
Network virtualizationDamian Parniewicz
?
Network virtualization allows sharing of physical network infrastructure between multiple virtual networks through abstraction and tunneling techniques. It provides benefits like increased infrastructure utilization, scalability, agility, and security. Common virtualization techniques include VLANs to divide switches into logical segments, DWDM to multiply fiber bandwidth, VRFs to partition routers, and tunneling protocols like GRE, VXLAN, and MPLS to encapsulate and transport traffic across physical networks. Overlay networks further abstract the physical underlay into virtual topologies to support multiple isolated tenant networks on shared infrastructure.VMware Presentation
VMware PresentationEmirates Computers
?
Virtualization allows multiple operating systems and applications to run on the same physical server at the same time. This increases hardware utilization and flexibility while reducing IT costs. VMware virtualization solutions can reduce energy costs by 80% through server consolidation and powering down unused servers without affecting applications or users. Virtualization makes hardware resources independent of operating systems and applications, treating them as single unified units that can be more easily deployed, maintained, and supported.Introduction to snowflake
Introduction to snowflakeSunil Gurav
?
Snowflake is an analytic data warehouse provided as software-as-a-service (SaaS). It uses a unique architecture designed for the cloud, with a shared-disk database and shared-nothing architecture. Snowflake's architecture consists of three layers - the database layer, query processing layer, and cloud services layer - which are deployed and managed entirely on cloud platforms like AWS and Azure. Snowflake offers different editions like Standard, Premier, Enterprise, and Enterprise for Sensitive Data that provide additional features, support, and security capabilities.Ceph Object Storage Performance Secrets and Ceph Data Lake Solution
Ceph Object Storage Performance Secrets and Ceph Data Lake SolutionKaran Singh
?
The document details performance optimization techniques for Ceph object storage, showcasing a comprehensive benchmarking study with around 1500 unique tests conducted on various configurations. Key findings indicate significant performance improvements, particularly for read and write operations by optimizing object sizes, server densities, and utilizing flash media for bucket indexing. Recommendations are provided based on workload types, highlighting optimal configurations for small and large object operations, as well as strategies for managing high object counts.CDW: SAN vs. NAS
CDW: SAN vs. NASSpiceworks
?
The document discusses the differences between network attached storage (NAS) and storage area network (SAN) solutions for small businesses. It outlines the key benefits and use cases of each technology. NAS is best for file sharing and backup, while SAN provides faster performance for databases and applications. The document also notes that a combination of NAS and SAN can provide the best of both worlds.IBM general parallel file system - introduction
IBM general parallel file system - introductionIBM Danmark
?
The document provides information about IBM's General Parallel File System (GPFS) 3.5 and introduces the GPFS Storage Server (GSS). It summarizes that GPFS is a scalable high-performance file management system that can scale from 1 to 8192 nodes. The GSS is a new storage solution using IBM servers and JBOD storage to provide high capacity and performance storage in a scalable building block approach. The GSS has no storage controllers and provides a single integrated storage solution built on GPFS software.Gfs
GfsShahbaz Sidhu
?
The document describes the Google File System (GFS), a scalable distributed file system designed and implemented by Google to meet its rapidly growing data storage needs. Key aspects of the GFS design include supporting large files and high throughput appending workloads on inexpensive commodity hardware in the face of frequent component failures. The GFS architecture uses a single master to manage metadata and multiple chunkservers to store and retrieve file chunks, providing fault tolerance through replication.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Room 3 - 1 - Nguy?n Xu?n Tr??ng L?m - Zero touch on-premise storage infrastru...
Room 3 - 1 - Nguy?n Xu?n Tr??ng L?m - Zero touch on-premise storage infrastru...Vietnam Open Infrastructure User Group
?
This document discusses Zero touch on-premise storage infrastructure with OpenStack Cinder. It describes Viettel's IT infrastructure with mixed storage resources and the challenges of managing it. The solution presented uses OpenStack Cinder and additional tools to automate the management and provisioning of block storage for bare metal servers and OpenStack instances. This removes manual configuration steps and improves performance by pre-zoning storage connections. The goal is to make volume management simpler and allow adding new storage resources without additional configuration through the unified management solution.Ceph Day Beijing - Ceph All-Flash Array Design Based on NUMA Architecture
Ceph Day Beijing - Ceph All-Flash Array Design Based on NUMA ArchitectureDanielle Womboldt
?
This document discusses an all-flash Ceph array design from QCT based on NUMA architecture. It provides an agenda that covers all-flash Ceph and use cases, QCT's all-flash Ceph solution for IOPS, an overview of QCT's lab environment and detailed architecture, and the importance of NUMA. It also includes sections on why all-flash storage is used, different all-flash Ceph use cases, QCT's IOPS-optimized all-flash Ceph solution, benefits of using NVMe storage, QCT's lab test environment, Ceph tuning recommendations, and benefits of using multi-partitioned NVMe SSDs for Ceph OSDs.Storage Technology Overview
Storage Technology Overviewnomathjobs
?
The document provides an overview of storage technology options including network attached storage (NAS), storage area networks (SANs), and discusses specific NAS and SAN products. It highlights the key features of an iSCSI SAN brick platform including software for snapshots, replication, and continuous data protection. Appliance strategies and partnerships are also summarized.Ibm spectrum scale fundamentals workshop for americas part 4 spectrum scale_r...
Ibm spectrum scale fundamentals workshop for americas part 4 spectrum scale_r...xKinAnx
?
This document provides information about replication and stretch clusters in IBM Spectrum Scale. It defines replication as synchronously copying file system data across failure groups for redundancy. While replication improves availability, it reduces performance and increases storage usage. Stretch clusters combine two or more clusters to create a single large cluster, typically using replication between sites. Replication policies and failure group configuration are important to ensure effective data duplication.Logical Data Fabric: Architectural Components
Logical Data Fabric: Architectural ComponentsDenodo
?
The document outlines the concept of a logical data fabric, emphasizing its ability to efficiently consolidate diverse data sources for analytics and insights automation. It highlights the key components and functionalities, such as data integration, virtualization, governance, and performance optimization supported by major analysts like Gartner and Forrester. Denodo's logical data fabric aims to enhance data management by delivering trusted data rapidly to various consumers.ZFS
ZFSmewandalmeida
?
The document discusses key features of the ZFS file system including its use of pooled storage, data integrity through checksumming, snapshots and clones, scalability, and dynamic striping. Some advantages of ZFS over traditional file systems are more efficient storage utilization through pooled devices, self-healing capabilities, and faster administration through instant snapshots and clones. Challenges of ZFS include limited adoption, higher CPU and power usage than some traditional file systems, and lack of built-in encryption.VMware NSX 101: What, Why & How
VMware NSX 101: What, Why & HowAniekan Akpaffiong
?
The document outlines a seminar presentation on VMware NSX, focused on its benefits, components, and use cases in software-defined networking. It explores NSX's capabilities such as advanced security features, dynamic provisioning of networks, and the virtualization of network services, including routing and micro-segmentation. Additionally, the document covers NSX architecture, deployment considerations, and the essential concepts of software-defined data centers.IBM Spectrum Scale for File and Object Storage
IBM Spectrum Scale for File and Object StorageTony Pearson
?
This document discusses IBM Spectrum Scale, which provides universal access to files and objects across data centers. It can scale to support up to 18 quintillion files per file system and 256 file systems per cluster. IBM Spectrum Scale provides high performance, proven reliability, and flexible access to data through various file and object protocols. It can be deployed as software on various systems, as pre-built systems, or as cloud services. The document outlines the various capabilities and uses of IBM Spectrum Scale, such as file management policies, caching, encryption, protocol servers, integration with Hadoop and backup/disaster recovery.Virtualization & cloud computing
Virtualization & cloud computingSoumyajit Basu
?
Virtualization allows multiple operating systems to run on a single machine by creating virtual versions of hardware resources. There are three main types of virtualization: partial, full, and para. A hypervisor manages virtual machines and allocates resources to guest operating systems. Cloud computing delivers computing as an on-demand utility over the internet by sharing resources. It provides software, platforms and infrastructure as services across public, private, hybrid and community clouds. Big data refers to massive volumes of structured and unstructured data that is difficult to process using traditional techniques and requires specialized infrastructure.Apache Hudi: The Path Forward
Apache Hudi: The Path ForwardAlluxio, Inc.
?
Apache Hudi is a serverless transactional layer designed for data lakes that supports both streaming and batch pipelines, enabling efficient data processing. It features components for table metadata management, indexing, and concurrency control, while ensuring scalability on Hadoop-compatible storage systems. The platform has an active community contributing to ongoing improvements and new features such as indexing, schema evolution, and integration with various data processing engines.Storage Basics
Storage BasicsMurali Rajesh
?
Storage systems include disks, disk shelves, controllers, and switches. Servers connect to storage using host bus adapters (HBAs) and software initiators to access disks over Fibre Channel (FCP) or iSCSI. NetApp uses its DataOntap operating system to manage disks aggregated into RAID groups and provisioned into volumes that provide file-level access over protocols like NFS, CIFS, iSCSI, and FC. Volumes contain file systems and can be accessed by servers over dedicated block storage devices called LUNs.Snowflake Datawarehouse Architecturing
Snowflake Datawarehouse ArchitecturingIshan Bhawantha Hewanayake
?
Snowflake is a SaaS data warehousing platform that operates on cloud infrastructure (AWS, Azure, GCP) without requiring hardware or software management from the user. Its architecture separates storage and compute, allowing for scalable and cost-efficient processing, while features like micro-partitioning and various data connectors enhance performance. Key use cases include data loading through bulk or continuous methods, and it offers a simplified approach compared to traditional databases.IBM Spectrum Scale Authentication for File Access - Deep Dive
IBM Spectrum Scale Authentication for File Access - Deep DiveShradha Nayak Thakare
?
This document discusses authentication and ID mapping in IBM Spectrum Scale. It provides an overview of authentication basics, UNIX and Windows authentication, and ID mapping. It then describes authentication and ID mapping in IBM Spectrum Scale, including supported authentication methods, ID mapping methods, and configuration prerequisites. Active Directory authentication with automatic, RFC2307, and LDAP ID mapping is explained in more detail.Modern Data Warehousing with the Microsoft Analytics Platform System
Modern Data Warehousing with the Microsoft Analytics Platform SystemJames Serra
?
The Microsoft Analytics Platform System (APS) is a turnkey appliance that provides a modern data warehouse with the ability to handle both relational and non-relational data. It uses a massively parallel processing (MPP) architecture with multiple CPUs running queries in parallel. The APS includes an integrated Hadoop distribution called HDInsight that allows users to query Hadoop data using T-SQL with PolyBase. This provides a single query interface and allows users to leverage existing SQL skills. The APS appliance is pre-configured with software and hardware optimized to deliver high performance at scale for data warehousing workloads.The Data Center Network Evolution
The Data Center Network EvolutionCisco Canada
?
The document discusses the evolution of data center networks, focusing on Software Defined Networking (SDN) and Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI). It emphasizes the decoupling of control and data planes, the use of overlay networks like VXLAN, and the integration of centralized management for enhanced automation and programmability. Furthermore, it highlights the inclusion of open standards and extensibility in network architecture to support both physical and virtual environments.Network virtualization
Network virtualizationDamian Parniewicz
?
Network virtualization allows sharing of physical network infrastructure between multiple virtual networks through abstraction and tunneling techniques. It provides benefits like increased infrastructure utilization, scalability, agility, and security. Common virtualization techniques include VLANs to divide switches into logical segments, DWDM to multiply fiber bandwidth, VRFs to partition routers, and tunneling protocols like GRE, VXLAN, and MPLS to encapsulate and transport traffic across physical networks. Overlay networks further abstract the physical underlay into virtual topologies to support multiple isolated tenant networks on shared infrastructure.VMware Presentation
VMware PresentationEmirates Computers
?
Virtualization allows multiple operating systems and applications to run on the same physical server at the same time. This increases hardware utilization and flexibility while reducing IT costs. VMware virtualization solutions can reduce energy costs by 80% through server consolidation and powering down unused servers without affecting applications or users. Virtualization makes hardware resources independent of operating systems and applications, treating them as single unified units that can be more easily deployed, maintained, and supported.Introduction to snowflake
Introduction to snowflakeSunil Gurav
?
Snowflake is an analytic data warehouse provided as software-as-a-service (SaaS). It uses a unique architecture designed for the cloud, with a shared-disk database and shared-nothing architecture. Snowflake's architecture consists of three layers - the database layer, query processing layer, and cloud services layer - which are deployed and managed entirely on cloud platforms like AWS and Azure. Snowflake offers different editions like Standard, Premier, Enterprise, and Enterprise for Sensitive Data that provide additional features, support, and security capabilities.Ceph Object Storage Performance Secrets and Ceph Data Lake Solution
Ceph Object Storage Performance Secrets and Ceph Data Lake SolutionKaran Singh
?
The document details performance optimization techniques for Ceph object storage, showcasing a comprehensive benchmarking study with around 1500 unique tests conducted on various configurations. Key findings indicate significant performance improvements, particularly for read and write operations by optimizing object sizes, server densities, and utilizing flash media for bucket indexing. Recommendations are provided based on workload types, highlighting optimal configurations for small and large object operations, as well as strategies for managing high object counts.CDW: SAN vs. NAS
CDW: SAN vs. NASSpiceworks
?
The document discusses the differences between network attached storage (NAS) and storage area network (SAN) solutions for small businesses. It outlines the key benefits and use cases of each technology. NAS is best for file sharing and backup, while SAN provides faster performance for databases and applications. The document also notes that a combination of NAS and SAN can provide the best of both worlds.Room 3 - 1 - Nguy?n Xu?n Tr??ng L?m - Zero touch on-premise storage infrastru...
Room 3 - 1 - Nguy?n Xu?n Tr??ng L?m - Zero touch on-premise storage infrastru...Vietnam Open Infrastructure User Group
?
Similar to IBM GPFS (20)
IBM general parallel file system - introduction
IBM general parallel file system - introductionIBM Danmark
?
The document provides information about IBM's General Parallel File System (GPFS) 3.5 and introduces the GPFS Storage Server (GSS). It summarizes that GPFS is a scalable high-performance file management system that can scale from 1 to 8192 nodes. The GSS is a new storage solution using IBM servers and JBOD storage to provide high capacity and performance storage in a scalable building block approach. The GSS has no storage controllers and provides a single integrated storage solution built on GPFS software.Gfs
GfsShahbaz Sidhu
?
The document describes the Google File System (GFS), a scalable distributed file system designed and implemented by Google to meet its rapidly growing data storage needs. Key aspects of the GFS design include supporting large files and high throughput appending workloads on inexpensive commodity hardware in the face of frequent component failures. The GFS architecture uses a single master to manage metadata and multiple chunkservers to store and retrieve file chunks, providing fault tolerance through replication.Gfs sosp2003
Gfs sosp2003îŁçů ´Ţ
?
The document describes the Google File System (GFS), a scalable distributed file system designed and implemented by Google to meet its rapidly growing data storage needs. Key aspects of GFS include using inexpensive commodity hardware, supporting large files and high throughput appending, and providing fault tolerance through replication across multiple servers. GFS differs from previous distributed file systems in its focus on high volume appending over rewriting, use of large files, and relaxed consistency to improve performance for Google's specific workload characteristics.GPFS Solution Brief
GPFS Solution BriefIBM India Smarter Computing
?
GPFS is an intelligent storage management solution that can optimize data management and boost return on investment. It provides scalable, high performance access to file data across multiple systems using a global namespace. GPFS leverages a cluster architecture to spread data automatically across storage devices for optimal use of storage and high performance access. It allows applications and users to share access to files simultaneously while maintaining data integrity.Distributed File System
Distributed File SystemNtu
?
The document provides an overview of distributed file systems, including NFS, AFS, Lustre, and others. It discusses key aspects like scalability, consistency, caching, replication, and fault tolerance. Lustre is highlighted as an example of a distributed file system that aims to remove bottlenecks and achieve high scalability through an object-based design with separate metadata and storage servers.Distributed file systems
Distributed file systemsSri Prasanna
?
The Google File System (GFS) was designed by Google to store massive amounts of data across cheap, unreliable hardware. It uses a single master to coordinate metadata and mutations across multiple chunkservers. Files are divided into fixed-size chunks which are replicated for reliability. The design focuses on supporting huge files that are written once and read through streaming, while tolerating high failure rates through replication and relaxed consistency. GFS has proven successful at meeting Google's storage needs at massive scale.Distributed Filesystems Review
Distributed Filesystems ReviewSchubert Zhang
?
The document summarizes and compares several distributed file systems, including Google File System (GFS), Kosmos File System (KFS), Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), GlusterFS, and Red Hat Global File System (GFS). GFS, KFS and HDFS are based on the GFS architecture of a single metadata server and multiple chunkservers. GlusterFS uses a decentralized architecture without a metadata server. Red Hat GFS requires a SAN for high performance and scalability. Each system has advantages and limitations for different use cases.Swiss National Supercomputing Center
Swiss National Supercomputing CenterIBM India Smarter Computing
?
The Swiss National Supercomputing Center (CSCS) needed a centralized storage solution to handle rapidly doubling data volumes from high performance computing simulations. CSCS implemented a solution using IBM General Parallel File System (GPFS) software on IBM hardware, including System x servers and System Storage arrays. GPFS provided high scalability, compatibility across operating systems, parallel access, and failover. The solution supports massively parallel read/write operations and provides extremely high availability and scalability to meet CSCS's growing storage needs.GFS presenttn.pptx
GFS presenttn.pptxEngTennysonSigauke
?
Google File System (GFS) is a distributed file system developed by Google to store and process large amounts of data across its infrastructure. It is highly scalable, fault-tolerant, and optimized for big data. GFS divides files into fixed-size chunks, replicates chunks across servers, and uses a master server to manage metadata and coordinate the system. It provides scalable storage and access to data.4. linux file systems
4. linux file systemsMarian Marinov
?
The document discusses Linux file systems. It begins with an overview of file system architecture, including inodes, dentries, superblocks, and how data is never erased but overwritten. It then covers various local file systems like Ext2, Ext3, Ext4, ReiserFS, and XFS. Next it discusses log-structured and pseudo file systems. It also covers network file systems like NFS and CIFS. Finally it summarizes cluster, distributed, and Hadoop file systems. The document provides a technical overview of Linux file system types, structures, features and capabilities.Course 102: Lecture 27: FileSystems in Linux (Part 2)
Course 102: Lecture 27: FileSystems in Linux (Part 2)Ahmed El-Arabawy
?
The document discusses filesystems in Linux, detailing how user applications interact with storage media through the Virtual File System (VFS) and various filesystem types like ext2, ext3, and ext4, highlighting their features and limitations. It explains the importance of journaling to prevent filesystem corruption and outlines specialized filesystems such as JFFS2 for flash memory and Cramfs for small ROMs. Additionally, it mentions NFS for networked filesystems and virtual filesystems like Procfs and Sysfs managed by the kernel.Topic 11: Google Filesystem
Topic 11: Google FilesystemZubair Nabi
?
The document discusses the Google Filesystem (GFS). It was designed by Google to meet its massive storage needs. The GFS architecture consists of a single master node that manages metadata, and multiple chunkservers that store file data sliced into fixed-size chunks. Each chunk is replicated on multiple servers for reliability. The master handles tasks like chunk leasing, migration, and garbage collection.PostgreSQL Portland Performance Practice Project - Database Test 2 Filesystem...
PostgreSQL Portland Performance Practice Project - Database Test 2 Filesystem...Mark Wong
?
The document discusses the performance evaluation of various Linux filesystems using PostgreSQL and outlines a project conducted at Portland State University. It emphasizes the importance of testing with your own hardware and filesystems, providing detailed results of benchmarks, configuration guidelines, and insights into RAID and I/O performance. The findings highlight that different filesystems and RAID configurations significantly impact performance, and users should consider their specific setups for tuning PostgreSQL effectively.Google file system GFS
Google file system GFSzihad164
?
Google File System is a distributed file system developed by Google to provide efficient and reliable access to large amounts of data across clusters of commodity hardware. It organizes clusters into clients that interface with the system, master servers that manage metadata, and chunkservers that store and serve file data replicated across multiple machines. Updates are replicated for fault tolerance, while the master and chunkservers work together for high performance streaming and random reads and writes of large files.Google file system
Google file systemAnurag Gautam
?
The document describes Google File System (GFS), which is a distributed file system developed by Google to store huge files across inexpensive commodity servers. GFS is fault-tolerant, scalable, and optimized for large streaming reads and appends. It works by dividing files into fixed-size chunks that are replicated and stored across multiple chunkservers, while a master server manages metadata and chunk placement.XFS.ppt
XFS.pptDmitryIg
?
This document provides an overview of journaling file systems and specifically discusses XFS, JFS, and other journaling file systems. It explains that journaling file systems maintain a journal that tracks metadata operations, allowing the file system to restart quickly after an unexpected shutdown by replaying the journal instead of running a lengthy integrity check. The document then describes the design and features of the XFS and JFS journaling file systems, including their use of asynchronous logging, extent-based allocation, support for large file systems and fast crash recovery times.8 1-os file system implementation
8 1-os file system implementationGol D Roger
?
This document discusses various aspects of file system implementation in operating systems. It covers file system structures, directory implementation methods, allocation techniques like contiguous, linked and indexed allocation, free space management using bitmaps and linked lists, performance optimization using caching, and recovery methods like journaling. It also describes network file systems like NFS, which allow remote access to files across networked machines in a transparent manner using client-server architecture and remote procedure calls.Cluster filesystems
Cluster filesystemsMarian Marinov
?
The document summarizes Marian Marinov's presentation on cluster filesystems at the 10th annual Linux User Group Bulgaria meeting. The presentation covered single disk, shared disk, and distributed disk filesystems as well as shared storage solutions like DRBD, iSCSI, and AoE. Specific cluster filesystems discussed included OCFS2, GFS2, PVFS2, and GFarm. Configuration examples and questions from the audience were also mentioned.Seminar Report on Google File System
Seminar Report on Google File SystemVishal Polley
?
The document is a seminar report on the Google File System (GFS), detailing its design, architecture, and operational algorithms, submitted as part of a Bachelor of Technology degree requirement. The GFS is a scalable distributed file system created by Google to efficiently manage large data applications using inexpensive commodity hardware, emphasizing fault tolerance, high availability, and optimized performance for large files. Key design features include a hierarchical structure, chunk-based storage, and a master-server model for metadata management.Network File System in Distributed Computing
Network File System in Distributed ComputingChandan Padalkar
?
NFS (Network File System) was developed by SUN Microsystems in 1984 to allow users to access and share files located on remote computers over a network. It builds on the ONC RPC system and uses a stateless protocol to store files on a network in a way that is easy to recover from failures. NFS is commonly used with UNIX systems but also supports other platforms. It has gone through several versions to support larger files, security improvements, and a stateful protocol in later versions. NFS allows applications on client computers to access and manipulate files on a server computer in a way that is transparent to the user.Ad
IBM GPFS
- 1. GPFS: General Parallel File System Why is it needed? What is GPFS and its features? Where it is being used?
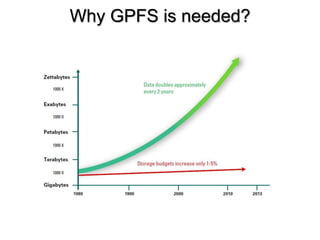
- 2. Why GPFS is needed?
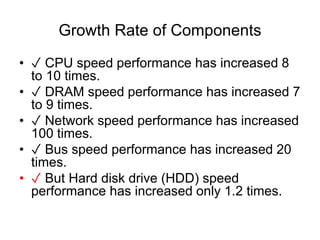
- 3. Growth Rate of Components ? ? CPU speed performance has increased 8 to 10 times. ? ? DRAM speed performance has increased 7 to 9 times. ? ? Network speed performance has increased 100 times. ? ? Bus speed performance has increased 20 times. ? ? But Hard disk drive (HDD) speed performance has increased only 1.2 times.
- 4. Three Important Functions of Enterprise Storage ? ? Store data ? ? Protect data from being lost ? ? Feed data to the computerˇŻs processors (so they can keep doing work)
- 5. Existing Solutions Inability ? DAS, NAS, SAN [alone] ? Many data centers have become victims of ˇ°filer-sprawlˇ± ? Data administration and management (such as migration, backups, archiving) costs to skyrocket! ? I/O performance & application workflow
- 6. What is GPFS ? The General Parallel File System (GPFS) is a high performance clustered file system. It can be deployed in shared disk or shared nothing distributed parallel modes. ? Developer(s): IBM ? Operating system: AIX / Linux / Windows Server ? License: Proprietary ? System Introduced: 1998 (AIX) ? Max. volume size: 8 YB ? Max. file size: 8 EB ? Max. number of files: 264 per file system ? File system permissions: POSIX
- 7. GPFS Current Usage ? It is used by many of the world's largest commercial companies, as well as some of the supercomputers on the Top 500 List. ? For example, GPFS was the filesystem of the ASC Purple Supercomputer which was composed of more than 12,000 processors and 2 petabytes of total disk storage spanning more than 11,000 disks. ? IBM,s GPFS is extensively used across multiple industries like Government, Oil and Gas, Life Sciences, Media/Entertainment, Financial services
- 8. GPFS Features Standard file system interface with POSIX semantics ¨C Metadata on shared storage ¨C Distributed locking for read/write semantics ? Highly scalable ¨C High capacity (up to 2^99 bytes file system size, up to 2^63 files per file system) ¨C High throughput (TB/s) ¨C Wide striping ¨C Large block size (up to 16MB) ¨C Multiple nodes write in parallel ? Advanced data management ¨C ILM (storage pools), Snapshots ¨C Backup HSM (DMAPI) ¨C Remote replication, WAN caching ? High availability ¨C Fault tolerance (node, disk failures) ¨C On-line system management (add/remove nodes, disks, ...)
- 9. References ? GPFS official homepage ? GPFS resources (including download) ? GPFS at Almaden ? GPFS Mailing List ? GPFS User Group ? IBM GPFS Product Documentation ? IBM GPFS Wiki
