image introduction and origin steps in DIP
- 1. Digital Image Fundamentals Introduction ŌĆō Fundamental Steps in Digital Image Processing ŌĆōComponents of an Image Processing System, Elements of Visual Perception ŌĆō Image Sensing and Acquisition ŌĆō Image Sampling and Quantization ŌĆō RGB and HSI color models.
- 2. Contents This lecture will cover: ŌĆō What is a digital image? ŌĆō What is digital image processing? ŌĆō History of digital image processing ŌĆō State of the art examples of digital image processing ŌĆō Key stages in digital image processing
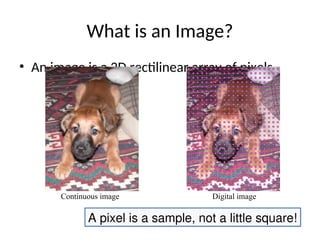
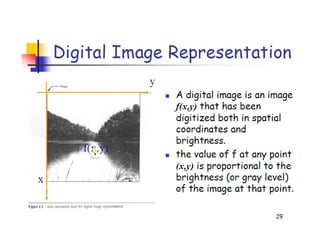
- 4. What is an Image? ŌĆó An image is a 2D rectilinear array of pixels Continuous image Digital image
- 5. What is an Image? ŌĆó An image is a 2D rectilinear array of pixels Continuous image Digital image A pixel is a sample, not a little square!
- 6. What is an Image? ŌĆó An image is a 2D rectilinear array of pixels A pixel is a sample, not a little square! Continuous image Digital image
- 7. What are images? ŌĆó An image is a 2-d rectilinear array of pixels
- 8. Pixels as samples ŌĆó A pixel is a sample of a continuous function
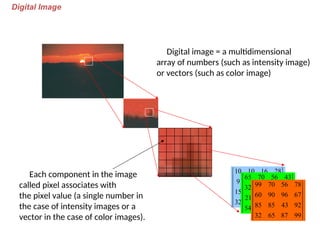
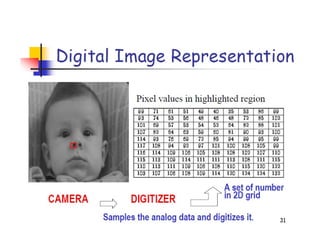
- 9. Digital Image Digital image = a multidimensional array of numbers (such as intensity image) or vectors (such as color image) Each component in the image called pixel associates with the pixel value (a single number in the case of intensity images or a vector in the case of color images). ’ā║ ’ā║ ’ā║ ’ā║ ’ā║ ’ā╣ ’ā¬ ’ā¬ ’ā¬ ’ā¬ ’ā¬ ’ā® 39 87 15 32 22 13 25 15 37 26 6 9 28 16 10 10 ’ā║ ’ā║ ’ā║ ’ā║ ’ā║ ’ā╣ ’ā¬ ’ā¬ ’ā¬ ’ā¬ ’ā¬ ’ā® 39 65 65 54 42 47 54 21 67 96 54 32 43 56 70 65 ’ā║ ’ā║ ’ā║ ’ā║ ’ā║ ’ā╣ ’ā¬ ’ā¬ ’ā¬ ’ā¬ ’ā¬ ’ā® 99 87 65 32 92 43 85 85 67 96 90 60 78 56 70 99
- 10. Common image formats include: ŌĆō 1 sample per point (B&W or Grayscale) ŌĆō 3 samples per point (Red, Green, and Blue) ŌĆō 4 samples per point (Red, Green, Blue, and ŌĆ£AlphaŌĆØ, a.k.a. Opacity) For most of this course we will focus on grey-scale images
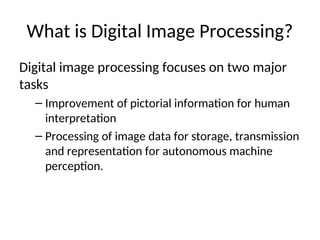
- 14. What is Digital Image Processing? Digital image processing focuses on two major tasks ŌĆō Improvement of pictorial information for human interpretation ŌĆō Processing of image data for storage, transmission and representation for autonomous machine perception.
- 15. How it works In the above figure , an image has been captured by a camera and has been sent to a digital system to remove all the other details , and just focus on the water drop by zooming it in such a way that the quality of the image remains the same.
- 19. History of Digital Image Processing Early 1920s: One of the first applications of digital imaging was in the news- paper industry ŌĆō The Bartlane cable picture transmission service ŌĆō Images were transferred by submarine cable between London and New York ŌĆō Pictures were coded for cable transfer and reconstructed at the receiving end on a telegraph printer Early digital image
- 20. History of DIP (contŌĆ”) Mid to late 1920s: Improvements to the Bartlane system resulted in higher quality images ŌĆō New reproduction processes based on photographic techniques ŌĆō Increased number of tones in reproduced images Improved digital image Early 15 tone digital image
- 21. History of DIP (contŌĆ”) 1960s: Improvements in computing technology and the onset of the space race led to a surge of work in digital image processing ŌĆō 1964: Computers used to improve the quality of images of the moon taken by the Ranger 7 probe ŌĆō Such techniques were used in other space missions including the Apollo landings A picture of the moon taken by the Ranger 7 probe minutes before landing
- 22. History of DIP (contŌĆ”) 1970s: Digital image processing begins to be used in medical applications ŌĆō 1979: Sir Godfrey N. Hounsfield & Prof. Allan M. Cormack share the Nobel Prize in medicine for the invention of tomography, the technology behind Computerised Axial Tomography (CAT) scans Typical head slice CAT image
- 23. History of DIP (contŌĆ”) 1980s - Today: The use of digital image processing techniques has exploded and they are now used for all kinds of tasks in all kinds of areas ŌĆō Image enhancement/restoration ŌĆō Artistic effects ŌĆō Medical visualisation ŌĆō Industrial inspection ŌĆō Law enforcement ŌĆō Human computer interfaces
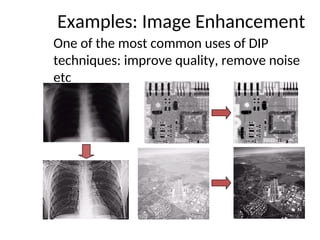
- 24. Examples: Image Enhancement One of the most common uses of DIP techniques: improve quality, remove noise etc
- 25. Examples: The Hubble Telescope Launched in 1990 the Hubble telescope can take images of very distant objects However, an incorrect mirror made many of HubbleŌĆÖs images useless Image processing techniques were used to fix this
- 26. Examples: Artistic Effects Artistic effects are used to make images more visually appealing, to add special effects and to make composite images
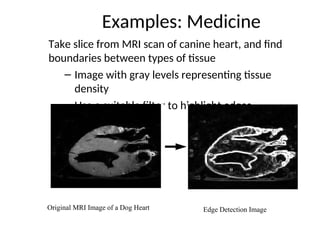
- 27. Examples: Medicine Take slice from MRI scan of canine heart, and find boundaries between types of tissue ŌĆō Image with gray levels representing tissue density ŌĆō Use a suitable filter to highlight edges Original MRI Image of a Dog Heart Edge Detection Image
- 28. Examples: GIS Geographic Information Systems ŌĆō Digital image processing techniques are used extensively to manipulate satellite imagery ŌĆō Terrain classification ŌĆō Meteorology
- 29. Examples: GIS (contŌĆ”) Night-Time Lights of the World data set ŌĆō Global inventory of human settlement ŌĆō Not hard to imagine the kind of analysis that might be done using this data
- 30. Examples: Industrial Inspection Human operators are expensive, slow and unreliable Make machines do the job instead Industrial vision systems are used in all kinds of industries Can we trust them?
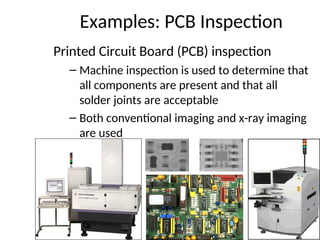
- 31. Examples: PCB Inspection Printed Circuit Board (PCB) inspection ŌĆō Machine inspection is used to determine that all components are present and that all solder joints are acceptable ŌĆō Both conventional imaging and x-ray imaging are used
- 32. Examples: Law Enforcement Image processing techniques are used extensively by law enforcers ŌĆō Number plate recognition for speed cameras/automated toll systems ŌĆō Fingerprint recognition ŌĆō Enhancement of CCTV images
- 33. Examples: HCI Try to make human computer interfaces more natural ŌĆō Face recognition ŌĆō Gesture recognition Does anyone remember the user interface from ŌĆ£Minority ReportŌĆØ? These tasks can be extremely difficult
- 34. Applications of Digital Image Processing ŌĆó Image sharpening and restoration ŌĆó Medical field ŌĆó Remote sensing ŌĆó Transmission and encoding ŌĆó Machine/Robot vision ŌĆó Color processing ŌĆó Pattern recognition ŌĆó Video processing ŌĆó Microscopic Imaging ŌĆó Others
- 35. Image sharpening and restoration ŌĆó Image sharpening and restoration refers here to process images that have been captured from the modern camera to make them a better image or to manipulate those images in way to achieve desired result. It refers to do what Photoshop usually does. ŌĆó This includes Zooming, blurring , sharpening , gray scale to color conversion, detecting edges and vice versa , Image retrieval and Image recognition. The common examples are: Original Zoomed Blurr
- 37. UV imaging ŌĆó In the field of remote sensing , the area of the earth is scanned by a satellite or from a very high ground and then it is analyzed to obtain information about it. One particular application of digital image processing in the field of remote sensing is to detect infrastructure damages caused by an earthquake.
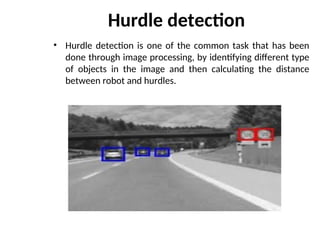
- 38. Hurdle detection ŌĆó Hurdle detection is one of the common task that has been done through image processing, by identifying different type of objects in the image and then calculating the distance between robot and hurdles.
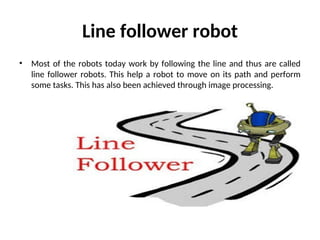
- 39. Line follower robot ŌĆó Most of the robots today work by following the line and thus are called line follower robots. This help a robot to move on its path and perform some tasks. This has also been achieved through image processing.
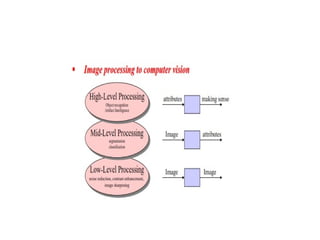
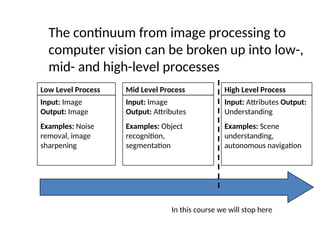
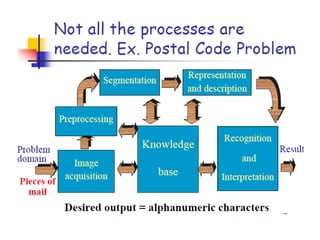
- 41. The continuum from image processing to computer vision can be broken up into low-, mid- and high-level processes Low Level Process Input: Image Output: Image Examples: Noise removal, image sharpening Mid Level Process Input: Image Output: Attributes Examples: Object recognition, segmentation High Level Process Input: Attributes Output: Understanding Examples: Scene understanding, autonomous navigation In this course we will stop here
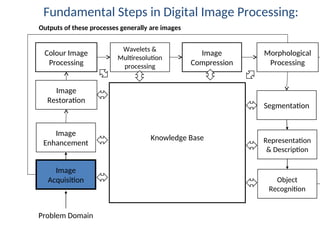
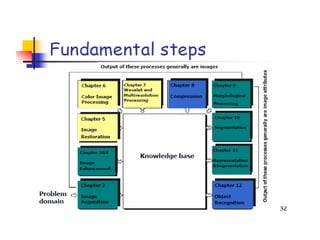
- 42. Fundamental Steps in Digital Image Processing: Image Acquisition Image Restoration Morphological Processing Segmentation Object Recognition Image Enhancement Representation & Description Problem Domain Colour Image Processing Image Compression Wavelets & Multiresolution processing Outputs of these processes generally are images Knowledge Base
- 44. Step 1: Image Acquisition The image is captured by a sensor (eg. Camera), and digitized if the output of the camera or sensor is not already in digital form, using analogue-to-digital convertor
- 45. Step 2: Image Enhancement The process of manipulating an image so that the result is more suitable than the original for specific applications. The idea behind enhancement techniques is to bring out details that are hidden, or simple to highlight certain features of interest in an image.
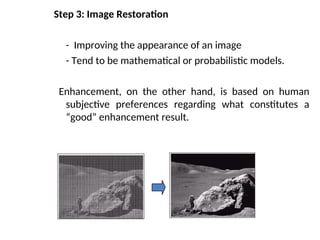
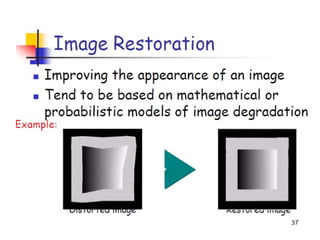
- 47. Step 3: Image Restoration - Improving the appearance of an image - Tend to be mathematical or probabilistic models. Enhancement, on the other hand, is based on human subjective preferences regarding what constitutes a ŌĆ£goodŌĆØ enhancement result.
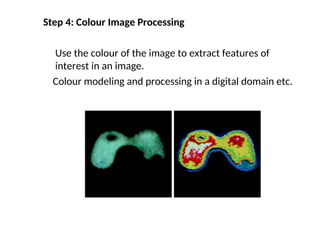
- 49. Step 4: Colour Image Processing Use the colour of the image to extract features of interest in an image. Colour modeling and processing in a digital domain etc.
- 50. Step 5: Wavelets Are the foundation of representing images in various degrees of resolution. It is used for image data compression where images are subdivided into smaller regions.
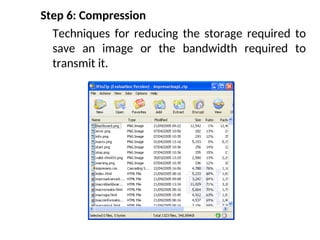
- 51. Step 6: Compression Techniques for reducing the storage required to save an image or the bandwidth required to transmit it.
- 53. Tools for extracting image components that are useful in the representation and description of shape. In this step, there would be a transition from processes that output images, to processes that output image attributes. Step 7: Morphological Processing
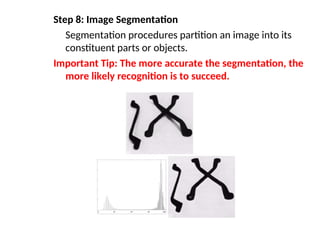
- 55. Step 8: Image Segmentation Segmentation procedures partition an image into its constituent parts or objects. Important Tip: The more accurate the segmentation, the more likely recognition is to succeed.
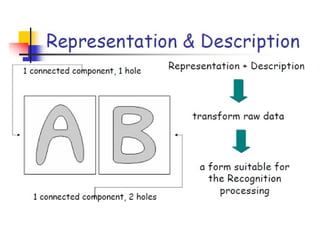
- 57. Step 9: Representation and Description - Representation: Make a decision whether the data should be represented as a boundary or as a complete region. It is almost always follows the output of a segmentation stage. - Boundary Representation: Focus on external shape characteristics, such as corners and inflections. - Region Representation: Focus on internal properties, such as texture or skeleton shape. Transforming raw data into a form suitable for subsequent computer processing. Description deals with extracting attributes that result in some quantitative information of interest or are basic for differentiating one class of objects from another.
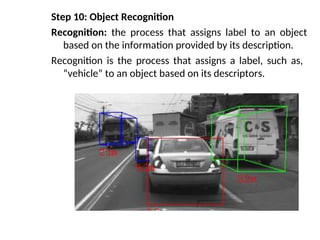
- 60. Step 10: Object Recognition Recognition: the process that assigns label to an object based on the information provided by its description. Recognition is the process that assigns a label, such as, ŌĆ£vehicleŌĆØ to an object based on its descriptors.
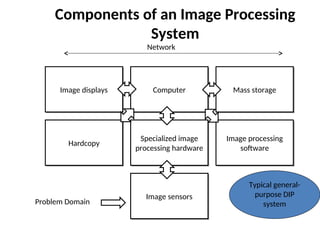
- 63. Components of an Image Processing System Network Image displays Computer Mass storage Hardcopy Specialized image processing hardware Image processing software Image sensors Problem Domain Typical general- purpose DIP system
- 64. Components of an Image Processing System 1. Image Sensors Two elements are required to acquire digital images. The first is the physical device that is sensitive to the energy radiated by the object we wish to image (Sensor). The second, called a digitizer, is a device for converting the output of the physical sensing device into digital form.
- 65. Components of an Image Processing System 2. Specialized Image Processing Hardware Usually consists of the digitizer, mentioned before, plus hardware that performs other primitive operations, such as an arithmetic logic unit (ALU), which performs arithmetic and logical operations in parallel on entire images. This type of hardware sometimes is called a front-end subsystem, and its most distinguishing characteristic is speed. In other words, this unit performs functions that require fast data throughputs that the typical main computer cannot handle.
- 66. Components of an Image Processing System 4. Image Processing Software Software for image processing consists of specialized modules that perform specific tasks. A well-designed package also includes the capability for the user to write code that, as a minimum, utilizes the specialized modules.
- 67. Components of an Image Processing System 5. Mass Storage Capability Mass storage capability is a must in a image processing applications. And image of sized 1024 * 1024 pixels requires one megabyte of storage space if the image is not compressed. Digital storage for image processing applications falls into three principal categories: 1. Short-term storage for use during processing. 2. on line storage for relatively fast recall 3. Archival storage, characterized by infrequent access
- 68. Components of an Image Processing System 5. Mass Storage Capability One method of providing short-term storage is computer memory. Another is by specialized boards, called frame buffers, that store one or more images and can be accessed rapidly. The on-line storage method, allows virtually instantaneous image zoom, as well as scroll (vertical shifts) and pan (horizontal shifts). On-line storage generally takes the form of magnetic disks and optical-media storage. The key factor characterizing on-line storage is frequent access to the stored data. Finally, archival storage is characterized by massive storage requirements but infrequent need for access.
- 69. Components of an Image Processing System 6. Image Displays The displays in use today are mainly color (preferably flat screen) TV monitors. Monitors are driven by the outputs of the image and graphics display cards that are an integral part of a computer system.
- 70. Components of an Image Processing System 7. Hardcopy devices Used for recording images, include laser printers, film cameras, heat-sensitive devices, inkjet units and digital units, such as optical and CD-Rom disks.
- 71. Components of an Image Processing System 8. Networking Is almost a default function in any computer system, in use today. Because of the large amount of data inherent in image processing applications the key consideration in image transmission is bandwidth. In dedicated networks, this typically is not a problem, but communications with remote sites via the internet are not always as efficient.
Editor's Notes
- #41: Give the analogy of the character recognition system. Low Level: Cleaning up the image of some text Mid level: Segmenting the text from the background and recognising individual characters High level: Understanding what the text says