Indifference curve
- 1. INDIFFERENCE CURVE
- 2. DEFINITION: IC An Indifference curve (IC) is the locus of all those combination of two goods which give the same level of satisfaction to the consumer. Thus consumer is indifferent towards all the combinations lying on the same indifference curve. In other words, consumer gives equal preference to all such combinations.
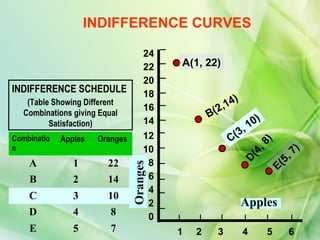
- 3. INDIFFERENCE CURVES 24 22 A(1, 22) 20 INDIFFERENCE SCHEDULE 18 ) (Table Showing Different 14 Combinations giving Equal 16 B(2, Satisfaction) 14 1 0) , Combinatio Apples Oranges 12 C(3 8) n 10 4, 7) D( 5, A 1 22 8 Oranges E( B 2 14 6 4 C 3 10 2 Apples D 4 8 0 E 5 7 1 2 3 4 5 6
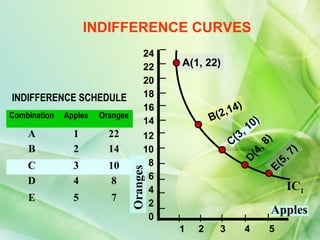
- 4. INDIFFERENCE CURVES 24 22 A(1, 22) 20 INDIFFERENCE SCHEDULE 18 ) 16 ,14 Combination Apples Oranges B(2 14 0) A 1 22 ,1 12 C(3 8) B 2 14 10 4, 7) D( 8 5, C 3 10 E( Oranges D 4 8 6 4 IC1 E 5 7 2 Apples 0 1 2 3 4 5
- 5. MARGINAL RATE OF SUBSTITUTION (MRS) The marginal rate of substitution of X for Y (MRSxy) is defined as the amount of Y, the consumer is just willing to give up to get one more unit of X and maintain the same level of satisfaction. Decrease in the Consumption of Y = (-) Ōłå Y M xy RS = Increase in the Consumption of X ŌłåX
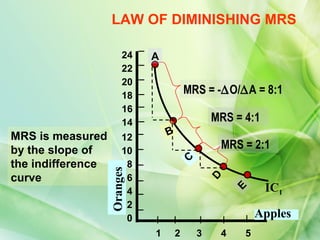
- 6. DIMINISHING MARGINAL RATE OF SUBSTITUTION Combination Apples Oranges MRS A 1 22 --- B 2 14 8:1 C 3 10 4:1 D 4 8 2:1 E 5 7 1:1 As the consumer increases the consumption of apples, then for getting every additional unit of apples, he will give up less and less of oranges, that is, 8:1, 4:1, 2:1, 1:1 respectively This is the Law of Diminishing MRS.
- 7. LAW OF DIMINISHING MRS 24 A 22 20 18 MRS = -ŌłåO/ŌłåA = 8:1 16 14 MRS = 4:1 MRS is measured 12 B by the slope of 10 MRS = 2:1 C the indifference 8 Oranges curve 6 D IC1 E 4 2 0 Apples 1 2 3 4 5
- 8. PROPERTIES OF IC 1. An Indifference curve has negative slope i.e. it slope downwards from left to right. 2. Indifference curve is always convex to the origin.
- 9. PROPERTIES OF IC 3. Two Indifference curves never each other.
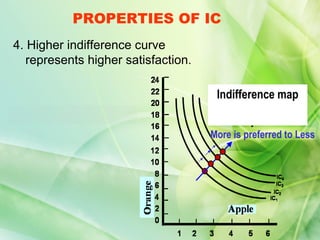
- 10. PROPERTIES OF IC 4. Higher indifference curve represents higher satisfaction. Indifference map More is preferred to Less
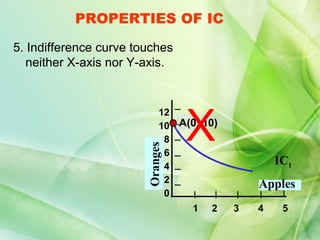
- 11. PROPERTIES OF IC 5. Indifference curve touches neither X-axis nor Y-axis. X 12 10 A(0, 10) 8 Oranges 6 IC1 4 2 Apples 0 1 2 3 4 5
Editor's Notes
- #8: 5