Innovation Methodology
- 1. Innovation is a methodology for solving problems See: The Missing Pieces of Innovation â a blog post This is a summary of the innovation methodology. ÂĐ Ved Sen
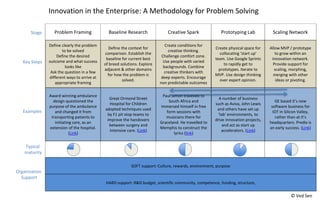
- 2. Award winning ambulance design questioned the purpose of the ambulance and changed it from transporting patients to initiating care, as an extension of the hospital. (Link) Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children adopted techniques used by F1 pit stop teams to improve the handovers between surgery and intensive care. (Link) Paul Simon travelled to South Africa and immersed himself in free form sessions with musicians there for Graceland. He travelled to Memphis to construct the lyrics (link) A number of business such as Aviva, John Lewis and others have set up âlabâ environments, to drive innovation projects, and act as start up accelerators. (Link) GE based itâs new software business for IOT in Silicon Valley, rather than at itâs headquarters. Predix is an early success. (Link) Define clearly the problem to be solved Define the desired outcome and what success looks like Ask the question in a few different ways to arrive at appropriate framing Define the context for comparison. Establish the baseline for current best of breed solutions. Explore adjacent & other domains for how the problem is solved. Create conditions for creative thinking. Challenge comfort zone. Use people with varied backgrounds. Combine creative thinkers with deep experts. Encourage non predictable outcomes Create physical space for collocating âstart upâ team. Use Google Sprints to rapidly get to prototypes. Iterate to MVP. Use design thinking over expert opinion. Allow MVP / prototype to grow within an innovation network. Provide support for scaling, morphing, merging with other ideas or pivoting. Problem Framing Baseline Research Creative Spark Prototyping Lab Scaling Network SOFT support: Culture, rewards, environment, purpose HARD support: R&D budget, scientific community, competence, funding, structure, Innovation in the Enterprise: A Methodology for Problem Solving Typical maturity Stage Key Steps Examples Organization Support ÂĐ Ved Sen
- 3. If you're not prepared to be wrong, you'll never come up with anything original â Sir Ken Robinson Image source: https://www.eurodiaconia.org/