Indication of RGP Lens in corneal abnormalties.pptx
- 1. INDICATION OF RGP LENS BY SATYENDRA SINGH SACHAN Asst Professor Rama University
- 6. ŌĆó Oxygen supply to the cornea ŌĆó Astigmatic correction ŌĆó regular ŌĆó irregular
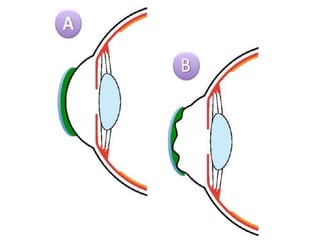
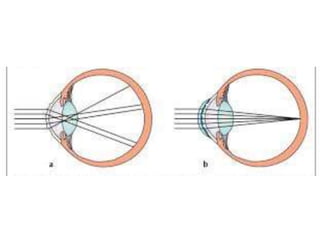
- 7. KERATOCONUS Keratoconus is a benign, usually bilateral, non- inflammatory thinning and ectasia of the cornea, resulting in a high degree of irregular myopic astigmatism
- 9. Prevalence of keratoconus in Central India (0.0003%- 2.3%) Gokhale NS. Epidemiology of keratoconus. Indian J Ophthalmol 2013 [cited 2020 Feb 3];61:382-3.
- 10. KERATOCONUS CLEK DATA: CORNEA ŌĆó 44.37 D(SD 1.6 D) ŌĆó 0.50 D Cyl (SD 0.18 D) ŌĆó Axis 175┬░ ŌĆó Corneal Tilt: 0.38’üä (SD 0.11) ŌĆó Base-Apex line: 56┬░ - 236┬░ ŌĆó 48.02 D (SD 3.88 D) ŌĆó 2.46 D Cyl (SD 0.99 D) ŌĆó Axis 26┬░ ŌĆó Corneal Tilt: 3.94’üä (SD 1.45) ŌĆó Base-Apex line: 69┬░ - 249┬░ Normals: 60 Eyes Keratoconics: 690 Eyes Raasch et al., 1998
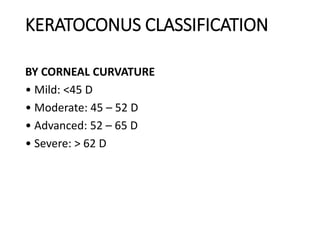
- 12. KERATOCONUS CLASSIFICATION BY CORNEAL CURVATURE ŌĆó Mild: <45 D ŌĆó Moderate: 45 ŌĆō 52 D ŌĆó Advanced: 52 ŌĆō 65 D ŌĆó Severe: > 62 D
- 13. Symptoms ŌĆó Initially, asymptomatic ŌĆó Visual degradation reported at or after time of puberty ŌĆó Progresses slowly over 5 ŌĆō 10 years ŌĆó Ghost image & photophobia
- 14. Sign ŌĆó Distorted keratometry mires ŌĆó Distorted photokeratoscopy rings ŌĆó Inferior steeping in videokeratoscopy maps ŌĆó Apical corneal thinning (stromal) ŌĆó Cone formation
- 18. KERATOGLOBUS It is a familial and hereditary bilateral congenital disorder characterized by thinning and hemispherical protrusion of the entire cornea. It is non- progressive and inherited as an autosomal recessive trait.
- 20. PENETRATING KERATOPLASTY Trephine Host button Donor button Double-armed suture Corneal button Diam.=Host+0.5 mm Sutures Corneal penetration > full thickness
- 24. BULLOUS KERATOPATHY (BK) POST-GRAFT Note: ŌĆó Avascular donor tissue ŌĆó One remaining suture
- 25. CORNEAL TOPOGRAPHY ŌĆó Incorrect placement of cardinal sutures ŌĆó Non-radial sutures ŌĆó Unequal suture tension(s) ŌĆó Pre-existing astigmatism in host or donor cornea ŌĆó Scar tissue in host cornea CAUSES OF ASTIGMATISM
- 27. GRAFT WITH 5 D CYL
- 28. ŌĆó RGPs (high Dk/t) when: ŌĆó patient wore RGPs previously ŌĆó postsurgical scarring present ŌĆó corneal irregularities present ŌĆó post-PK corneal ectasia ŌĆó Scleral lenses (gas permeable) in cases of: ŌĆó irregular corneas ŌĆó sensitive corneas after Bufidis et al., 2005
- 29. LENS SELECTION ŌĆó Rigid gas permeable lenses are the modality of choice following penetrating keratoplasty ŌĆó maximum correction of cylinder
- 30. RGP LENS ŌĆó Oxygen supply ŌĆó Correction of astigmatism ŌĆó Level of visual acuity
- 31. RGP LENS ŌĆó Correction of irregular astigmatism ŌĆó Provide high oxygen transmissibility ŌĆó Custom designs available
- 36. THANK YOU
Editor's Notes
- #17: According to Rabinowitz (1995, 1998), a diagnosis of keratoconus can be made if the patient has keratometry readings greater than 47.20 D, inferior corneal steepening of more than 1.20 D greater than the superior cornea, and skewing of the radial axis of astigmatism by more than 21 degrees. ┬Ā ┬Ā
- #23: ║▌║▌▀Ż 18 shows a case of Bullous Keratopathy (BK) that developed after trauma to an eye that already had FuchŌĆÖs dystrophy.
- #24: ║▌║▌▀Ż 21 shows a ŌĆśquietŌĆÖ eye some time after surgery but before suture removal. In this case, there is also evidence of early crystalline lens changes.
- #25: ║▌║▌▀Ż 19 shows the same patient after a PK. It is noteworthy that the donor tissue has remained avascular whereas the host tissue was/is quite vascularized. The reason for the one suture remaining is unknown.
- #29: Suggested lens types according to Bufidis et al. (2005) appear as slide 172.






![Prevalence of
keratoconus in
Central India (0.0003%-
2.3%)
Gokhale NS. Epidemiology of keratoconus. Indian J
Ophthalmol 2013 [cited 2020 Feb 3];61:382-3.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indicationofrgplens-240430063016-37fed5ac/85/Indication-of-RGP-Lens-in-corneal-abnormalties-pptx-9-320.jpg)