Inheritance in c++ part1
- 1. Inheritance in C++ Dr.Mirza Waseem Hussain 1 By: Dr. Mirza Waseem Hussain Lecturer Computer Science
- 2. Table of Contents 1. Concept of Inheritance 2. Advantages of Inheritance 3. General Syntax of Inheritance 4. Inheritance Access specifier/ Visibility modes. ïķPublic mode. ïķProtected mode. ïķPrivate mode. Dr.Mirza Waseem Hussain 2
- 3. 1. Concept of inheritance: ïInheritance is one of the feature of Object Oriented Programming System(OOPs), it allows the child class to acquire the properties (the data members) and functionality (the member functions) of parent class. ïInheritance is a process in which one object acquires all the properties and behaviors of its parent object automatically. ïThe technique of deriving a new class from an old one is called inheritance. ïInheritance is a mechanism in which one class acquires the property of another class. ï§ For example, a child inherits the traits of his/her parents. ïIt allows user to create a new class (derived class, subclass, child class) from an existing class(base class, super class, parent class). ï§ The derived class inherits all the features from the base class and can have additional features of its own. Dr.Mirza Waseem Hussain 3
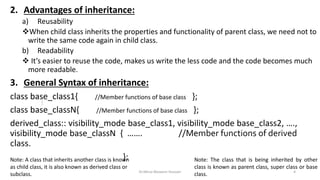
- 4. 2. Advantages of inheritance: a) Reusability ïķWhen child class inherits the properties and functionality of parent class, we need not to write the same code again in child class. b) Readability ïķ Itâs easier to reuse the code, makes us write the less code and the code becomes much more readable. 3. General Syntax of inheritance: class base_class1{ //Member functions of base class }; class base_classN{ //Member functions of base class }; derived_class:: visibility_mode base_class1, visibility_mode base_class2, âĶ., visibility_mode base_classN { âĶâĶ. //Member functions of derived class. }; Dr.Mirza Waseem Hussain 4 Note: A class that inherits another class is known as child class, it is also known as derived class or subclass. Note: The class that is being inherited by other class is known as parent class, super class or base class.
- 5. 4. Inheritance Access specifier/ Visibilty modes: ïAccess Specifiers defines the visibility of the Property /Fields/ Variable/ Methods of a class. ïAccess modifiers (or access specifiers) are keywords in object-oriented languages that set the accessibility of classes, methods, and other members. ïThere are three types of Access specifiers in C++ to define the visibility modes of inheritance. âĒ Private. âĒ Public . âĒ Protected. A. Public mode: ïIf we derive a sub class from a public base class. Then the public member of the base class will become public in the derived class and protected members of the base class will become protected in derived class. syntax: class derive_class::public base_class{ âĶ //Member functions of derived class }; Dr.Mirza Waseem Hussain 5
- 6. B. Protected: ïIf we derive a sub class from a Protected base class. Then both public member and protected members of the base class will become protected in derived class. syntax: class derive_class::protected base_class{ âĶ //Member functions of derived class }; C. Private: ïIf we derive a sub class from a Private base class. Then both public member and protected members of the base class will become Private in derived class. syntax: class derive_class::private base_class{ âĶ //Member functions of derived class }; Dr.Mirza Waseem Hussain 6 Note:The private members in the base class cannot be directly accessed in the derived class, while public and protected members can be directly accessed.
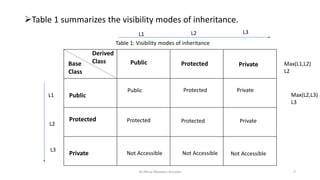
- 7. ïTable 1 summarizes the visibility modes of inheritance. Dr.Mirza Waseem Hussain 7 Base Class Derived Class Public Public Protected Protected Private Public Protected Private Protected Protected Private Private Not Accessible Not Accessible Not Accessible Table 1: Visibility modes of inheritance Max(L1,L2) L2 L1 L2 L3 L1 L2 L3 Max(L2,L3) L3
- 8. // C++ Implementation to show that a derived class // doesnât inherit access to private data members. // However, it does inherit a full parent object class A { public: int x; protected: int y; private: int z; }; class B : public A { // x is public // y is protected // z is not accessible from B }; class C : protected A { // x is protected // y is protected // z is not accessible from C }; class D : private A // 'private' is default for classes { // x is private // y is private // z is not accessible from D }; Dr.Mirza Waseem Hussain 8
- 10. Dr.Mirza Waseem Hussain 10
- 11. Source: âĒ https://www.javatpoint.com/cpp-inheritance âĒ https://www.w3schools.in/cplusplus-tutorial/inheritance/ âĒ https://www.tutorialcup.com/cplusplus/inheritance.htm âĒ https://www.learncpp.com/cpp-tutorial/112-basic-inheritance-in-c/ âĒ https://beginnersbook.com/2017/08/cpp-inheritance/ âĒ https://www.programiz.com/cpp-programming/inheritance âĒ https://www.tutorialspoint.com/cplusplus/cpp_inheritance.htm âĒ https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/inheritance-in-c/ Dr.Mirza Waseem Hussain 11
- 12. Dr. Mirza Waseem Hussain 12