ICT4D Plan US Workshop Sept 09
- 1. ICT for Development Background
- 2. Information Communication Technology: Technology used to inform and communicate Uses: To gather, access and store information. To communicate, disseminate and exchange. To process, organise and consolidate information. Convergence: ICTs have different functions and applications They can be used together to broaden their scope and use. What is ICT?
- 3. The many faces of connectivity in Africa
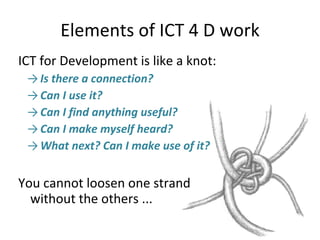
- 4. Elements of ICT 4 D work ICT for Development is like a knot: Is there a connection? Can I use it? Can I find anything useful? Can I make myself heard? What next? Can I make use of it? You cannot loosen one strand without the others ...
- 5. Information and Communication needs How do I & C support rights-based development work? Information Know your rights and entitlements Access services Improve your livelihoods Design appropriate programmes Study and learn Communication Convince others to join you Influence decisions and policies Share ideas and experiences Learn from others Coordinate and organise
- 6. How can ICTs help to meet development goals? ICT can support development work in 3 ways: Directly ŌĆō address the digital divide through improved connectivity, capacity, access Strategically ŌĆō apply ICTs to enhance the impact of development projects and programmes Indirectly ŌĆō improve the efficiency and effectiveness of development organisations
- 7. 1: Direct ICT4D work Direct work to address the (local, national, regional, global) digital divide such as: Access: Support telecentres for public access to internet, telephone, fax and other information services and training. Provide computers and internet connections for schools, CBOs and other public places/ groups. Policy: Ensuring that ICT policy is oriented to development needs. Protecting the right to information. Content: Ensuring that appropriate information is available in the right language, place, format etc. Capacity: Training and resource materials for ICT skills
- 8. 2: Strategic use of ICT4D Using ICT to enhance the impact of existing work, to: Connect people: strengthen networks and partnerships, facilitate forums and exchanges, improve relationships between stakeholders. Inform people: about their rights and entitlements and services, to support their livelihoods and education, share learning. Raise awareness: collect data on rights, promote local knowledge, share sustainable practices, provide advice and support. Build capacity: Develop and share content for training, advice and follow-up support. Networking participants and peers. Increase participation: Expand debates, facilitate dialogue, improve CBO effectiveness, increase transparency, mobilise lobbying.
- 9. 2: Examples of strategic use of ICT4D Market information: Preventative Healthcare: CitizensŌĆÖ media: Emergencies: Others?:
- 10. 2: Examples of strategic use of ICT4D Market information: In Senegal, Manobi have developed a service to give price data on different crops collected from different markets around the country. Farmers receive the information on the crop they are interested in on their mobile phone allowing them to make decisions about where to sell, who to sell to, or even when to harvest. Health prevention: In Mali P├®sinet agents use mobiles to collect data on the weight gain of young children from low-income families, and send it to a database which can alert the paediatrician to cases of concern. The doctor can examine the risk curves and send SMS to the community agent who can inform the family and advise them to take the child for examination. CitizensŌĆÖ media: Voices of Africa train people to report on local events and news from their mobiles and upload them onto the internet. It is hoped that the stories and images will trigger reactions from users and provide an alternative view of African current affairs, and strengthen democracy and governance. Social support: In South Africa, Cell-life use instant messaging to enable a peer support and counselling group for positive living, and send HIV positive subscribers SMS reminders to take their drugs, or attend appointments. Climate change adaptation: In Senegal ENDA use mobile phones to facilitate discussions with poor farmers around adaptation to climate change. Examples from the Mobiles for Development guide.
- 11. 3: ICT for Development organisations Increase the efficiency and effectiveness of organisational processes: Well informed: Bringing diverse perspectives and knowledge into planning, implementing and monitoring projects and programmes. In touch: Facilitate communication and sharing of learning amongst staff, and with partners, donors and supporters. Accountable: Support timely gathering of data and reporting to staff and stakeholders, including sponsors. Facilitate feedback. Up to date: Build skills and capacity of staff, develop and share new methods, tools and resources, access the latest news and resources. In time: Increase the efficiency and timeliness of emergency responses and other logistical operations.
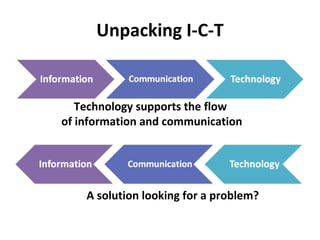
- 12. Unpacking I-C-T Technology supports the flow of information and communication A solution looking for a problem?
- 13. Unpacking I-C-T To create a strong, useful and sustainable ICT4D initiative you need to consider both: Information and Communication identify the needs you want to meet Understand the realities of the context Technology Know what is possible and available Be inspired!
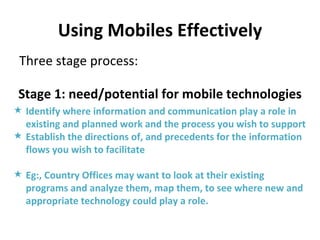
- 14. Using Mobiles Effectively Three stage process: Stage 1: need/potential for mobile technologies Identify where information and communication play a role in existing and planned work and the process you wish to support Establish the directions of, and precedents for the information flows you wish to facilitate Eg:, Country Offices may want to look at their existing programs and analyze them, map them, to see where new and appropriate technology could play a role.
- 15. Using Mobiles Effectively Three stage process: Stage 2: Socio-technical context Identify social issues which may have an impact on communication effectiveness Analyze barriers and opportunities for control, use and impact of mobile technologies in the context
- 16. Using Mobiles Effectively For example (stage 2) How do people currently get information? How is it different for women, men, children, adults, etc. What sources do they trust? Who does the information you are collecting belong to in the end? Etc. What are the most commonly used comms technologies in the area? Are people using mobile phones? How? Who controls access in the village or household? What are the barriers to mobile phone access? (language? Literacy? Pricing? Control?) Is text or voice more popular? Who are the intermediaries? Each context varies ŌĆō what is the pricing structure? Policy and regulations? Network used? What mobile applications do stakeholders commonly use now? Who supplies the mobiles?
- 17. Using Mobiles Effectively Three stage process: Stage 3: choose the technology and content Based on the prior analysis, identify the technical components which fit your aims, context and budget Ensure relevant content and capacity exists to create the desired impact
- 18. We all have our ways to communicate!
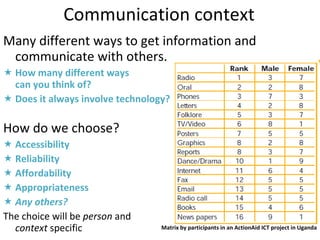
- 19. Communication context Many different ways to get information and communicate with others. How many different ways can you think of? Does it always involve technology? How do we choose? Accessibility Reliability Affordability Appropriateness Any others? The choice will be person and context specific Matrix by participants in an ActionAid ICT project in Uganda
- 20. Things to remember Information and communications comes first, and technology comes later Programs will have different IC components that work together ŌĆō both non-tech and tech ŌĆō depending on your prior analyses Technology is not a silver bullet ŌĆō itŌĆÖs still complicated and brings its own challenges like anything in development ŌĆ£ ItŌĆÖs all about understanding the agents of change and thatŌĆÖs anthropology, not technologyŌĆØ (Mark Davies)
Editor's Notes
- #3: 1 ŌĆō get people to offer examples: Mobile phone, computer, internet, video, GPS, radio, Possible exercise (5 mins): ask people to turn to their neighbour and list types of ICTs they use. 2. Technologies are used to help people to access and share information and to communicate. Possible exercise (10 mins): ask people in pairs to think of examples from their personal and work lives when they need to: collect information/ data access information share information communicate with others What means and media do you use? digital? Paper? Face to face? 3. Q ŌĆō what is the difference between a mobile phone and a computer? The difference in use can be because of size, price, transportability, quality etc not just function. Convergence means using more than one type of technology in a chain or network to increase the use and complexity. For example, a radio station which uses the internet to get access to information for programme content, broadcasts the shows on the radio frequencies (and the internet) and uses the phone to get listener participation ŌĆō phone-ins, text-ins, listener clubs etc.
- #5: Ask people to think of some of the activities involved in each of these elements: Connection ŌĆō infrastructure, investment, policy Use it ŌĆō location, gender, age, literacy, price, lanugage, skills ŌĆō Useful ŌĆō content, language, support, culture, relevant What next ŌĆō how to make use of information and communication ŌĆō link it to personal or community development goals? Influence? Learning? Application to livelihoods?
- #8: ACCESS ŌĆō in urban areas the private sector are quick to provide, but in areas where investment is higher and returns lower the government and NGOs have to step in. However, sustainability is an issue ŌĆō equipment is expensive and difficult to maintain, conditions are hard and income potential is low.
- #9: These are all connected ŌĆō most of the time you inform and learn and communicate at the same time... But ICT can be used more one-way or two-way ŌĆō top-down, bottom-up, sharing and exchange. Examples from the mobiles report: Village Diary!
- #10: Group discussion - Are any of these examples inspiring? Why?
- #20: Face to face or via technology such as video, telephone etc. Choose the means for communication/ information depending on many reasons... Is it reliable? Do you trust it? Is it available in your language? Do you have the right skills? (literacy, IT skills) Can you afford it? Is it culturally appropriate? Gender is an important consideration in ICT for Development, along with age, literacy, poverty etc, because these are issues which affect the ability of people to use ICT. For example, in Uganda there were many radio programmes on womenŌĆÖs issues and rights, because surveys had shown that radio was available in almost every household in rural Uganda. However, a participatory ICT project looked at the types of media women in particular could access, and found that the radios in the households belonged to the men, who controlled what could be listened to and took it, or the batteries, with them when they travelled. So the women were not able to listen to the programmes designed for them unless it interested men and played at a time the men were home.