Immune system2
- 1. Immune System 6th Grade Science
- 2. I. Function A. Remove germs B. Aid in repair
- 3. II. Barriers A. Skin B. Respiratory System (nose, mucus, ciliaâĶ) C. Digestive System (acid, membranesâĶ)
- 4. III. Non-Specific A. Chemical Signals 1. Attract immune cells to site 2. Make blood vessels leaky B. Phagocyte 1. Eats anything not marked as you C. Inflammation 1. Massive increase in blood flow i. Warm and Swelling D. Fever 1. Used to kill germs by cooking them
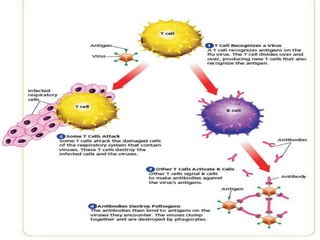
- 5. IV. Specific A. T-Lymphocytes (T-Cells) 1. Recognize specific germs (antigens) 2. Destroy cells if infected B. B-Lymphocytes (B-Cells) 1. Produce antibodies i. Mark and clump germs together
- 7. V. Damage and Disease A. Immunodeficiency 1. Lack of sleep 2. Poor nutrition 3. Lack of exercise 4. Aging 5. Organ transplanting
- 8. B. Allergies 1. Body attacks object as dangerous threat i. Foods ii. Oils iii. Venom
- 9. C. Autoimmune Disease 1. Body attacks own cells (overactive) i. LUPUS ii. Arthritis iii. Diabetes
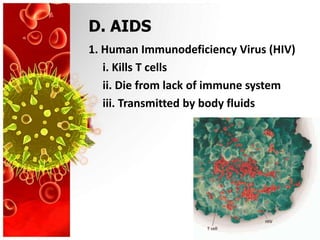
- 10. D. AIDS 1. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) i. Kills T cells ii. Die from lack of immune system iii. Transmitted by body fluids
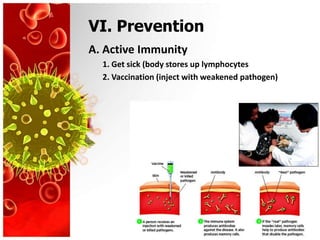
- 11. VI. Prevention A. Active Immunity 1. Get sick (body stores up lymphocytes 2. Vaccination (inject with weakened pathogen)
- 12. B. Intervention 1. Antibiotics (Kill bacteria)
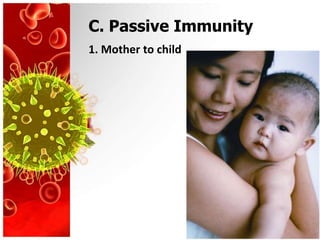
- 13. C. Passive Immunity 1. Mother to child