Image captioning
- 1. Rajesh Shreedhar Bhat & Souradip Chakraborty Image Captioning using Attention Models
- 2. ? Intro to Image Captioning ? Real life use cases of image captioning. ? History & Evolution of Image Captioning ? Sequence to Sequence Learning in NLP ? Show and Tell : Sequence to Sequence Learning in Vision ? Intuition of Attention Mechanism from Translation perspective ? Show Attend and Tell : Image Captioning with Attention ? Beam search in generative framework ? Code walk-through in PyTorch Session Agenda
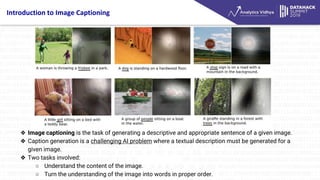
- 3. Introduction to Image Captioning ? Image captioning is the task of generating a descriptive and appropriate sentence of a given image. ? Caption generation is a challenging AI problem where a textual description must be generated for a given image. ? Two tasks involved: ° Understand the content of the image. ° Turn the understanding of the image into words in proper order.
- 4. Real Life Use Cases of Image Captioning ? Search using image captions. ? Getting live captions from CCTV/Surveillance cameras. ? Aid to visually impaired people.
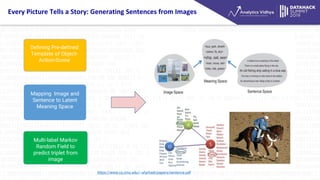
- 5. Every Picture Tells a Story: Generating Sentences from Images Defining Pre-defined Template of Object- Action-Scene Mapping Image and Sentence to Latent Meaning Space Multi-label Markov Random Field to predict triplet from image https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~afarhadi/papers/sentence.pdf
- 6. From Captions to Visual Concepts and Back Word Detection Stage Sentence Generation Stage Ranking Generated Sentences Word Detection Stage & Multiple Instance Learning https://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_cvpr_2015/papers/Fang_From_Captions_to_2015_CVPR_paper.pdf
- 7. E nc ode rs & D e c ode rs in s e que nc e -to- s e que nc e le a rning ? Encoder: processes each word in the input sequence and compiled information is put into context vector C. ? Context vector C is passed to the decoder. ? The decoder also maintains a hidden states that it passes from one time step to the next. Sequence-to-Sequence models ? The encoder-decoder architecture has received a lot of popularity in solving sequence to sequence problems in NLP domain. ? Example ®C Language Translation, Chatbots, Text summarization, etc.
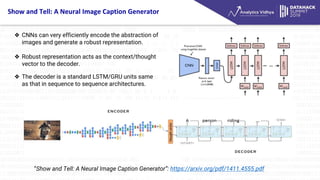
- 8. Show and Tell: A Neural Image Caption Generator °∞Show and Tell: A Neural Image Caption Generator°±: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1411.4555.pdf ? CNNs can very efficiently encode the abstraction of images and generate a robust representation. ? Robust representation acts as the context/thought vector to the decoder. ? The decoder is a standard LSTM/GRU units same as that in sequence to sequence architectures.
- 9. Attention Mechanism Intuition Source: https://distill.pub/2016/augmented-rnns/
- 10. Sequence to Sequence Model with Attention
- 11. Obtaining Context Vector using Attention Source: http://jalammar.github.io/visualizing-neural-machine-translation-mechanics-of-seq2seq-models-with-attention/
- 12. Attention is all you need: Brief Overview
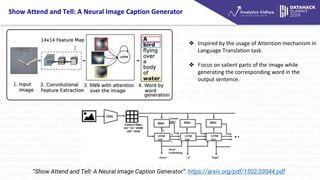
- 13. Show Attend and Tell: A Neural Image Caption Generator ? Inspired by the usage of Attention mechanism in Language Translation task. ? Focus on salient parts of the image while generating the corresponding word in the output sentence. °∞Show Attend and Tell: A Neural Image Caption Generator°±: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1502.03044.pdf
- 14. Caption Generation using Beam Search ? The greedy approach to choose the word with the highest score and use it to predict the next word is not optimal. ? Reason: the rest of the sequence hinges on that first word you choose. ? Beam Search is useful for any language modeling problem because it finds the most optimal sequence. Beam Size = 2
- 15. Code walkthrough - PyTorch https://github.com/rajesh-bhat/dhs_summit_2019_image_captioning
- 16. Thank you!