Infra temporal space infection ppt
- 1. INFRA TEMPORAL SPACE INFECTION PRESENTED BY AILEEN THANKACHAN K 3rd BDS KVG DC
- 2. CONTENTS .INTRODUCTION .CLASSIFICATIONS OF FACIAL SPACES .ANATOMICAL BOUNDARIES OF INFRA TEMPORAL SPACES .CONTENTS OF INFRATEMPORAL SPACES .SOURCES OF INFECTION .CLINICAL FEATURES .SPREAD OF INFECTION .COMPLICATION .TREATMENT .CONCLUSION .REFERENCE
- 3. INTRODUCTION ïą Fascial spaces are potential spaces between various layers of fascia normally filled with loose connective tissue and bounded by anatomical barriors,usually ofbone,muscles or fascial layers ïą Fascia is described under :- ïą 1) Superfical fascia ïą 2) Deep fascia .Superfical fascia :-ensheathes platysma and muscles of fascial expressions
- 4. ïą Deep fascia:- a) superfical or anterior or investing layer b)middle or pretracheal layer c) posterior or prevertebral layer d) carotid sheath : The infections in orofacial region tends to accumulate in these potential spaces around head and neck. Many of these spaces communicate witheach other - SPACE INFECTIONS
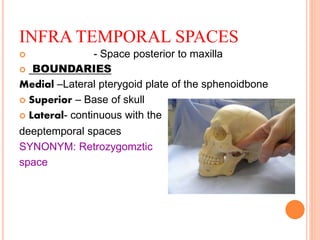
- 7. INFRA TEMPORAL SPACES ïą - Space posterior to maxilla ïą BOUNDARIES Medial âLateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoidbone ïą Superior â Base of skull ïą Lateral- continuous with the deeptemporal spaces SYNONYM: Retrozygomztic space
- 9. CONTENTS OF INFRA TEMPORAL SPACE ïą Pterygoid plexus ïą Maxillary artery and veins ïą Mandibular nerves ïą Chorda tympani ïą Otic Ganglion .Medial Pterygoid muscle
- 10. ETIOLOGY ïą It is rarely infected ïą Cause is usually an infection of maxillary molars Especially 3rd molar ïą Spread of infection from pterygomandibular,parotid or lateral pharyngeal region ïą local anesthesia injections with Contaminated needle in area of tuberosity
- 11. CLINICAL FEATURES ïą Extra oral : trismus bulging of temporalis muscle swelling of face infront of ear,overTMJ behind zygomatic process Intra oral: swelling in tube rosity area elevated temp upto140 degree
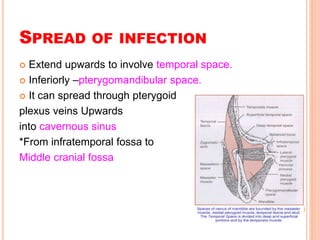
- 13. SPREAD OF INFECTION ïą Extend upwards to involve temporal space. ïą Inferiorly âpterygomandibular space. ïą It can spread through pterygoid plexus veins Upwards into cavernous sinus *From infratemporal fossa to Middle cranial fossa
- 15. MANAGEMENT ïą MEDICAL SUPPORT TO THE PATIENT ïą 1.Rehydrate pt.as dehydration may be present ïą 2.Treat conditions that predispose pt . To infections (DM) ïą 3. oral pain,trismus and swelling can be addressed by appropriate analgesia and treatment undelying infections.
- 16. NON â SURGICAL APPROACH * INTRAVENOUS ANTIBIOTICS ïą Early infections(first 3 dayof symptoms or mild immunocompromised pt) ïą Rx. ïą Pencillin ïą Clindamycin ïą Cephalexin (or other 1 st gen cephalosporin)
- 17. ïą Late infections( after 5 days of symptoms or severe immunocompromised pt.) ïą Rx ïą Clindamycin ïą Pencillin and metronidazole ïą Ampicillin ïą Cephalosporin( 1st or 2nd gen)
- 18. INCISION & DRAINAGE ïą * Intra oral approach : incision is given in buccal vestibule opposite of 2 nd and 3rd molar exploration is carried out medial to coronoid process and temporalis muscle upwards backwards with sinus forcep ,space is entered and drained
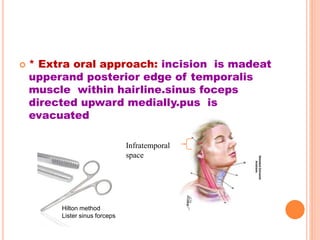
- 19. ïą * Extra oral approach: incision is madeat upperand posterior edge of temporalis muscle within hairline.sinus foceps directed upward medially.pus is evacuated Infratemporal space Hilton method Lister sinus forceps
- 20. COMPLICATION ïą 1. Brain Abcess ïą 2. Meningitis ïą 3.Cavernous sinus thrombosis ïą 4.Multiple space involment ïą 5.Hemorrhage ïą 6.sepsis
- 21. CONCLUSION ïą Incidence and severity have diminished with advent of medical therapy ïą Deep fascial infection must be recognized promptly and treated as an emergency ïą Repeat diagnostic and therapeutic measures may be necessary until the very end point ïą Identify possible complications ïą Resolve the associated infection ïą A through knowledge of anatomy of face and neck is necessary to predict pathway of spread of infection and its drainage
- 22. REFERENCE ïą Textbook of oral &maxillofacial surgery-Neelima Malik ïą Textbook of Human Anatomy â BD Chaurasia ïą Shaferâs Textbook of Oral pathology 8th edition