Interactive work proyecto_iii
- 1. UNDERSTANDING EXPECTATIONS: THE WHO, WHAT AND WHY OF THE PROJECT UNIVERSITY OF THE ARMED FORCES ESPE APPLIED LINGUISTICS IN ENGLISH PROGRAM INTEGRATIVE PROJECT III STUDENT┬┤S NAME: ŌĆóMARGARITA PAZMI├æO ŌĆóYAKEE ACOSTA HERRERA TUTOR┬┤S NAME: DR. MIGUEL VINICIO PONCE
- 2. THREE MAIN COMPONENTS THAT DEFINE A PROJECT SPECIFIC SCOPE DESIRED RESULTS OR PRODUCTS SCHEDULE ESTABLISHED DATES WHEN PROJECT WORK STARTS AND ENDS REQUIRED RESOURCES NECESSARY AMOUNTS OF PEOPLE, FUNDS AND OTHER RESOURCES
- 3. STAGES OF A PROJECT STARTING THE PROJECT INVOLVES GENERATING EVALUATING FRAMING THE BUSINESS GENERAL APPROACH TO PERFORMING IT AGREEMENT TO PREPARE A PROJECT PLAN ORGANIZING AND PREPARING DEVELOPING A PLAN THAT SPECIFIES DESIRED RESULTS WORK TO DO THE TIME THE COST OTHER RESOURCES REQUIRED CARRYING OUT THE WORK INVOLVES ESTABLISHING THE PROJECT TEAM PERFORMING THE PLAN MONIYORING AND CONTROLLING CLOSING THE PROJECT INVOLVES ASSESSING PROJECT RESULTS OBTAINING CUSTOMER APPROVALS TRANSITION FROM TEAM MEMBERS TO NEW ASSIGNMENTS CLOSING FINANCIAL ACCOUNTS POST- PROJECT EVALUATION
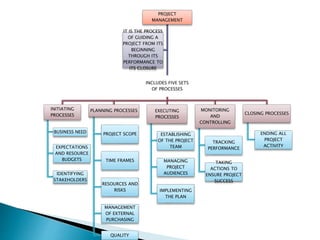
- 4. PROJECT MANAGEMENT INCLUDES FIVE SETS OF PROCESSES INITIATING PROCESSES BUSINESS NEED EXPECTATIONS AND RESOURCE BUDGETS IDENTIFYING STAKEHOLDERS PLANNING PROCESSES PROJECT SCOPE TIME FRAMES RESOURCES AND RISKS MANAGEMENT OF EXTERNAL PURCHASING QUALITY EXECUTING PROCESSES ESTABLISHING OF THE PROJECT TEAM MANAGING PROJECT AUDIENCES IMPLEMENTING THE PLAN MONITORING AND CONTROLLING TRACKING PERFORMANCE TAKING ACTIONS TO ENSURE PROJECT SUCCESS CLOSING PROCESSES ENDING ALL PROJECT ACTIVITY IT IS THE PROCESS OF GUIDING A PROJECT FROM ITS BEGINNING THROUGH ITS PERFORMANCE TO ITS CLOSURE
- 5. PROJECT┬┤S SCOPE STATEMENT SHOULD INCLUDE JUSTIFICATION WHY THE PROJECT CAME TO BE NEEDS IT ADRESSES SCOPE OF WORK HOW IT AFFECTS OR OS AFFECTED OBJECTIVES PRODUCTS AND SERVICES (DELIVERABLES) PRODUCT SCOPE DESCRIPTION FEATURES AND FUNCTIONS OF DELIVERABLES PRODUCT ACCEPTANCE CRITERIA THE PROCESS AND CRITERIA FOR ACCEPTING DELIVERABLES CONSTRAINTS RESTIRCTIONS THAT LIMIT ACHIEVEMENT ASSUMPTIONS HOW YOU WILL ADDRESS UNCERTAIN INFORMATION WRITTEN CONFIRMATION OF THE RESULTS AND THE TERMS AND CONDITIONS YOU┬┤LL PERFORM YOUR WORK
- 6. HOW YOUR PROJECT FITS IN INVOLVES IDENTIFYING THE INITIATOR WHO HAD THE ORIGINAL IDEA THAT LED TO YOUR PROJECT RECOGNIZING OTHER PEOPLE THAT MAY BENEFIT FROM THE PROJECT DISTINGUISHI NG THE PROJECT CHAMPION ORGANIZATI ON THAT STRONGLY SUPPORTS YOUR PROJECT CONSIDERIN G PEOPLE WHO WILL IMPLEMENT THE RESULTS OF YOUR PROJECT DETERMININ G YOUR PROJECT┬┤S DRIVERS┬┤REA L EXPECTATIO NS AND NEEDS CONFIRMING THAT YOUR PROJECT CAN ADDRESS PEOPLE┬┤S NEEDS UNCOVERING OTHER ACTIVITIES THAT RELATE TO YOUR PROJECT PROJECT┬┤S IMPORTANCE TO YOUR ORGANIZATI ON WHERE YOUR PROJECT STARTS AND STOPS STATING YOUR PROJECT┬┤S OBJECRTIVES UNDERSTANDING THE SITUATION AND THOUGHT PROCESSES HELP ENSURE YOUR PROJECT MEETS PEOPLE┬┤S EXPECTATIONS
- 7. MAKING YOUR OBJECTIVES CLEAR AND SPECIFIC TIPS BE BRIEF DON┬┤T USE TECHNICAL JARGON OR ACRONYMS MAKE YOUR OBJECTIVE SMART SPECIFIC MEASURABLE AGGRESSIVE REALISTIC TIME SENSITIVE INCLUDE THE DATE BY WHICH YOU┬┤LL ACHIEVE THE OBJECTIVES MAKE YOUR OBJECTIVES CONTROLLAB LE THE TEAM MUST BELIEVE THEY CAN INFLUENCE THE SUCCESS OF EACH OBJECTIVE IDENTIFY ALL OBJECTIVES BE SURE DRIVERS AND SUPPORTERS AGREE ON YOUR PROJECT┬┤S OBJECTIVES
- 8. PROJECT CONSTRAINTS TYPES LIMITATIONS TYPES RESULTS TIME FRAMES RESOURCES ACTIVITY PERFORMANCE DEFINITION RESTRICTIONS OTHE PEOPLE PLACE NEEDS DEFINITION REQUIREMENTS YOU STIPULATE MUST BE MET TYPES RESOURCE RELATED NEEDS PERSONNEL BUDGET OTHER RESOURCES
- 9. Understanding your project┬┤s audiennce. Knowing your project┬┤s audience . Assessing your audience┬┤s power and interest. . Confirming your audience┬┤s authority. Making the most of your audience┬┤s involvements. Using differents methods to keep your audience involved. . Deciding when to involve your audience . Considering the Driver┬┤s, supporters┬┤s and observes in your audience.. Using an audience template. Ensuring your audience list is complete and up-to date.. Developing an audience list is.
- 10. Developing an audience list. Starting your audience list. Using specific categories. Examing a sample of audience list. Considering audience that are often overlooked. internal external Support groups End users of your projectŌĆÖs products People who will maintain or support the final product. Groups normally involved Team members End usersl Upper management:l Requesters: Project manager Groups needed just for this project Vendors, suppliers, and contractors Clients or customers Collaboratorsl Regulators:l Professional societies:l The public: Facilities finanza Prouremen t or contractin g Human resource s Legal services Quality Security Project managem ent office It helps ensure that the goods and services produced are as easy as possible which increases the chances to implement the products successfully . It allows them to become familiar with the products. and effectively build their maintenanc e into existing procedures
- 11. Ensuring your audience list is complete and up-to-date Eventually identify each audience by position description and name Speak with a wide range of people Allow sufficient time to develop your audience list. Include audiences who may play a role at any time during your project. Include team membersŌĆÖ functional managers Include a personŌĆÖs name on the audience list for every role she plays. Continue to add and remove names from your audience list throughout your project initially identify people from sales and marketing as an audience. Check with people in different organizational units. Ask every person whether she can think of anyone else you should speak with Develop your list as soon as you become project manager. Identify names Decide whether, when, and how to involve these people they have the resources necessary to perform their project assignments Include your bossŌĆÖs name twice . Plan to review your list at regular intervals throughout the project to identify names that should be added or deleted.
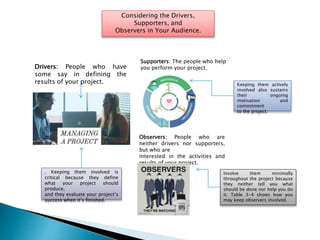
- 12. Considering the Drivers, Supporters, and Observers in Your Audience. Drivers: People who have some say in defining the results of your project. Supporters: The people who help you perform your project. Observers: People who are neither drivers nor supporters, but who are interested in the activities and results of your project. . Keeping them involved is critical because they define what your project should produce, and they evaluate your projectŌĆÖs success when itŌĆÖs finished. Keeping them actively involved also sustains their ongoing motivation and commitment to the project. Involve them minimally throughout the project because they neither tell you what should be done nor help you do it. Table 3-4 shows how you may keep observers involved.
- 13. Developing Your Game Plan: Creating and Displaying Your Work Breakdown Structure Divide and Conquer: Working on Your Project in Manageable Chunks: Documentin g What You Need to now about Your Planned Project Work Identifying Risks While Detailing Your Work Develop a logical framework to define all work thatŌĆÖs necessary to complete the project. You can use several different schemes to develop and display your projectŌĆÖs WBS, WBS helps you identify unknowns that may cause problems when you attempt to perform that work. take some time to gather essential information about all work packages
- 14. Creating and Displaying Your Work Breakdown Structure SCHEMES OF WBS Product components Functions Geographical areas Project phases Organizational units Training manuals Floor plan Screen design Design launch review, or test Design or construction Marketing operations facilities ,, Initiation Region Approaches to develop WBS Top-down: Brainstorming Specify all Level 2 components for the entire project . Determine all necessary Level 3 components for each Level 2 Specify the Level 4 components for each Level 3 component Continue in this way until youŌĆÖve detailed all project deliverablee Use brainstorming projects involving untested methods Theyare moreused
- 15. Identifying Risks While Detailing Your Work Unknown information A known unknown: An unknown unknown: Information you know you need that someone else has but you donŌĆÖt Information you know you need that neither categories Estrategies Buying insurance minimize damage that occurs to Developing contingency plans follow if something doesnŌĆÖt turn out the way you expected to Trying to influence what the information eventually turns out to be. Address this risk Develop a contingency plan. Take steps to reduce the likelihood that coffee is spilled on your data tape.