Induction of labor
- 1. Name: Sohayla Mahmoud Felfel ID..558 Induction of labour
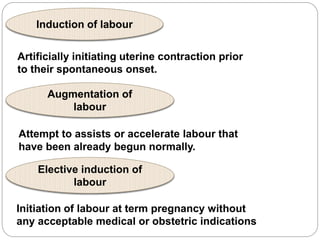
- 2. Induction of labour Augmentation of labour Elective induction of labour Artificially initiating uterine contraction prior to their spontaneous onset. Attempt to assists or accelerate labour that have been already begun normally. Initiation of labour at term pregnancy without any acceptable medical or obstetric indications
- 3. INDICATIONS MATERNAL ï§ Preeclampsia, eclampsia ï§ PROM ï§ Postterm pregnancy ï§ Abruptio placenta ï§ Chorioamnionitis ï§ Medical conditions- DM,Heart ds, Renal ds,Chr. HTN etc FETAL ï§ IUFD ï§ postmaturity ï§ Fetal anomaly incompatible with life ï§ Severe IUGR ï§ Rh isoimmunisation ï§ Macrosomia
- 4. ï Severe degree CPD ï Major degree placenta previa ï Transverse lie or breech presentation ï Previous classical CS, Myomectomy ï Contracted pelvis ï Grand multipara or old primigravida ï Active genital herpes ï Hypersensitivity to the inducing agent CONTRAINDICATIONS
- 5. ï Failure leading to CS ï Uterine hyperstimulation ï Fetal distress,death ï Rupture uterus ï Intrauterine infection,sepsis ï Iatrogenic delivery of preterm infant ï Precipitate/dysfunctional labour ï Inc. risk of operative vaginal delivery ï Inc. risk of birth trauma ï Inc. risk of PPH Complications
- 6. Decision taken to induce labour Cervical status Bishop score Cervix ripes Cervix doesnât ripe Induce labour Ripe cervix then induce labour assessme nt
- 8. Methods of cervical ripening natural mechanical pharmacological âĒ Walking âĒ Having sex âĒ Nipple stimulation âĒ Enema âĒ Acupressu re âĒ Hygroscopi c dilators âĒ Transcervic al catheter âĒ Stripping the membranes âĒ Prostaglandin E2: (dinoproston e) âĒ Prostaglandin E1
- 10. Methods of induction labour Surgical Pharmacological Amniotomy âĒ Oxytocin âĒ prostaglandins
- 12. Adminstration âĒ IV infusion Advantages: âĒ it is potent and easy to titrate, âĒ Has a short half-life (one to five minutes) âĒ Well tolerated.
- 13. âĒ Oxytocin infusion should be given in the smallest possible volume, commencing at a rate of 1 mU/min âĒ Usually start by 5 units in 500mls of normal saline or Ringerâs solution [10 mU/ml] âĒ Increase infusion rate (by doubling drops / min) at intervals of 30 min, until there are 3-5 good contractions every 10 min each lasting 45-60 sec. [1 ml=15-drops] âĒ If 60 drop/min rate is reached with no efficient contractions replace the infusion with 10 units oxytocin in 500 mls âĒ Total dose of oxytocin should not exceed 5 units Oxytocin Regimen:











![âĒ Oxytocin infusion should be given in the smallest
possible volume, commencing at a rate of 1
mU/min
âĒ Usually start by 5 units in 500mls of normal
saline or Ringerâs solution [10 mU/ml]
âĒ Increase infusion rate (by doubling drops / min)
at intervals of 30 min, until there are 3-5 good
contractions every 10 min each lasting 45-60 sec.
[1 ml=15-drops]
âĒ If 60 drop/min rate is reached with no efficient
contractions replace the infusion with 10 units
oxytocin in 500 mls
âĒ Total dose of oxytocin should not exceed 5 units
Oxytocin Regimen:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inductionoflabor-171231030646/85/Induction-of-labor-13-320.jpg)
