Ice Cube gag
Download as pptx, pdf0 likes258 views
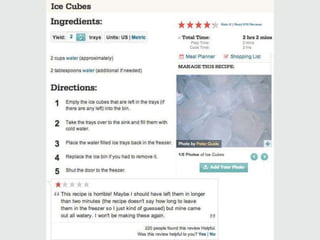
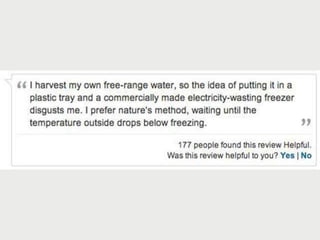
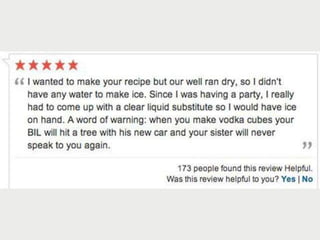
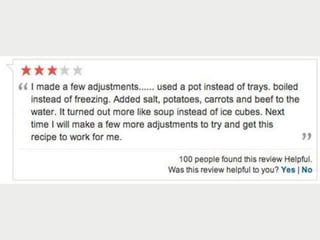
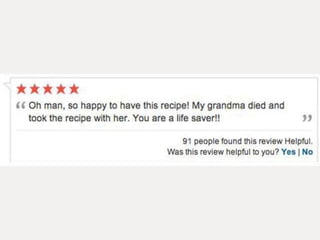
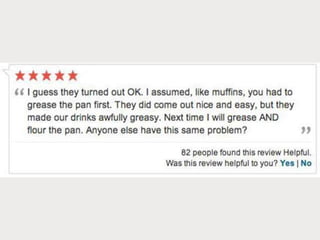
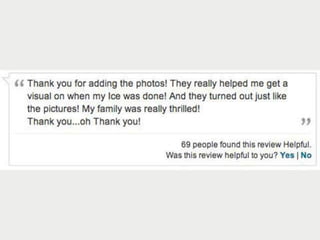
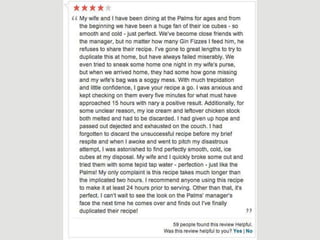
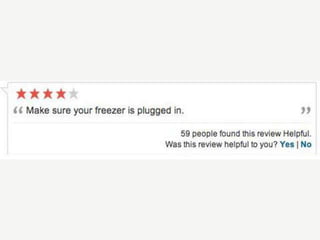
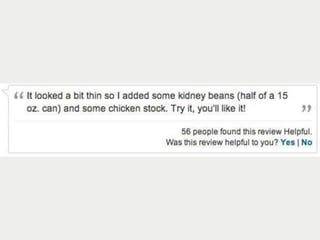
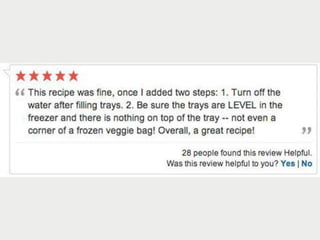
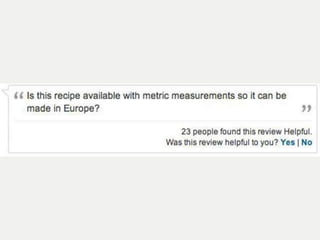
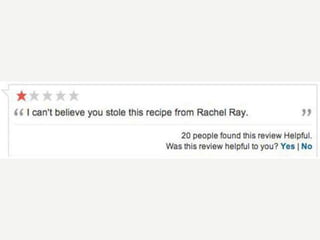
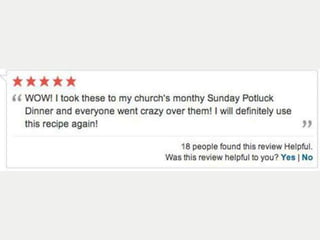
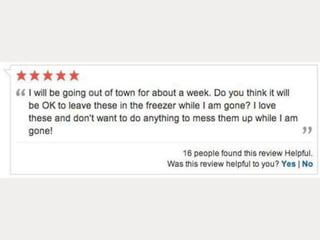
A cooking forum user has uploaded an ice cube recipe to the forum, that led to a funny comment extravaganza.
1 of 17
Download to read offline


Ad
Recommended
Fibre to garments overview
Fibre to garments overviewadanen12
?
The document provides an overview of the processes involved in converting fibres into garments, including:
1) Fibres are converted into yarns through processes like spinning or filament production. Yarns are then converted into fabrics using looms or knitting machines.
2) Fabrics then undergo chemical processes like dyeing, printing, and finishing to add color and properties before being made into garments.
3) The document describes the various fibre types and the key processing stages of yarn production, weaving, knitting, dyeing, printing and finishing that convert fibres into finished garments.Eatless Ice Cube Diet Presentation
Eatless Ice Cube Diet Presentationaliciapuma73
?
The document describes the Ice Cube Diet, which uses fresh frozen Hoodia from the Kalahari Desert to curb appetite and help people eat less and lose weight. Tests showed that participants using the Ice Cube Diet lost significant weight and felt full faster compared to a placebo. The Ice Cube Diet product is produced and frozen within 24 hours of harvesting Hoodia to maintain its natural properties without additives.Ecology review 1
Ecology review 1Fauquier Horticulture
?
The document discusses key concepts in ecology including the principles of energy conservation and transfer through ecosystems. It explains that the sun is the primary source of energy which is captured through photosynthesis and passed between trophic levels in a food web, with energy being lost at each transfer. Due to this energy loss, most food webs only support 4-5 trophic levels before little energy remains.Ice cube experiment photos
Ice cube experiment photosminimoths
?
The document explores an experiment comparing the melting rates of ice cubes treated with coarse and fine salt. It highlights visual changes in the ice due to the addition of food coloring and poses a question about the impact of salt on ice in Antarctica. Additionally, the document mentions an ice water challenge to test how long participants can endure cold water.Textile processing
Textile processing Farhan ullah baig
?
This document provides an overview of various textile processing steps, including:
1) Singeing, which burns off loose fibers to improve fabric quality;
2) Desizing to remove starch sizing using water, acid, or enzymes;
3) Scouring to remove oils and dirt to make fabric absorbent;
4) Bleaching to remove color using hydrogen peroxide, sodium hypochlorite, or sodium chlorite;
5) Dyeing by immersing fabric in dye solutions using different dyes for different fibers.Cellulosic Textile Fibres _ A Review_H?m?l?inen Anu
Cellulosic Textile Fibres _ A Review_H?m?l?inen AnuAnu H?m?l?inen
?
This document is a report on cellulosic textile fibres that provides an overview of:
1) Global fibre production trends showing that cellulosic fibres now account for 6% of the 90 million tons of annual textile fibre production.
2) The major cellulosic fibre technologies including viscose, modal, acetate, lyocell, and emerging technologies like Ioncell and Biocelcol.
3) Viscose production which involves reacting wood pulp with caustic soda and carbon disulfide to form a solution that is spun through a spinneret into a sulphuric acid bath.Fibre to fabric
Fibre to fabricgobilladraksharani
?
1. Sheep flock together for protection but some breeds are more solitary. Wool fibers come from sheep fleece and are processed through several steps like shearing, scouring, sorting, and spinning into yarn.
2. Silk fibers are produced by silkworm caterpillars spinning cocoons; the female moth lays eggs and caterpillars eat mulberry leaves then spin cocoons from which fibers are reeled to make silk cloth.
3. Alpacas graze in herds in the Andes mountains and are smaller than llamas, which were domesticated as beasts of burden.Ice Age
Ice AgeSuresh Singh
?
The document discusses plans by Ice Age Ltd. to set up ice cream manufacturing and parlors in India. It analyzes the Indian ice cream market, which is currently dominated by domestic brands. Ice Age Ltd. will produce different ice cream flavors at its production site and distribute them to company parlors. It discusses locating parlors in major malls in Delhi and conducting market research to understand customers, competitors, and the external environment. The company aims to offer healthy, low-sugar ice cream options. Future plans include expanding franchises and manufacturing facilities across India.fibre to fabric
fibre to fabricprincespriya
?
This document discusses different animals that are sources of wool and the properties of their wool. It lists yak, angora goat, kashmiri goat, camel, alpaca, llama as wool yielding animals. It then provides details about each animal's origin, the properties of wool obtained from it and its uses. The document also summarizes the steps involved in processing wool obtained from sheep into usable fibers like sorting, scouring, dyeing, combing and rolling into yarn.Ice syndrome
Ice syndromeLaxmi Eye Institute
?
This document presents a case study of a 27-year-old female patient with iridocorneal endothelial syndrome (ICE) in her left eye. Her symptoms included diminished vision and pain in the left eye for 2 months. Ocular examination revealed findings consistent with ICE including iris defects, irregular anterior chamber depth, and specular microscopy showing polymegathism with a silver beaten appearance in the left eye. The patient was diagnosed with refractive error in the right eye and ICE in the left eye. She was prescribed eye drops and followed up regularly, with her IOP remaining controlled.Tutorial desactivar notificaciones en el mailICE
?
Este documento proporciona un tutorial de 3 pasos para desactivar las notificaciones por correo electrónico del aula virtual. Primero, los usuarios deben hacer clic en su foto de perfil y luego en "Perfil y Preferencias". Segundo, deben hacer clic en la pesta?a "Preferencias" y desmarcar la opción "Recibir noticias". Por último, deben guardar los cambios haciendo clic en "Guardar".Fibre to fabric
Fibre to fabricanshul tomar
?
Wool comes from sheep and other animals like goats, muskoxen, and rabbits. There are different breeds of sheep that produce wool suitable for various purposes. Nali sheep from Rajasthan and Punjab produce wool for carpets. Patanwadi sheep from Gujarat produce wool for hosiery clothing. Rampur bushair sheep from Uttar Pradesh and Himachal Pradesh produce brown fleece wool. Sheep require different foods in winter and summer and their wool is sheared or removed mechanically in spring. The wool is then scoured to remove dirt before being sorted by texture and quality for various end uses like clothing or rugs.Wet processing of cellulose textiles.1
Wet processing of cellulose textiles.1Oliyad Ebba
?
The document discusses the chemical processing and pre-treatment of cotton fabrics, detailing the objectives and importance of fabric preparation to remove impurities for effective dye uptake and improved appearance. It outlines various preparatory operations such as singeing, desizing, scouring, and bleaching, including the chemicals involved and their mechanisms. The document also covers quality control measures and the effects of bleaching on fabric properties, emphasizing the balance between desired whiteness and strength retention.Textile Fiber & Yarn
Textile Fiber & Yarn faruq2013
?
The document provides a comprehensive overview of various types of textile fibers, detailing natural and synthetic fibers, including their characteristics, yarn types, and pricing. It also includes flow charts for yarn production processes and methods for measuring yarn count and fabric properties. Additionally, it discusses the pricing of various yarns and offers a price quotation for knit yarn from a Bangladeshi textile company.Fibre to fabric
Fibre to fabricSasi Palakkad
?
This document discusses various natural and synthetic fibers used for clothing and textiles, including fibers obtained from animals like sheep, goats, llamas, alpacas and camels. It also outlines plant-based fibers like cotton, jute, coconut and banana and how they are obtained from plants. The document provides details about the cultivation of important natural fibers like cotton and jute in countries like India.Textile fibre
Textile fibreHadiul Islam
?
This document discusses the fundamentals of textiles and classification of fibers. It covers natural, regenerated, and synthetic man-made fibers. The key fiber production processes of melt, dry, and wet spinning are compared. Melt spinning involves melting the polymer and extruding filaments. Dry spinning uses solvent evaporation. Wet spinning hardens the filaments through chemical coagulation in a bath. Viscose rayon and lyocell manufacturing processes are also outlined.Fibre to Fabric
Fibre to Fabricfazalrehmani
?
Fibres are classified into two main groups:
1) Natural fibres from plant and animal sources like cotton, jute, silk, and wool.
2) Man-made fibres produced from chemical substances like rayon, polyester, nylon, and acrylic.
Fibres are also classified based on their length as either staple (short) fibres or filament (long) fibres. Fibres are spun into yarns which are made up of twisted fibres. Yarns are then interlaced in various weaves and knitting techniques to form fabrics for clothing and other uses.Textile fiber theory
Textile fiber theory Niket Bhandari
?
Textile fibers are the basic building blocks used to manufacture fabric. They come in two main lengths - staple fibers which are short, and filament fibers which are very long. Fibers also come from natural, regenerated, or synthetic sources. Cotton is a widely used natural staple fiber obtained from plant seeds. It has good strength and absorbency but is relatively inelastic. Cotton burns readily with the smell of burning paper and is damaged by concentrated acids.Fiber To Fabrics Textile
Fiber To Fabrics TextileDeepanshu Singh Kushwaha
?
This document summarizes textile processing techniques across the textile supply chain, from fiber production through recycling and disposal. It is split into seven main sections: fiber production, fiber to fabric, preparative treatments, textile coloration, finishing processes, fabric aftercare, and recycling/disposal. Under fiber production, it describes the cultivation of cotton, rearing of sheep, sericulture (silk production), and manufacturing of synthetic fibers like polyester, nylon, acrylic, and viscose. It provides details on the key steps for each natural and synthetic fiber production method.Cellulose presentation
Cellulose presentationGazi A. Rahman Nahid
?
The document provides an overview of cellulose, detailing its formation, structure, properties, and various applications. Cellulose is identified as a polysaccharide composed of glucose units, serving as a key structural component in plants and a promising carbon sequestering material. It highlights its uses in textiles, pharmaceuticals, and biofuel production, among others.Difference between reactive dye and disperse dye on fabric
Difference between reactive dye and disperse dye on fabricAzmir Latif Beg
?
The document discusses the significance and procedures for using reactive and disperse dyes in fabric dyeing, particularly emphasizing their applications to cotton and polyester fabrics. It explains the chemical reactions, optimal conditions (such as pH and temperature), and common practices for dyeing processes to achieve desired color fastness and properties. Additionally, it differentiates between reactive and disperse dyes regarding their characteristics, methodologies, and implications for dyeing efficiency.Fabric & fibres
Fabric & fibresDr. Sunil Kumar
?
This document provides information about textile fibers and fabrics. It begins by defining what a textile is. It then classifies textile fibers into two main categories: natural fibers and man-made fibers. Several examples are provided for each type of fiber. The document also discusses the processes involved in transforming fibers into yarns and then into various types of fabrics, including weaving techniques like plain weave, satin weave, twill weave and more. Fabric treatments and care are also briefly mentioned.Textiles Basic Processes
Textiles Basic ProcessesMuhammad Shaoib Asad Khalid
?
The document outlines the key processes involved in simple textile production from spinning yarns through weaving fabrics and basic garment construction including blowing, carding, drawing, ring spinning, warping, sizing, drawing-in, weaving, inspection, mending, pretreatment, bleaching, mercerizing, dyeing, printing, finishing, pattern design, cutting, bundling, embellishment, and stitching. The processes transform fibers into yarns, yarns into fabrics, and fabrics into useable garments or home textiles through various mechanical and chemical treatments.Cellulose and it's properties
Cellulose and it's propertiesMd. Sajjad Hossain Tuhin
?
The document discusses cellulose, including its structure, properties, production in plants, and uses. Some key points:
- Cellulose is the most abundant organic substance on Earth and is made of linear chains of glucose molecules linked together.
- It has a crystalline structure that gives it strength and it forms microfibrils in plant cell walls.
- Plants produce cellulose at their plasma membranes using enzyme complexes that spin the cellulose chains.
- Cellulose is strong, stable, and insoluble but can absorb some water. It is used to make products like cotton, paper, cellophane, and cellulose derivatives.Textile Fiber ppt by B.A
Textile Fiber ppt by B.ABademaw Abate
?
The document provides an introduction to textile fibers, defining key terms such as fiber, fabric, and apparel, and explaining the essential characteristics and classifications of different fiber types. It discusses both natural and man-made fibers, their properties, and the process of converting them into yarn and fabric. Additionally, it highlights the importance of elasticity, strength, and other attributes that determine the suitability of fibers for textile applications.Costa Rica
Costa RicaMihex
?
The beautiful shores, the views, the forests and the welcoming people are some of the reason Costa Rica became such a popular tourist destination. Jay-Z's Problems
Jay-Z's ProblemsMihex
?
The designer Ali Graham takes a shot at figuring out what are those 99 problems Jay-Z keeps talking about.The Solar Impulse
The Solar ImpulseMihex
?
For the first time ever a fully solar powered solar plane the "Solar Impulse", made a coast to coast flight.IKEA Folding House
IKEA Folding HouseMihex
?
IKEA came up with this design as a temporary housing solution for natural disaster refugees.Food on Instagram
Food on InstagramMihex
?
Well, this is a well known internet phenomena - Food on Instagram. Everybody take pictures of their meal and upload it.More Related Content
Viewers also liked (17)
fibre to fabric
fibre to fabricprincespriya
?
This document discusses different animals that are sources of wool and the properties of their wool. It lists yak, angora goat, kashmiri goat, camel, alpaca, llama as wool yielding animals. It then provides details about each animal's origin, the properties of wool obtained from it and its uses. The document also summarizes the steps involved in processing wool obtained from sheep into usable fibers like sorting, scouring, dyeing, combing and rolling into yarn.Ice syndrome
Ice syndromeLaxmi Eye Institute
?
This document presents a case study of a 27-year-old female patient with iridocorneal endothelial syndrome (ICE) in her left eye. Her symptoms included diminished vision and pain in the left eye for 2 months. Ocular examination revealed findings consistent with ICE including iris defects, irregular anterior chamber depth, and specular microscopy showing polymegathism with a silver beaten appearance in the left eye. The patient was diagnosed with refractive error in the right eye and ICE in the left eye. She was prescribed eye drops and followed up regularly, with her IOP remaining controlled.Tutorial desactivar notificaciones en el mailICE
?
Este documento proporciona un tutorial de 3 pasos para desactivar las notificaciones por correo electrónico del aula virtual. Primero, los usuarios deben hacer clic en su foto de perfil y luego en "Perfil y Preferencias". Segundo, deben hacer clic en la pesta?a "Preferencias" y desmarcar la opción "Recibir noticias". Por último, deben guardar los cambios haciendo clic en "Guardar".Fibre to fabric
Fibre to fabricanshul tomar
?
Wool comes from sheep and other animals like goats, muskoxen, and rabbits. There are different breeds of sheep that produce wool suitable for various purposes. Nali sheep from Rajasthan and Punjab produce wool for carpets. Patanwadi sheep from Gujarat produce wool for hosiery clothing. Rampur bushair sheep from Uttar Pradesh and Himachal Pradesh produce brown fleece wool. Sheep require different foods in winter and summer and their wool is sheared or removed mechanically in spring. The wool is then scoured to remove dirt before being sorted by texture and quality for various end uses like clothing or rugs.Wet processing of cellulose textiles.1
Wet processing of cellulose textiles.1Oliyad Ebba
?
The document discusses the chemical processing and pre-treatment of cotton fabrics, detailing the objectives and importance of fabric preparation to remove impurities for effective dye uptake and improved appearance. It outlines various preparatory operations such as singeing, desizing, scouring, and bleaching, including the chemicals involved and their mechanisms. The document also covers quality control measures and the effects of bleaching on fabric properties, emphasizing the balance between desired whiteness and strength retention.Textile Fiber & Yarn
Textile Fiber & Yarn faruq2013
?
The document provides a comprehensive overview of various types of textile fibers, detailing natural and synthetic fibers, including their characteristics, yarn types, and pricing. It also includes flow charts for yarn production processes and methods for measuring yarn count and fabric properties. Additionally, it discusses the pricing of various yarns and offers a price quotation for knit yarn from a Bangladeshi textile company.Fibre to fabric
Fibre to fabricSasi Palakkad
?
This document discusses various natural and synthetic fibers used for clothing and textiles, including fibers obtained from animals like sheep, goats, llamas, alpacas and camels. It also outlines plant-based fibers like cotton, jute, coconut and banana and how they are obtained from plants. The document provides details about the cultivation of important natural fibers like cotton and jute in countries like India.Textile fibre
Textile fibreHadiul Islam
?
This document discusses the fundamentals of textiles and classification of fibers. It covers natural, regenerated, and synthetic man-made fibers. The key fiber production processes of melt, dry, and wet spinning are compared. Melt spinning involves melting the polymer and extruding filaments. Dry spinning uses solvent evaporation. Wet spinning hardens the filaments through chemical coagulation in a bath. Viscose rayon and lyocell manufacturing processes are also outlined.Fibre to Fabric
Fibre to Fabricfazalrehmani
?
Fibres are classified into two main groups:
1) Natural fibres from plant and animal sources like cotton, jute, silk, and wool.
2) Man-made fibres produced from chemical substances like rayon, polyester, nylon, and acrylic.
Fibres are also classified based on their length as either staple (short) fibres or filament (long) fibres. Fibres are spun into yarns which are made up of twisted fibres. Yarns are then interlaced in various weaves and knitting techniques to form fabrics for clothing and other uses.Textile fiber theory
Textile fiber theory Niket Bhandari
?
Textile fibers are the basic building blocks used to manufacture fabric. They come in two main lengths - staple fibers which are short, and filament fibers which are very long. Fibers also come from natural, regenerated, or synthetic sources. Cotton is a widely used natural staple fiber obtained from plant seeds. It has good strength and absorbency but is relatively inelastic. Cotton burns readily with the smell of burning paper and is damaged by concentrated acids.Fiber To Fabrics Textile
Fiber To Fabrics TextileDeepanshu Singh Kushwaha
?
This document summarizes textile processing techniques across the textile supply chain, from fiber production through recycling and disposal. It is split into seven main sections: fiber production, fiber to fabric, preparative treatments, textile coloration, finishing processes, fabric aftercare, and recycling/disposal. Under fiber production, it describes the cultivation of cotton, rearing of sheep, sericulture (silk production), and manufacturing of synthetic fibers like polyester, nylon, acrylic, and viscose. It provides details on the key steps for each natural and synthetic fiber production method.Cellulose presentation
Cellulose presentationGazi A. Rahman Nahid
?
The document provides an overview of cellulose, detailing its formation, structure, properties, and various applications. Cellulose is identified as a polysaccharide composed of glucose units, serving as a key structural component in plants and a promising carbon sequestering material. It highlights its uses in textiles, pharmaceuticals, and biofuel production, among others.Difference between reactive dye and disperse dye on fabric
Difference between reactive dye and disperse dye on fabricAzmir Latif Beg
?
The document discusses the significance and procedures for using reactive and disperse dyes in fabric dyeing, particularly emphasizing their applications to cotton and polyester fabrics. It explains the chemical reactions, optimal conditions (such as pH and temperature), and common practices for dyeing processes to achieve desired color fastness and properties. Additionally, it differentiates between reactive and disperse dyes regarding their characteristics, methodologies, and implications for dyeing efficiency.Fabric & fibres
Fabric & fibresDr. Sunil Kumar
?
This document provides information about textile fibers and fabrics. It begins by defining what a textile is. It then classifies textile fibers into two main categories: natural fibers and man-made fibers. Several examples are provided for each type of fiber. The document also discusses the processes involved in transforming fibers into yarns and then into various types of fabrics, including weaving techniques like plain weave, satin weave, twill weave and more. Fabric treatments and care are also briefly mentioned.Textiles Basic Processes
Textiles Basic ProcessesMuhammad Shaoib Asad Khalid
?
The document outlines the key processes involved in simple textile production from spinning yarns through weaving fabrics and basic garment construction including blowing, carding, drawing, ring spinning, warping, sizing, drawing-in, weaving, inspection, mending, pretreatment, bleaching, mercerizing, dyeing, printing, finishing, pattern design, cutting, bundling, embellishment, and stitching. The processes transform fibers into yarns, yarns into fabrics, and fabrics into useable garments or home textiles through various mechanical and chemical treatments.Cellulose and it's properties
Cellulose and it's propertiesMd. Sajjad Hossain Tuhin
?
The document discusses cellulose, including its structure, properties, production in plants, and uses. Some key points:
- Cellulose is the most abundant organic substance on Earth and is made of linear chains of glucose molecules linked together.
- It has a crystalline structure that gives it strength and it forms microfibrils in plant cell walls.
- Plants produce cellulose at their plasma membranes using enzyme complexes that spin the cellulose chains.
- Cellulose is strong, stable, and insoluble but can absorb some water. It is used to make products like cotton, paper, cellophane, and cellulose derivatives.Textile Fiber ppt by B.A
Textile Fiber ppt by B.ABademaw Abate
?
The document provides an introduction to textile fibers, defining key terms such as fiber, fabric, and apparel, and explaining the essential characteristics and classifications of different fiber types. It discusses both natural and man-made fibers, their properties, and the process of converting them into yarn and fabric. Additionally, it highlights the importance of elasticity, strength, and other attributes that determine the suitability of fibers for textile applications.More from Mihex (20)
Costa Rica
Costa RicaMihex
?
The beautiful shores, the views, the forests and the welcoming people are some of the reason Costa Rica became such a popular tourist destination. Jay-Z's Problems
Jay-Z's ProblemsMihex
?
The designer Ali Graham takes a shot at figuring out what are those 99 problems Jay-Z keeps talking about.The Solar Impulse
The Solar ImpulseMihex
?
For the first time ever a fully solar powered solar plane the "Solar Impulse", made a coast to coast flight.IKEA Folding House
IKEA Folding HouseMihex
?
IKEA came up with this design as a temporary housing solution for natural disaster refugees.Food on Instagram
Food on InstagramMihex
?
Well, this is a well known internet phenomena - Food on Instagram. Everybody take pictures of their meal and upload it.Planets Suitable For Life
Planets Suitable For Life Mihex
?
During the years of space research NASA came across a number of planets and moon that are suitable for the development of life as we know it. Here are some of them. Floods In India
Floods In IndiaMihex
?
With the monsoon season in full rage, wast areas of India are suffering from extensive flood damage. The National Geographic Photo Contest 2013
The National Geographic Photo Contest 2013Mihex
?
The amazing entrees of the National Geographic magazine photo contest for the year 2013.Turkey Protests
Turkey ProtestsMihex
?
The big wave of protests that started on the 28th of May 2013 in Turkey, brought about 2.5 million people to the streets.The Graffiti Church
The Graffiti ChurchMihex
?
This church in Atlanta, Georgia, wanted to update it's look, so it asked the graffiti artist Hense for help.Real Life Hobbit House
Real Life Hobbit HouseMihex
?
An enthusiastic admirer of J.R.R. Tolkien have built a real life hobbit house with all the details.Affordable Housing In New York
Affordable Housing In New YorkMihex
?
The housing prices in New York are so high, that those terrible places qualify as "Affordable Housing". Lamborghini Egoista
Lamborghini EgoistaMihex
?
Lamborghini are celebrating their 50th anniversary with this very special model, that can only host the driver.Spring
SpringMihex
?
Beautiful photography of my favorite time of the year, the spring, when everything is in bloom and so fresh.Surprising Historical Facts
Surprising Historical Facts Mihex
?
We think we know some historical items for facts' but the real case can be very surprising. Traveler Photo Contest 2013
Traveler Photo Contest 2013Mihex
?
The excellent finalists of the annual nature Photo Contest held by the Traveler magazine for 2013.American Ghetto
American Ghetto Mihex
?
Pictures, some of them with a touch of humor, of how it is to live in an American Ghetto.Ad
Recently uploaded (17)
Top 1 app watch girls livestream (1).docx
Top 1 app watch girls livestream (1).docxjonhsey0009
?
hotlive51 Platform Live Terbaik
hotlive51 tampilkan hot 51 live via hot51 live mod apk stabil. Streaming lancar tanpa lag! #hot51 #hot51live #hot51idid
hot 51 mod apk Tanpa Iklan
hot 51 mod apk berikan akses ke hot51 live dan apk hot51 lengkap. Tanpa gangguan iklan! #hot51 #hot51live #hot51idid
hot51 apk Versi Resmi 2024
hot51 apk terbaru mendukung hot live melalui hot51 live mod apk teroptimasi. Unduh sekarang! #hot51 #hot51live #hot51idid
原版一样(滨奥鲍毕业证书)美国印第安纳卫斯里大学毕业证在线购买
原版一样(滨奥鲍毕业证书)美国印第安纳卫斯里大学毕业证在线购买taqyed
?
鉴于此,办理IWU大学毕业证印第安纳卫斯里大学毕业证书【q薇1954292140】留学一站式办理学历文凭直通车(印第安纳卫斯里大学毕业证IWU成绩单原版印第安纳卫斯里大学学位证假文凭)未能正常毕业?【q薇1954292140】办理印第安纳卫斯里大学毕业证成绩单/留信学历认证/学历文凭/使馆认证/留学回国人员证明/录取通知书/Offer/在读证明/成绩单/网上存档永久可查!
如果您处于以下几种情况:
◇在校期间,因各种原因未能顺利毕业……拿不到官方毕业证
◇面对父母的压力,希望尽快拿到;
◇不清楚认证流程以及材料该如何准备;
◇回国时间很长,忘记办理;
◇回国马上就要找工作,办给用人单位看;
◇企事业单位必须要求办理的
◇需要报考公务员、购买免税车、落转户口
◇申请留学生创业基金
【办理印第安纳卫斯里大学成绩单Buy Indiana Wesleyan University Transcripts】
购买日韩成绩单、英国大学成绩单、美国大学成绩单、澳洲大学成绩单、加拿大大学成绩单(q微1954292140)新加坡大学成绩单、新西兰大学成绩单、爱尔兰成绩单、西班牙成绩单、德国成绩单。成绩单的意义主要体现在证明学习能力、评估学术背景、展示综合素质、提高录取率,以及是作为留信认证申请材料的一部分。
印第安纳卫斯里大学成绩单能够体现您的的学习能力,包括印第安纳卫斯里大学课程成绩、专业能力、研究能力。(q微1954292140)具体来说,成绩报告单通常包含学生的学习技能与习惯、各科成绩以及老师评语等部分,因此,成绩单不仅是学生学术能力的证明,也是评估学生是否适合某个教育项目的重要依据!Jordan Minnesota - The Town Where Your Diet Comes to Die
Jordan Minnesota - The Town Where Your Diet Comes to DieForklift Trucks in Minnesota
?
You ever try to pick a place to eat in Jordan, Minnesota? It’s like being dropped in the middle of a delicious labyrinth with no map, no compass, and way too many good smells coming from all directions. One minute you’re thinking, “Eh, I’ll just grab something quick,” and the next thing you know, you’re halfway through a plate of brisket that tastes like it was slow-cooked by angels and blessed by a pitmaster with a doctorate in flavor.
Pizza? They've got enough cheesy, crusty goodness to start a small but passionate fan club. Tacos? Yes, please—and not the kind that fall apart the second you look at them sideways. We're talking hand-held miracles. Craving something sweet? Boom—bakery case. Cookies the size of your face, pies that look like they should be in a museum, and cupcakes that actually spark joy.
There’s no “just grab a bite” in Jordan. You either commit to the flavor adventure or get out of the way. Trying to decide where to go is like arguing with your stomach in five languages. It's not a question of if you'll find something good—it’s how many meals you can fit into one afternoon without needing a forklift to get back to your car.Dana Guerin - A Film Producer And Philanthropist
Dana Guerin - A Film Producer And PhilanthropistDana Guerin
?
Dana Guerin is a film producer and philanthropist dedicated to advancing healthcare access and supporting the arts. She serves as a commissioner on the Los Angeles County Prevention and Community Health Task Force, co-leading the Black Maternal Health and Infant Mortality Ad Hoc. As the founder of Guerin Children’s at Cedars-Sinai, she has been pivotal in expanding pediatric healthcare. Her film career specializes in horror productions, with notable works including The Taking of Deborah Logan and Hargrove.办理学历认证鲍厂颁学生证西班牙圣地亚哥德孔波斯特拉大学电子毕业证,鲍厂颁成绩单防伪
办理学历认证鲍厂颁学生证西班牙圣地亚哥德孔波斯特拉大学电子毕业证,鲍厂颁成绩单防伪Taqyea
?
1:1原版西班牙圣地亚哥德孔波斯特拉大学毕业证文凭【Q微:1954 292 140】鉴于此,USCdiploma圣地亚哥德孔波斯特拉大学挂科处理解决方案USC毕业证成绩单专业服务学历认证【Q微:1954 292 140】一比一还原国外大学毕业证,定制国外大学学历,制作国外大学文凭,复刻国外大学毕业证书。学位证1:1完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。
【圣地亚哥德孔波斯特拉大学成绩单一站式办理专业技术完美呈现Universidad de Santiago de Compostela Transcripts】
购买日韩成绩单、英国大学成绩单、美国大学成绩单、澳洲大学成绩单、加拿大大学成绩单(q微1954292140)新加坡大学成绩单、新西兰大学成绩单、爱尔兰成绩单、西班牙成绩单、德国成绩单。成绩单的意义主要体现在证明学习能力、评估学术背景、展示综合素质、提高录取率,以及是作为留信认证申请材料的一部分。
圣地亚哥德孔波斯特拉大学成绩单能够体现您的的学习能力,包括圣地亚哥德孔波斯特拉大学课程成绩、专业能力、研究能力。(q微1954292140)具体来说,成绩报告单通常包含学生的学习技能与习惯、各科成绩以及老师评语等部分,因此,成绩单不仅是学生学术能力的证明,也是评估学生是否适合某个教育项目的重要依据!
国外留学无法毕业的留学生(即没有获得毕业证书和学位证书的情况下)想要在中国进行学历认证,通常不能通过正常的学历认证流程进行认证,因为正常的学历认证需要提供有效的毕业证书和学位证书,以及其他相关的学业文件。
在这种情况下,留学生可以选择通过留学服务中心的留信认证来尝试认证他们的学习经历。具体来说,留信认证是针对没有获得正规学位或毕业证书的学生,通过提供学习经历、课程成绩等材料,进行学业经历的认证。16 Billions Google Leaked Password Alert in 2025
16 Billions Google Leaked Password Alert in 2025Harshh Goel
?
In 2025, Google issued a critical alert after discovering over 16 billion usernames and passwords exposed in a massive global data breach. The Google Leaked Password Alert warns users that their login credentials may be part of a leaked password database, putting personal accounts at serious risk. This unprecedented password data leak highlights the urgent need for strong, unique passwords and immediate security action.
For More Information Visit Our Website - www.Bumppy.com
Rice Genomics & Whole Genome Sequencing.pptx
Rice Genomics & Whole Genome Sequencing.pptxLikhithHR
?
This presentation delves into the fascinating journey of rice genomics and whole genome sequencing, charting the evolution from early marker development to cutting-edge genome editing and pan-genomics. Rice (Oryza sativa) is not only a staple crop feeding over half the global population but also a model organism for cereal genomics due to its relatively small genome, rich genetic diversity, and high synteny with other grasses like wheat and maize. The presentation outlines why rice was the first crop plant to be fully sequenced and traces the contributions of international consortia such as IRGSP, Syngenta, and Monsanto, along with India’s role in sequencing chromosome 11 through the Indian Initiative for Rice Genome Sequencing (IIRGS). Detailed insights are provided into map-based sequencing methods, clone-by-clone strategies, and hierarchical shotgun sequencing, including how BAC and PAC libraries enabled high-quality genome assemblies. The sequencing of Nipponbare (japonica) laid the foundation for comprehensive rice genome annotation, revealing over 37,000 coding genes, extensive gene duplications, and a high density of transposable elements. The presentation explores the impact of rice genomic data on the development of molecular markers (SSRs, SNPs, InDels, ILPs), comparative genomics, structural and functional annotation, and custom-made markers for precision breeding. Advances post-genome era, including the 3K Rice Genome Project and updates in the Rice Genome Annotation Project (RGAP), are discussed along with emerging tools like pan-genomics, synteny maps, and RNA-seq-based expression profiling. Special attention is given to the sequencing and functional relevance of rice mitochondrial and chloroplast genomes, which play roles in energy metabolism, cytoplasmic male sterility, and hybrid breeding. Recent breakthroughs such as the activation of BBM1 and WOX9A genes for clonal seed development highlight the potential of synthetic apomixis. The talk concludes with reflections on the transformative impact of rice genome sequencing on crop improvement, enabling breeders to enhance yield, stress resilience, and nutritional quality through genomics-assisted selection and genome editing. This presentation serves as a comprehensive guide for students, researchers, and breeders navigating the landscape of rice genomics in the era of precision agriculture在线购买西班牙毕业证安东尼奥·德·内夫里哈大学文凭鲍础狈贰学费单
在线购买西班牙毕业证安东尼奥·德·内夫里哈大学文凭鲍础狈贰学费单Taqyea
?
1:1原版安东尼奥·德·内夫里哈大学毕业证+UANE成绩单【Q微:1954 292 140】鉴于此,UANEdiploma安东尼奥·德·内夫里哈大学挂科处理解决方案UANE毕业证成绩单专业服务学历认证【Q微:1954 292 140】办理教育部学历认证,留学回国证明,安东尼奥·德·内夫里哈大学毕业证、安东尼奥·德·内夫里哈大学成绩单、安东尼奥·德·内夫里哈大学文凭(留信学历认证+永久存档查询)办理本科+硕士+博士毕业证成绩单学历认证,我们一直是留学生的首选,质量行业第一,诚信可靠。
【安东尼奥·德·内夫里哈大学成绩单一站式办理专业技术完美呈现Universidad Antonio de Nebrija Transcripts】
购买日韩成绩单、英国大学成绩单、美国大学成绩单、澳洲大学成绩单、加拿大大学成绩单(q微1954292140)新加坡大学成绩单、新西兰大学成绩单、爱尔兰成绩单、西班牙成绩单、德国成绩单。成绩单的意义主要体现在证明学习能力、评估学术背景、展示综合素质、提高录取率,以及是作为留信认证申请材料的一部分。
安东尼奥·德·内夫里哈大学成绩单能够体现您的的学习能力,包括安东尼奥·德·内夫里哈大学课程成绩、专业能力、研究能力。(q微1954292140)具体来说,成绩报告单通常包含学生的学习技能与习惯、各科成绩以及老师评语等部分,因此,成绩单不仅是学生学术能力的证明,也是评估学生是否适合某个教育项目的重要依据!
【主营项目】
一.毕业证【q微1954292140】成绩单、使馆认证、教育部认证、雅思托福成绩单、学生卡等!
二.真实使馆公证(即留学回国人员证明,不成功不收费)
三.真实教育部学历学位认证(教育部存档!教育部留服网站永久可查)
四.办理各国各大学文凭(一对一专业服务,可全程监控跟踪进度)tiranga ritik baclink indexing on google
tiranga ritik baclink indexing on googleJalwa Game
?
https://docs.google.com/document/d/e/2PACX-1vSxIF1IqzJzVdfn-DgKgG61T7BPE-jhWREkaZIm96Mi4DDv39p82OsCx_HwsViHgb2vxXtXlr_0XejZ/pub仿制颁厂鲍厂学费单美国加利福尼亚州立大学萨克拉门托分校毕业证范本,颁厂鲍厂文凭
仿制颁厂鲍厂学费单美国加利福尼亚州立大学萨克拉门托分校毕业证范本,颁厂鲍厂文凭taqyed
?
鉴于此,办理CSUS大学毕业证加利福尼亚州立大学萨克拉门托分校毕业证书【q薇1954292140】留学一站式办理学历文凭直通车(加利福尼亚州立大学萨克拉门托分校毕业证CSUS成绩单原版加利福尼亚州立大学萨克拉门托分校学位证假文凭)未能正常毕业?【q薇1954292140】办理加利福尼亚州立大学萨克拉门托分校毕业证成绩单/留信学历认证/学历文凭/使馆认证/留学回国人员证明/录取通知书/Offer/在读证明/成绩单/网上存档永久可查!
如果您处于以下几种情况:
◇在校期间,因各种原因未能顺利毕业……拿不到官方毕业证
◇面对父母的压力,希望尽快拿到;
◇不清楚认证流程以及材料该如何准备;
◇回国时间很长,忘记办理;
◇回国马上就要找工作,办给用人单位看;
◇企事业单位必须要求办理的
◇需要报考公务员、购买免税车、落转户口
◇申请留学生创业基金
【办理加利福尼亚州立大学萨克拉门托分校成绩单Buy California State University, Sacramento Transcripts】
购买日韩成绩单、英国大学成绩单、美国大学成绩单、澳洲大学成绩单、加拿大大学成绩单(q微1954292140)新加坡大学成绩单、新西兰大学成绩单、爱尔兰成绩单、西班牙成绩单、德国成绩单。成绩单的意义主要体现在证明学习能力、评估学术背景、展示综合素质、提高录取率,以及是作为留信认证申请材料的一部分。
加利福尼亚州立大学萨克拉门托分校成绩单能够体现您的的学习能力,包括加利福尼亚州立大学萨克拉门托分校课程成绩、专业能力、研究能力。(q微1954292140)具体来说,成绩报告单通常包含学生的学习技能与习惯、各科成绩以及老师评语等部分,因此,成绩单不仅是学生学术能力的证明,也是评估学生是否适合某个教育项目的重要依据!The Bet - Concept Teaser v06 Storyboards
The Bet - Concept Teaser v06 StoryboardsJim Mortensen
?
"THE BET" : God & the Devil wagering on which one of them is better at convincing a family to stick with them despite ruining their lives on a daily basis.Strategy & Survival in Aliens Another Glorious Day in the Corps!
Strategy & Survival in Aliens Another Glorious Day in the Corps!BoardGamesNMore
?
Dive into the high-stakes world of Aliens: Another Glorious Day in the Corps! This PPT explores key strategies, survival tips, and co-op mechanics that make this game a must-play for sci-fi and board game enthusiasts. Perfect for fans of tactical teamwork!Breaking the Romance Narrative – Why I Wrote “Hello”
Breaking the Romance Narrative – Why I Wrote “Hello”itstriggerhere
?
? Hello isn’t just another Telugu R&B track.
It’s a rebellion wrapped in melody. A conversation I’ve had with love, boundaries, and personal freedom.
As a music producer and artist, I’ve always felt stuck between two extremes — either glorify love or completely reject it.
But what if we showed the grey?
The emotional chaos? The unapologetic detachment?
"Hello" is for everyone who’s tired of being boxed in — the bad boys, the misunderstood ones, the ones who choose themselves.
The lyrics touch on:
Romantic fatigue
Sarcastic surrender
Self-realization
Hyper-masculinity vs vulnerability
All layered with smooth hip hop and R&B textures.
? Listen to it, and you'll either judge me or feel seen.
Either way, the conversation starts here.
Let’s normalize songs that don’t glorify suffering in love.
Let’s talk about freedom.
Let’s challenge tropes.
Drop your bias. Play the song.
Hello out July 11.
@itstriggerhere — Musician. Disruptor. Storyteller.Ad
