Infographic: Common Drilling Mud Problems - Causes and Solutions
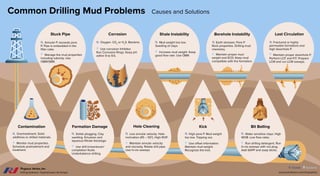
- 1. Run drilling detergent. Run hi-vis sweeps with nut plug. Add SAPP and soap sticks. Water sensitive clays. High WOB. Low flow rates. Bit Balling Use offset information. Maintain mud weight. Recognize the kick. High pore P. Mud weight too low. Tripping out. Kick Hole Cleaning Maintain annular velocity and viscosity. Rotate drill pipe. Use hi-vis sweeps. Low annular velocity. Hole inclination (45 ŌĆō 50┬░). High ROP. Formation Damage Use drill-in/workover/ completion fluids. Underbalance drilling. Solids plugging. Clay swelling. Emulsion and aqueous-filtrate blockage. Monitor mud properties. Schedule pretreatment and treatment. Overtreatment. Solid additives or drilled materials. Contamination Maintain proper downhole P. Perform LOT and FIT. Prepare LCM and run LCM sweeps. Fractured or highly permeable formations and high downhole P. Lost Circulation Borehole Instability Maintain proper mud weight and ECD. Keep mud compatible with the formation. Earth stresses. Pore P. Rock properties. Drilling mud chemistry. Increase mud weight. Keep good flow rate. Use OBM. Mud weight too low. Swelling of clays. Shale Instability Corrosion Use corrosion Inhibitor. Run Corrosion Rings. Keep pH within 9 to 9.5. Oxygen. C02 or H2 S. Bacteria. Annular P. exceeds pore P. Pipe is embedded in the filter cake. Manage the mud properties including lubricity. Use OBM/SBM. Stuck Pipe Causes Solutions Common Drilling Mud Problems Causes and Solutions www.pvisoftware.com/infographics Drilling Software | Sophisticated Yet Simple