Insect pests of tea
- 1. Insect pests of Tea and their management Dr M Thippaiah Professor Department of Entomology University of Agricultural Sciences GKVK, Bangalore- 65
- 2. ï India is the second largest producer of tea and fourth position in foreign export. ï Insect and mite pests (arthropods) are the most destructive, resulting in 5 â55% crop loss. ï As many as 147 insect pests have been recorded on this crop. These insect pests mainly includes â 1. Protoplast - feeding mites 2. Sap suckers of leaf and stem tissues, viz., tea mosquito bug, green flies, thrips, and mealy bugs 3. Nibblers and defoliators, viz., loopers, red slug caterpillars, leaf roller, flush worm and tea tortrix 4. Stem borers, viz., shot-hole borer and red borer (5) Collar and root feeders, viz., termites and white grubs. Dr. M. Thippaiah
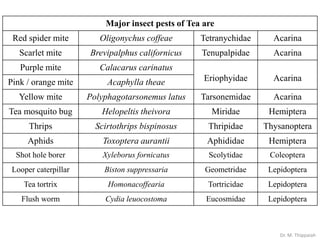
- 3. Major insect pests of Tea are Red spider mite Oligonychus coffeae Tetranychidae Acarina Scarlet mite Brevipalphus californicus Tenupalpidae Acarina Purple mite Calacarus carinatus Eriophyidae AcarinaPink / orange mite Acaphylla theae Yellow mite Polyphagotarsonemus latus Tarsonemidae Acarina Tea mosquito bug Helopeltis theivora Miridae Hemiptera Thrips Scirtothrips bispinosus Thripidae Thysanoptera Aphids Toxoptera aurantii Aphididae Hemiptera Shot hole borer Xyleborus fornicatus Scolytidae Coleoptera Looper caterpillar Biston suppressaria Geometridae Lepidoptera Tea tortrix Homonacoffearia Tortricidae Lepidoptera Flush worm Cydia leuocostoma Eucosmidae Lepidoptera Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 4. Tea Mites : there are five species mites reported on tea crop 1. Read spider mite â Oligonychus coffeae 2. Scarlet mite â Brevipalpus californicus 3. Purple mite â Calacarus carinatus 4. Pink mite or orange mite â Acaphylla theae 5. Yellow mite â polyphagotarsonemus latus Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 5. 1. Red spider mite - Oligonychus coffeae ( Tetranychidae : Acarina) O. coffeae is the largest of all tea mites ï Adult - female is elliptical in shape, bright crimson colour anteriorly and dark puplish brown colour posteriorly ï Mite spin a web of silken threads on the leaf Eggs: are laid on upper surface of matured leaves Eggs are reddish in colour and spherical in shape and provided small filament I.P â 4-6 days Nymphs : It will pass through a larval stage and two nymphal stages before become adult Dr. M. Thippaiah
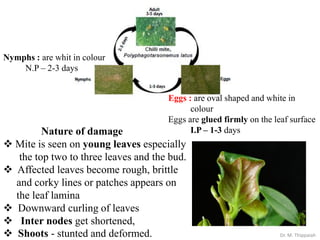
- 6. Nature of damage ïķ Nymphs and adults infest the upper surface of mature leaves. ïķ Infestation starts along midrib and veins and spreads to the entire upper surface of leaves. ïķ Affected leaves â turns brownish or bronze colour, dry and crumpled. Developmental stages include six legged larva, protonymph and deutonymph Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 7. 2. Scarlet mite : Brevipalpus californicus ( Tenuipalpidae : Acarina) Adult mite is scarlet red in colour and ovate in shape with black marks dorsally and slightly bigger then eriophyid mite Eggs - are bright red colour and elliptical in shape and laid in clusters on the under surface of leaves I.P - 7-10 days Nymphs : Developmental stages include three legged larva, protonymph, and deutonymph and each developmental stage is followed by a quiescent stage N.P â 23-26 days TLC- 30-36 days Adult Reproduction is by parthenogenesis Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 8. Nature of damage: ï Mites congregate on the under surface of matured leaves and later spread to entire leaf ï Feeding by scarlet mites leads to brown discolouration of leaves and severe infestation leads to defoliation Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 9. 3. Purple mite - Calacarus carinatus ( Eriophyidae : Acarina) This mite is characteristics with a spindle shaped deep purple body, with five longitudinal white waxy ridges on the dorsal side. This is a major pest in South India in Tea plantation / wide distribution Eggs : are laid on under surface of matured leaves I.P- 2-3 days Nymphs : there are two nymphal stages and they are white in colour, young one moult three times N.P â 3-6 days TLC â 7-15 days Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 10. Coppery brown discolouration Nature of damage ïķ Purple mites feed on the under surface of mature leaves. ïķ Presence of numerous white cast skins of the mites along with live mites ïķ Damaged leaves â characterized by coppery brown discolouration ïķ Assam type of tea - more susceptible to purple mite Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 11. 4. Pink mite (or) Orange mite - Acaphylla theae (Eriophyidae : Acarina) Important mite pest of tea in Southern India causes considerable damage Adult are very minute, orange coloured spindle shaped / carrot shaped mite Eggs : are shiny, globular in shape and lay singly on the under surface of the leaves I.P â 2-3 days Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 12. Nature of damage ï Mites are found on the under surface of young leaves ï During early stages of attack leaves turn pale colour and curl upwards ï In severe infestation â the affected leaves become discoloured and leathery ï The veins show a pinkish colouration Nymphs : there are two nymphal stages and they are white in colour population builds up in November / December Attain peak in February / March and declined during May / June N.P â 4-6 days Young ones moult three times NP â 3-5 days with two nymphal stages TLC- 6-9 days Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 13. ïThe bushes in general a sickly appearance ï Assam hybrids are more susceptible Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 14. 5. Yellow mite - Polyphagotarsonemus latus ( Tarsonemidae : Acarina) ï It appears in the North-East Indian plantations ï Yellow mite is a polyphagous pest attacking tomato, cotton, pulses, potato, chillies etc. ïķ The adult is yellow colour with white stripes dorsally ïķ Male mites are small and white to pale yellow in colour and emerging earlier and carrying the female nymphs on their back ïķ Females are yellowish and bigger than the males ïķ Yellow mites are active and fast moving mites. Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 15. Eggs : are oval shaped and white in colour Eggs are glued firmly on the leaf surface I.P â 1-3 days Nymphs : are whit in colour N.P â 2-3 days Nature of damage ïķ Mite is seen on young leaves especially the top two to three leaves and the bud. ïķ Affected leaves become rough, brittle and corky lines or patches appears on the leaf lamina ïķ Downward curling of leaves ïķ Inter nodes get shortened, ïķ Shoots - stunted and deformed. Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 16. Management practices for mites ïķ Grow nurseries away from infested crop and avoid planting next to infested field ïķ Grow healthy crops, avoid water and nutrient stress ïķ Apply mulch and incorporate organic matter into the soil to improve the water holding capacity and reduce evaporation ïķ Keep perennial edge such as pigeon pea, they are said to encourage predatory mites ïķ Uproot and burn the infested plants â this can be successful during the early stages of infestation when mite concentrate on a few plants ïķ Keep the field free of weeds ïķ Remove and burn the infested crop residues immediately after harvest Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 17. ïķ Collect and destroy all types of damaged parts along with mites ïķ Spray the crop with dicofol 18.5 % EC @ 2 ml / lit or ethion 50 % EC @ 2 ml / lit or fenazaquin 10 % EC @ 400 ml in 160-320 lit. / acre or Fenopropathrin 30 % EC @ 66-80 ml in 160-200 lit. / acre or propargite 57 % EC @ 300 â 500 ml in 160 lit / acre or spiromesifen 22.9 % EC @ 160 ml in 160 lit. of water ïķ Application of wettable sulphur 80 % WP @ 2g / lit using hand operated sprayer to ensure proper coverage of spray solution Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 18. Tea mosquito bug, Helopeltis theivora ( Miridae : Hemiptera) ïķ It is considered to be a serious pest of a tea and widely distributed in Karnataka, Goa, Maharashtra and TN ïķ The damage more severe in shaded areas. ï The Adult is small , active elongated bug with black or olive green coloured head and black coloured thorax, and greenish black coloured abdomen and greenish brown wings ï Body of the bug is small, slender with long legs and antennae ï An erect knobbed process on the scutellum is characteristic of the species Bugs are active in the early morning and late evening hours and hide among the bushes during remaining period Dr. M. Thippaiah
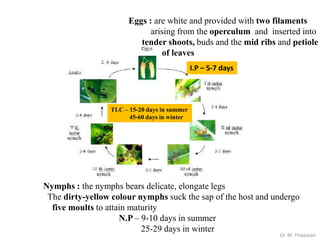
- 19. Eggs : are white and provided with two filaments arising from the operculum and inserted into tender shoots, buds and the mid ribs and petiole of leaves I.P â 5-7 days Nymphs : the nymphs bears delicate, elongate legs The dirty-yellow colour nymphs suck the sap of the host and undergo five moults to attain maturity N.P â 9-10 days in summer 25-29 days in winter TLC â 15-20 days in summer 45-60 days in winter Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 20. Nature of damage Adults and nymphs suck the sap from young leaves, buds and tender stems By puncturing the plant tissues with their needle like stylets and inject toxic saliva These punctures appear as reddish brown spots. Due to intensive feeding leaves curl up, badly deformed and remain small gradually shoots are dry up Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 21. Damage caused and life stages of Helopeltis theivora on tea Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 22. Management practices ïķ Removal of the alternate hosts of H. theivora such as Guava, Sesbania, Jack fruit, Mulberry, Ornamental Jasmine etc., ïķ The bug prefers moist conditions and mild temperature, for this reason, populations of this pest are often higher under heavy shade condition Regulate the shade in densely shaded areas and looping of the lower branches of shade trees ïķ Collect and destroy the damaged plant parts ïķ Entomopathogen, Beauveria bassiana @ 1.2 Kg / acre minimized infestation in field condition ïķ Spray clothianidin 50% WDG @ 48gm in 200 lit. of water / acre or profenophos 50 % EC @ 320 â 400 ml in 160 lit. / acre or Thiacloprid 21.7 % SC @ 150ml in 160 lit. / acre or Thiamethoxam 25 % WG @ 40gm in 160-200 lit. / acre Dr. M. Thippaiah
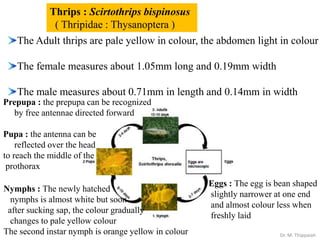
- 23. The Adult thrips are pale yellow in colour, the abdomen light in colour The female measures about 1.05mm long and 0.19mm width The male measures about 0.71mm in length and 0.14mm in width Thrips : Scirtothrips bispinosus ( Thripidae : Thysanoptera ) Eggs : The egg is bean shaped slightly narrower at one end and almost colour less when freshly laid Nymphs : The newly hatched nymphs is almost white but soon after sucking sap, the colour gradually changes to pale yellow colour The second instar nymph is orange yellow in colour Prepupa : the prepupa can be recognized by free antennae directed forward Pupa : the antenna can be reflected over the head to reach the middle of the prothorax Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 24. Nature of damage ïķ Thrips prefer young leaves and buds. ïķ As a result creating feeding scars, distortion of leaves and discolouration of buds ïķ The infested leaves curl upward, crumble and shed down ïķ Infested buds become brittle and drop down Management practices ï The recommendation on shade management, If adopted, will help to prevent the excessive built up of thips and mites ï Spray dimethoate 30 EC (or) chlorpyriphos 20 EC @ 2 ml/lit. Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 25. Aphids : Toxoptera aurantii ( Aphididae : Hemiptera) Adults are small, black to dark brown soft-bodied insects with two long antennae that resemble horns Most aphids have short cornicles ( horns) to wards the posterior end of abdomen Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 26. Eggs : A tiny eggs found in the crevices of bud, stems and barks of the plant Aphids do not lay eggs in warmer parts of the world I.P â 2-3 days Nymphs : young aphids they are look like wingless adults but smaller in size N.P â 7-10 days Nature of damage ïķ Colonies of aphids are seen on tender shoots immediately after pruning, due to feeding by aphids ïķ Leaves curl up and shoot growth is stunted. ïķ Aphids are attended by ants. ïķ Honey dew secreted development of sooty moulds. Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 27. Management practices ï§ Collect and destroy the infested plant parts ï§ Spray dimethoate 30 EC (or) chlorpyriphos 20 EC@ 2 ml/lit. ï§ Spray phosalone @ 2 ml/lit. Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 28. Shot hole borer : Xyloborus fornicatus (Scolytidae : Coleptera ) ïAdult is minute beetle measuring about 3-4mm in length ïFemale - small, black colour and elongated beetle. ï Male is half the size of female, devoid of wings The female bores and excavates vertical tunnels with side branches Eggs : are laid at each junction and on the openings of side branches and covered with a damp of saw dust which produces necessary conditions for growth of Ambrosia fungus on which the larva feeds ï Intensive tunnelling with in the stems interferes with sap flow, weakening the stems and making them liable to attack by wood rotting fungus Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 29. Nature of damage Presence of round shot holes in primary branches. The attack results in mortality of buds and dieback symptoms in branches. Presence of circular or longitudinal tunnels inside the stem. The infested branches may break off at the slightest pressure Management practices ïķ Remove and destroy affected twigs. ïķ Spray lindane 20 EC @ 2 ml / lit using hand sprayer immediately after pruning Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 30. Looper caterpillar : Biston suppressaria ( Geometridae : Lepidoptera) ïķ It is serious pest of tea in North-East India ïķ Adult moth have grey coloured wings speckled with light brown or black markings and irregular wavy yellow lines Eggs : the female lays eggs in groups of 200-600 and these eggs are covered with a buff coloured hairs The most common site for deposition of eggs in the trunk of shade trees or any other tall trees in the vicinity of tea fields Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 31. Nature of damage ï Young caterpillar feed on tender leaves, making punctures along the margin while mature larvae preferred older leaves ï Grown up larvae feed on entire leaves and defoliate the plants Larva: The young caterpillar is dark brown with greenish white lines along the back and side ïThe body colour soon turns to light greenish and with age, it acquires a brownish grey colour similar to that of a mature twig of tea ï There are five larval instars L.P â 24-36 days Pupa : The full grown caterpillar moves down to ground for pupation at a depth of 2.5 to 5cm in the soil under tea bushes P. P â 20-22 days TLC â 72 days during March â May 60 days during June - July Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 32. Tea tortrix: Homona coffearia ( Tortricidae : Lepidoptera) It is a important pest of tea in Srilanka ï Adult is a small brownish yellow in coloured moth and bell shaped in out line at rest ï Fore wings have oblique band and few transverse wavy lines ï The male moth is smaller than female moth Eggs : Eggs are laid in masses of 100-150 on the upper surface of mature leaves. I.P â 6 - 8 days Larva : larva green in colour L.P - 20-30 days Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 33. Nature of damage Caterpillars make leaf nests by webbing the leaves using silken threads and feed from inside Single caterpillar makes several cases Young larvae prefer tender leaves while the older larvae are seen in mature leaves Pupa : Pupation takes place inside the leaf cases P.P - 8 â 10 days. Nursery plants suffers maximum damage Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 34. Flushworm: Cydia leuocostoma ( Eucosmidae : Lepidoptera) ï Adult is a small moth, blackish brown in colour with yellow and white streaks on fore wings ï Measures about 10-13mm across expanded wings Eggs: are pale yellow and laid singly on the under surface of mature leaves. I.P - 4-5 days Larva : larva brown in colour L.P -19-25 days Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 35. Nature of damage ïķ Caterpillar ties up the margin of tender leaves and forms a case / fold enclosing the bud. ïķ Feed on the upper epidermis of leaves. ïķ Affected leaves - rough, crinkled and leathery. ïķ Bud - Shoot growth is arrested ïķ The presence of the larval frass in the leaf fold may deteriorate the quality of tea Pupa : Full grown larva, the mature leaves folds its margin and pupate inside . P.P - 8 â 10 days. Dr. M. Thippaiah
- 36. Control measures for leaf feeders ï§ Collect and destroy damaged leaves along with caterpillars ï§ Collection and destruction of the infested buds along with caterpillars ï§ Spray the crop with NSKE 5 % or neem based oil formulations or Spray phosalone or cholrpyriphos or fenitrothion or malathion @ 2ml / lit Dr. M. Thippaiah