INSERVICE TRAINING SCHOOL BASED2023 PRESENTATION.pptx
- 1. Agenda Session 10A: Numbers and Number Sense Session 10B: Place Value and Decimal System Session 11: Multi-Digit Addition and Substraction 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 1
- 2. Session 10A: The Concept of Number Sense and Counting Venia G. Asuero
- 3. Number Sense and Numeration Overview of Big Concept
- 4. Numbers & Number Sense ŌĆó is one of the key contents in K-12 Mathematics Curriculum ŌĆó Numbers and Number Sense as a strand include concepts of numbers, properties, operations, estimation, and their applications. ŌĆó personŌĆÖs ability to understand, relate, and connect numbers. 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 4
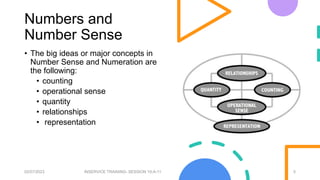
- 5. Numbers and Number Sense ŌĆó The big ideas or major concepts in Number Sense and Numeration are the following: ŌĆó counting ŌĆó operational sense ŌĆó quantity ŌĆó relationships ŌĆó representation 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 5
- 6. General Principles of Instruction 1. Representations of concepts promote understanding and communication. 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 6
- 7. General Principles of Instruction 2. Problem solving should be the basis for most mathematical learning. 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 7
- 8. General Principles of Instruction 3. Students need frequent experiences using a variety of resources and learning strategies. 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 8 This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND
- 9. General Principles of Instruction 4. As students confront increasingly more complex concepts, they need to be encouraged to use their reasoning skills 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 9
- 10. Counting Its Key Concept and Instruction/Strategies in Teaching Counting
- 11. Key Concepts of Counting ŌĆó Counting includes both the recitation of a series of numbers and the conceptualization of a symbol as representative of a quantity. ŌĆó Making the connection between counting and quantity ŌĆó Counting is a powerful early tool intricately connected with the future development of studentsŌĆÖ conceptual understanding of quantity, place value, and the operations. 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 11
- 12. Key Concepts of Counting Stable order ŌĆō the idea that the counting sequence stays consistent; it is always 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, . . . , not 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8 1 Order irrelevance ŌĆō the idea that the counting of objects can begin with any object in a set and the total will still be the same. 2 Conservation ŌĆō the idea that the count for a set group of objects stays the same no matter whether the objects are spread out or are close together 3 Abstraction ŌĆō the idea that a quantity can be represented by different things (e.g 5 apples) 4 One-to-one correspondence ŌĆō the idea that each object being counted must be given one count and only one count. 5 Cardinality ŌĆō the idea that the last count of a group of objects represents the total number of objects in the group. 6 Movement is magnitude ŌĆō the idea that, as one moves up the counting sequence, the quantity increases by 1 7 Unitizing ŌĆō the idea that, in the base ten system, objects are grouped into tensonce the count exceeds 9 8 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 12
- 13. General Strategies For Teaching Counting ŌĆó link the counting sequence with objects (especially fingers) or movement on a number line, so that students attach the counting number to an increase in quantity or, when counting backwards, to a decrease in quantity; ŌĆó model strategies that help students to keep track of their count (e.g., touching each object and moving it as it is counted); ŌĆó provide activities that promote opportunities for counting both inside and outside the classroom (playing hide-and- seek and counting to 12 before ŌĆ£seekingŌĆØ; counting students as they line up for recess); 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 13
- 14. General Strategies For Teaching Counting ŌĆó link the counting sequence with objects (especially fingers) or movement on a number line, so that students attach the counting number to an increase in quantity or, when counting backwards, to a decrease in quantity; ŌĆó model strategies that help students to keep track of their count (e.g., touching each object and moving it as it is counted); ŌĆó provide activities that promote opportunities for counting both inside and outside the classroom (playing hide-and- seek and counting to 12 before ŌĆ£seekingŌĆØ; counting students as they line up for recess); 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 14
- 15. General Strategies For Teaching Counting ŌĆó continue to focus on traditional games and songs that encourage counting skills for the earliest grades but also adapt those games and songs, so that students gain experience in counting from anywhere within the sequence (e.g., counting from 4 to 15 instead of 1 to 10), and gain experience with the teen numbers, which are often difficult for Kindergarteners; ŌĆó link the teen words with the word ten and the words one to nine (e.g., link eleven with the words ten and one; link twelve with ten and two) to help students recognize the patterns to the teen words, which are exceptions to the patterns for number words in the base ten number system; 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 15
- 16. General Strategies For Teaching Counting ŌĆó help students to identify the patterns in the numbers themselves (using a hundreds chart). These patterns in the numbers include the following: ŌĆō The teen numbers (except 11 and 12) combine the number term and teen (e.g., 13, 14, 15). ŌĆō The number 9 always ends a decade (e.g., 29, 39, 49). ŌĆō The pattern of 10, 20, 30, . . . follows the same pattern as 1, 2, 3, . . . . ŌĆō The tens follow the pattern of 1, 2, 3, . . . within their decade; hence, 20 combines with 1 to become 21, then with 2 to become 22, and so on. ŌĆōThe pattern in the hundreds chart is reiterated in the count from 100 to 200, 200 to 300, and so on, and again in the count from 1000 to 2000, 2000 to 3000, and so on 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 16
- 17. Teacher , how do you teach counting? Please share your classroom strategies 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 17
- 18. Session 10B: Place Value and the Decimal System Venia G. Asuero
- 19. Place Value and Decimal System Key Concepts in Teaching
- 20. What is Place Value? Place value is the numeric value of a digit, which changes depending upon its position in a number. 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 20 This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-SA-NC
- 21. Key Concepts in Teaching Place value and Decimal System ŌĆó The numeration system currently used in the Philippines, the Hindu-Arabic or decimal system, is a numeration system that employs place or positional value (the position or place of a numeral defines its value in multi-digit numerals) ŌĆó Learning about place value entails the ability to count groups as though they were individual objects ŌĆó Using the place value system requires the conservation of number ŌĆó Children need to explore the place value system first by manipulating materials (concept/concrete level), then by relating these experiences with their corresponding symbols (connecting stage) and eventually by recording these experiences using their corresponding symbols (symbolic stage) 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 21
- 22. Its time to showcase your strategy: ŌĆó Group yourself according to the grade level you are in. ŌĆó You have 5 minutes to list down the strategies you do to introduce place value and decimal system. ŌĆó Choose only the best 2 strategies you are familiar with and the best strategy for the grade level you are teaching and prepare to demonstrate it to the entire group. 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 22
- 23. Some of the strategies to teach place value and decimal system: Use Manipulatives to Introduce and Teach Place Value- Manipulatives include any hand-on materials, tools or resources that help students to build conceptual understanding through concrete activities. 1 Use Money as a Manipulative When Teaching Place Value- consider money (REAL money ŌĆō not plastic coins and paper play money!!) to be one of the best manipulatives you can use when teaching place value. 2 The CPA (Concrete, Pictorial, Abstract) approach helps pupils connect a physical representation of a number (concrete manipulatives) to that same quantity as shown in drawings or graphics (pictorial), and finally to the actual written name and symbol for that number (abstract). 3 Give Many Opportunities for Your Students to Practice Place Value- explore activities that your children will have fun and enjoy. 4 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 23
- 24. Session 11: Multi- Digit Addition and Substraction Venia G. Asuero
- 25. Operational Sense Key Concepts in Teaching
- 26. Key Concepts in Teaching Basic Operations ŌĆó StudentsŌĆÖ effectiveness in using operations depends on the counting strategies they have available, on their ability to combine and partition numbers, and on their sense of place value. ŌĆó Students learn the patterns of the basic operations by learning effective counting strategies, working with patterns on number lines and in hundreds charts, making pictorial representations, and using manipulatives.
- 27. Key Concepts in Teaching Basic Operations ŌĆó The operations are related to one another in various ways (e.g., addition and subtraction are inverse operations). Students can explore these relationships to help with learning the basic facts and to help in problem solving. ŌĆó Students gain a conceptual understanding of the operations when they can work flexibly with algorithms, including those of their own devising, in real contexts and problem- solving situations.
- 28. General Instruction in the Operations 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 28 ŌĆó The following are general strategies for teaching the operations. Teachers should: ŌĆó focus on problem-solving contexts that create a need for computations; ŌĆó create situations in which students can solve a variety of problems that relate to an operation (e.g., addition) in many different ways, so that they can build confidence and fluency;
- 29. General Instruction in the Operations 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 29 ŌĆó encourage students to use manipulatives or pictorial representations to model the action in the problems; ŌĆó allow students to discover their own strategies for solving the problems; ŌĆó use open-ended probes and questioning to help students understand what they have done and communicate what they are thinking;
- 30. General Instruction in the Operations 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 30 ŌĆó prompt students to move to more efficient strategies (e.g., counting on, counting back, using derived facts, making tens); ŌĆó most importantly, encourage students to talk about their understandings with the teacher and with their classmates; ŌĆó use what they have learned about the mathematical thinking of individual students to ŌĆ£assess on their feetŌĆØ in order to provide immediate, formative feedback to students about their misconceptions and about any of their ideas that need more exploration.
- 31. Thank you 02/07/2023 INSERVICE TRAINING- SESSION 10-A-11 31 VENIA G. ASUERO Email address: vinia.galasi@deped.gov.ph
Editor's Notes
- #5: Other strands are Measurement, Geometry, Patterns & Algebra and Statistics and Probability.
- #6: These big ideas are conceptually interdependent, equally significant, and overlapping. For example, meaningful counting includes an understanding that there is a quantity represented by the numbers in the count. Being able to link this knowledge with the relationships that permeate the base ten number system gives students a strong basis for their developing number sense. And all three of these ideas ŌĆō counting, quantity relationships ŌĆō have an impact on operational sense, which incorporates the actions of mathematics. Present in all four big ideas are the representations that are used in mathematics, namely, the symbols for numbers, the algorithms, and other notation, such as the notation used for decimals and fractions
- #7: (e.g., manipulatives, pictures, diagrams, or symbols).
- #8: Learning basic facts through a problem-solving format, in relevant and meaningful contexts, is much more significant to children than memorizing facts without purpose
- #9: e.g., number lines, hundreds charts or carpets, base ten blocks, interlocking cubes, ten frames, calculators, math games, math songs, physical movement, math stories)
- #10: . It is important for students to realize that math ŌĆ£makes senseŌĆØ and that they have the skills to navigate through mathematical problems and computations. Students should be encouraged to use reasoning skills such as looking for patterns and making estimates