Infrared instrumentation
- 1. PRESENTED BY :- SAURABH VERMA M.S. PHARM ,NIPER ,KOLKATA
- 2. Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy IR deals with the interaction of infrared radiation with matter. The IR spectrum of a compound can provide important information about its chemical nature and molecular structure. Most commonly, the spectrum is obtained by measuring the absorption of IR radiation, although infrared emission and reflection are also used. Widely applied in the analysis of organic materials, also useful for polyatomic inorganic molecules and for organometallic compounds.
- 3. INFRARED REGION NEAR INFRARED or OVERTONE: 1.2 -2.5 ïm, MID INFRARED or VIBRATION: 2.5 - 25 ïm, FAR INFRARED or ROTATION: 25 - 400 ïm, X-RAY ULTRAVIOLET INFRARED MICRO- WAVE RADIO FREQUENCY Ultraviolet Visible Vibrational Infrared (Mid-IR) Nuclear magnetic resonance 200 nm 400 nm 800 nm 2.5 ïm 25 ïm 1 m 5 m BLUE RED 0.78-1000 ÉĨM
- 4. ORGANIC STRUCTURE DETERMINATION How do we know How atoms are connected together? Which bonds are single, double, or triple? What functional groups exist in the molecule? If we have a specific stereoisomer?
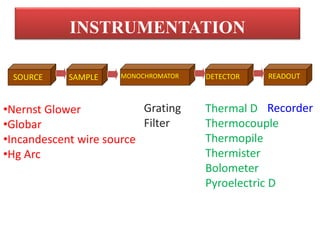
- 5. SOURCE SAMPLE MONOCHROMATOR DETECTOR READOUT âĒNernst Glower âĒGlobar âĒIncandescent wire source âĒHg Arc Grating Filter Thermal D Thermocouple Thermopile Thermister Bolometer Pyroelectric D Recorder INSTRUMENTATION
- 6. 1. IR radiation source Be continuous over the wavelength range used. Cover a wide wavelength range. Be constant over long periods of time.
- 7. 1. The Nernst Glower They electrically heated to about 2000 °C. It composed of a mixture of rare earth oxides such as zirconium oxide (ZrO2), yttrium oxide (Y2O3) and thoria. sealed by a platinum leads to the ends to permit electrical connection. Consist of cylindrical hollow rod or tube having a diameter of 1- 2 mm and length of 30 mm.
- 8. its lifetime depends on the operating temperature and the care taken in handling it It provide maximum radiation about 7100cm-1 (1.4 ï)
- 9. 2. The Globar source The power consumption is normally higher than that of the Nernst Glower It provide maximum radiation about 5200cm-1 . Heated to about 2000 °C. Itâs sintered silicon carbide rod, usually about 50 mm in length and 5 mm in diameter
- 10. Less convenient to use, more expensive & less intense than Nernst Glower. Water cooling is needed to cool the metallic electrodes attached to the rod
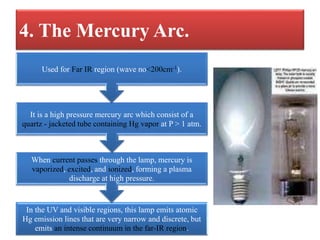
- 11. 4. The Mercury Arc. In the UV and visible regions, this lamp emits atomic Hg emission lines that are very narrow and discrete, but emits an intense continuum in the far-IR region. When current passes through the lamp, mercury is vaporized, excited, and ionized, forming a plasma discharge at high pressure. It is a high pressure mercury arc which consist of a quartz - jacketed tube containing Hg vapor at P > 1 atm. Used for Far IR region (wave no<200cm-1).
- 12. 3. Incandescent Wire Source Incandescent wire sources are longer lasting but of lower intensity than the glower or globar. A similar source is a rhodium wire heater sealed in a ceramic cylinder. A tightly wound spiral of nichrome wire heated to about 1100 k by an electric current. Lower intensity IR source but longer life than the Globar or Nernst glower.
- 13. 2. MONOCHROMATORS A. Prism:- âĒ Used as dispersive element. âĒ Constructed of various metal halide salts âĒ Sodium chloride is most commonly prism salt used. âĒ These salts are subjected to mechanical & thermal instability or water solubility. âĒ Protection against damage must be continuously exercised.
- 14. B. Grating âĒ Gratings are nothing but rulings made on some materials like glass, quartz or alkylhalides depending upon the instrument, The mechanism is that diffraction produces reinforcement. The rays which are incident upon the gratings gets reinforced with the reflected rays.
- 15. Advantages over Prism:- Made with materials like aluminium which are not attacked by moisture. Used over cosiderable wavelength range.
- 16. 3. Sample cell & Sampling of substance Infrared spectra may be obtained for gases, liquids or solids (neat or in solution) âĒ Material containing sample must be transparent to the IR radiation. So, the salts like NaCl, KBr are only used.
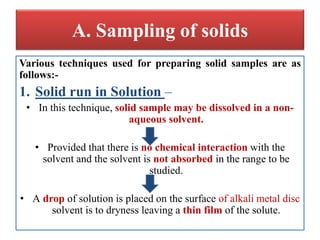
- 17. A. Sampling of solids Various techniques used for preparing solid samples are as follows:- 1. Solid run in Solution â âĒ In this technique, solid sample may be dissolved in a non- aqueous solvent. âĒ Provided that there is no chemical interaction with the solvent and the solvent is not absorbed in the range to be studied. âĒ A drop of solution is placed on the surface of alkali metal disc solvent is to dryness leaving a thin film of the solute.
- 18. 2. Solid film technique âĒ If the solid is amorphous in nature. âĒ Then the sample is deposited on the surface of a KBr or NaCl cell by evaporation of a solution of the solid. âĒ Ensured that the film is not too thick to pass the radiation
- 19. 3. Pressed pellet technique âĒ In this technique, a small amount of finely ground solid sample is mixed with 100 times its weight of potassium bromide and compressed. âĒ To form thin transparent pellet(1-2mm thick & 1cm in diameter) using a hydraulic press. âĒ These pellets are transparent to IR radiation and it is used for analysis.
- 20. Advantages:- âĒ Kbr pellets stored for long period of time. âĒ Resolution of spectrum is superior. Disadvantages:- âĒ Always have a band at 3450cm-1 due to OH group of moisture. âĒ Due to high pressure(~25000 psig) polymorphic changes occurs. âĒ Not successful for polymers. (diffcult to grind with Kbr.)
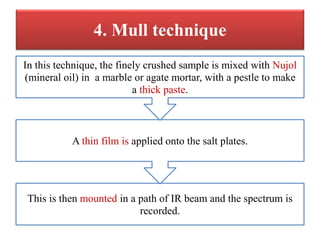
- 21. 4. Mull technique This is then mounted in a path of IR beam and the spectrum is recorded. A thin film is applied onto the salt plates. In this technique, the finely crushed sample is mixed with Nujol (mineral oil) in a marble or agate mortar, with a pestle to make a thick paste.
- 22. 2. Sampling of liquids Some salt plates are highly soluble in water, so the sample and washing reagents must be anhydrous For most liquids, the sample cell thickness is 0.01-0.05 mm. The sample thickness should be selected so that the transmittance lies between 15- 20%. Aqueous solvents cannot be used because they cannot dissolve alkali halides. Organic solvents like chloroform can be used. Liquid sample cells can be sandwiched using liquid sample cells of highly purified alkali halides, normally NaCl. & KBr can also be used.
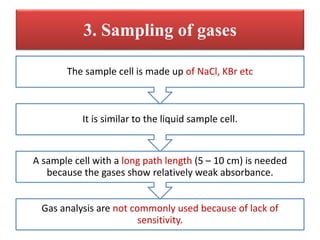
- 23. 3. Sampling of gases Gas analysis are not commonly used because of lack of sensitivity. A sample cell with a long path length (5 â 10 cm) is needed because the gases show relatively weak absorbance. It is similar to the liquid sample cell. The sample cell is made up of NaCl, KBr etc
- 24. DETECTORS âĒ The detectors can be classified into three categories: 1. Thermal detectors:- Their responses depend upon the heating effect of radiation . 2. Pyroelectric detectors:- Pyroelectric effect depends on the rate of change of the detector temperature rather than on the temperature itself. 3. Photoconducting detectors:- Most sensitive .
- 25. Thermocouples If one welded joint (called the hot junction) becomes hotter than the other joint (the cold junction), a small electrical potential develops between the joints A thermocouple is made by welding together at each end two wires made from different metals.
- 26. Response time ~60m sec. The potential difference generated in the wires is a function of the temperature difference between the junctions and, therefore, of the intensity of IR radiation falling on the hot junction. The hot junction is xposed to the IR radiation, which increases the temperature of the junction. In IR spectroscopy, the cold junction is carefully screened in a protective box and kept at a constant temperature.
- 27. To enhance sensitivity several thermocouples connected in series are called a âthermopileâ
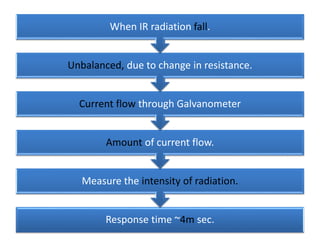
- 28. Bolometer Bridge remain balance. When no radiation fall on bolometer. A similar strip of metal used as balancing arm of bridge. A bolometer is made one arm of Wheatstone Bridge. It consist of thin metal conductor. A bolometer is a type of resistance thermometer.
- 29. Response time ~4m sec. Measure the intensity of radiation. Amount of current flow. Current flow through Galvanometer Unbalanced, due to change in resistance. When IR radiation fall.
- 30. THERMISTORS Made of fused mixture of metal oxides. As the temp. of mixture increases, itâs electrical resistance decreases. (opposed to Bolometer) Response time very slow...