Integrated logistics and supply chain framework
- 1. SUPPLY CHAIN/LOGISTICS OVERVIEW FOR TIPQC LM 393 STUDENTS
- 2. Learning Objectives Understand the role and importance of logistics in organizations. Discuss the impact of logistics on the economy and how effective logistics management contributes to the vitality of the economy. Understand the value-added roles of logistics on both the macro and micro level. Explain logistics systems from several perspectives. Chapter 2 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed.
- 3. Learning Objectives Understand the relationship between logistics and the other important functional areas in a company, including manufacturing, marketing, and finance. Discuss the important management activities in the logistics function. Chapter 2 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed.
- 4. SUPPLY CHAIN/LOGISTICS OVERVIEW TOPICS FOR DISCUSSION DEFINITION & CONCEPTS SUPPLY CHAIN MGMT LOGISTICS MGMT PHYSICAL DISTRIBUTION SUPPLY CHAIN FLOW DIAGRAM
- 5. SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT The art and science of managing the flow of materials and products from source to user.
- 6. ╠²
- 7. LOGISTICS MANAGEMENT - DEFINITION Logistics is the management of the flow of goods , information and other resources, including energy and people, between the point of origin and the point of consumption in order to meet the requirements of consumers (frequently, and originally, military organizations). Logistics involves the integration of information, transportation , inventory , warehousing , material-handling, and packaging , and occasionally security . Logistics is a channel of the supply chain which adds the value of time and place utility.
- 8. LOGISTICS MANAGEMENT ŌĆō ORIGIN The term "logistics" originates from the ancient Greek " ╬╗Žī╬│╬┐Žé " (" logos "ŌĆö"ratio, word, calculation, reason, speech, oration"). Logistics is considered to have originated in the military's need to supply themselves with arms, ammunition and rations as they moved from their base to a forward position. In ancient Greek, Roman and Byzantine empires, there were military officers with the title ŌĆś Logistikas ŌĆÖ who were responsible for financial and supply distribution matters.
- 9. LOGISTICS MANAGEMENT ŌĆō ORIGIN The Oxford English dictionary defines logistics as: ŌĆ£The branch of military science having to do with procuring, maintaining and transporting material, personnel and facilities. ŌĆØ Another dictionary definition is: "The time related positioning of resources." As such, logistics is commonly seen as a branch of engineering which creates " people systems " rather than " machine systems. "
- 10. What is Logistics? Popular logistics terms: Logistics Management Business Logistics Management Integrated Logistics Management Materials Management Physical Distribution Management Marketing Logistics Industrial Logistics Distribution Chapter 2 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed.
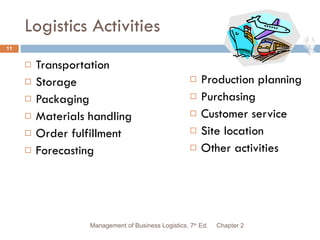
- 11. Logistics Activities Transportation Storage Packaging Materials handling Order fulfillment Forecasting Production planning Purchasing Customer service Site location Other activities Chapter 2 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed.
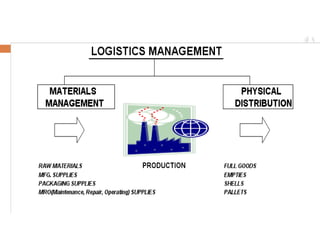
- 12. PHYSICAL DISTRIBUTION Refers to the portion of a Logistics System concerned with the outward movement of materials from the Plants to the Sales Offices
- 13. PHYSICAL DISTRIBUTION - DEFINITION Physical distribution is the set of activities concerned with efficient movement of finished goods from the end of the production operation to the consumer. Physical distribution takes place within numerous wholesaling and retailing distribution channels, and includes such important decision areas as customer service, inventory control, materials handling, protective packaging, order procession, transportation, warehouse site selection, and warehousing. Physical distribution is part of a larger process called "distribution," which includes wholesale and retail marketing, as well the physical movement of products.
- 14. PHYSICAL DISTRIBUTION KEY OBJECTIVE To contribute to the efficient and profitable operation of the Company by ensuring the right quantity of products at the Sales Offices at the right time and employing optimum quality and cost.
- 15. INTEGRATED LOGISTICS & SUPPLY CHAIN SUPPLIERSŌĆÖ SUPPLIER LOGISTICS/ SUPPLIER MATERIALS MGMŌĆÖT SUPPLY CHAIN MANUFACTURER DISTRIBUTOR DISTRIBUTION MGMŌĆÖT TRADE CHANNELS CONSUMERS
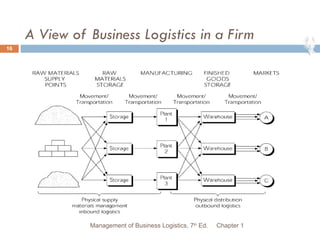
- 16. A View of Business Logistics in a Firm Chapter 1 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed.
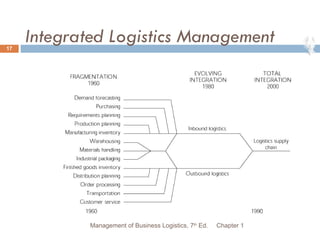
- 17. Integrated Logistics Management Chapter 1 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed.
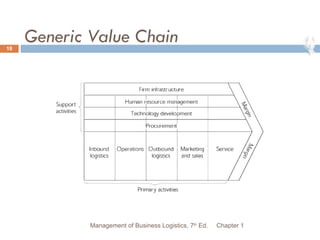
- 18. Generic Value Chain Chapter 1 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed.
- 19. Logistics Supply Chain Chapter 1 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed.
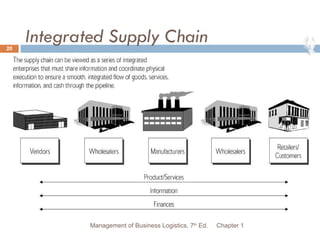
- 20. Integrated Supply Chain Chapter 1 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed.
- 21. TYPICAL COMPANY SUPPLY CHAIN FLOW DIAGRAM SALES FORECASTING PRODŌĆÖN PLANNING MATŌĆÖLS IPC PROCUREMENT IN-BOUND SHIPMENTS- RAW/PACKAGING MATŌĆÖLS WARE- HOUSING PLANT OUT-BOUND SHIPMENTS ŌĆō RAW/PACKGNG MATŌĆÖLS SCRAP DISPOSAL MFG/ PRODŌĆÖN OUT-BOUND SHIPMENTS- FIN GOODS WAREHOUSING SALES DEPOT ORDER FULFILLMENT ROUTE DISTRIBUTION/ SETTLEMENT
- 22. SALES FORECASTING ŌĆō SALES & MARKETING Establish Sales Volume Forecast AOP ŌĆō Annual Operating Plan Trending
- 23. PRODUCTION PLANNING / SCHEDULING 2. Establish production schedules for the Plant and/or its Toll Packers considering Sales Forecast Finished Goods Floor Stock Inventory Materials on hand
- 24. MATERIALS INVENTORY PLANNING & CONTROL 3. Compute Raw and Packaging Materials Requirements for: Plant Toll Packers Other Provincial Plants Relay Raw and Packaging Materials Requirements to Procurement
- 25. PROCUREMENT/ PURCHASING 4. Place Order for the Quantity of Items Needed Considering: Price Supplier ŌĆō Imported or Local Minimum Order Quantity Delivery Lead Times
- 26. INBOUND SHIPMENT OF RAW & PACKAGING MATERIALS ŌĆō PLANT WHSE 5. Receive Raw/Packaging Materials Including Indirect Materials, Spare Parts and Marketing Collaterals Ensuring: Proper documentation/recording in Computerized system of the quantity received Coordinate with QA for quality checking/ acceptance
- 27. IN-PLANT WAREHOUSING 6. Store Received Items Ensuring these are Protected from: Pilferage/Theft Spoilage/Expiration thru proper stock rotation Weather elements/excessive dusts/ vermin to ensure quality and prolonged freshness Optimization of storage space thru the use of racking system
- 28. OUT-BOUND SHIPMENTS OF RAW/PACKAGING MATERIALS 7. Receive Weekly Material Request by the Plants, Consolidate and Ship to them in Time to Replenish their Buffer Stocks Luzon Plants ŌĆō Truckers VISMIN Plants ŌĆō RORO and Container Vans using local Shipping Lines
- 29. SCRAP SALE/DISPOSAL 8. Management of Scrap Disposal consisting of the following: Setting the right disposal procedures and bidding process to identify and award scrap sale agreement Managing the scrap buyer ensuring: Proper documentation of transactions That the scrap buyer collect and move out the dayŌĆÖs accumulation of scrap materials Scrap area is kept clean and orderly
- 30. MANUFACTURING/ PRODUCTION 9.Produce/manufacture the products required by Sales following the schedule set by Plant PD
- 31. OUT-BOUND SHIPMENT OF FINISHED GOOD 10.Allocate Production Output to Provide for the needs of the Different Plants/Business Units/Sales Offices Ship the Finished Goods Following the Product Allocation Set by the PD
- 32. SALES OFFICE OPERATIONS/ DELIVERY 11.Receive Finished Goods and Deliver these to the Customers as follows: Process sales orders and allocate these to the delivery trucks Load the trucks as per sales order Deliver the orders as per delivery list, collect payment, retrieve and sort empties, settle and remit collections
- 33. TRANSPORT, TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT & LOG. SERVICE PROVIDER GROUPS NETWORKING ŌĆō PD/CSSO/PAM 14.Coordinate and make proper representation with the Government and private agencies pertaining to PD/Logistics to ensure Availability of truckers, forklift rental providers, warehouses, shipping lines, etc. Trouble-free shipping operations in the area Availability of information regarding road repairs, infrastructure projects, ships for dry docking, etc. that may affect shipping operations