intermolecular forces.ppt.pptx
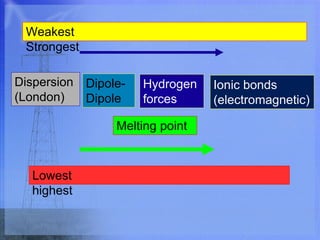
- 2. We have been working on intramolecular force (forces in bonds). Intermolecular forces- forces which hold full molecules together. -ionic molecules have the strongest attraction due to their full positive and negative charges. -this high electromagnetic attraction (+ and -) results in ionic molecules staying more tightly together than covalent molecules. = higher melting point for ionics!
- 3. Covalent intermolecular forces: (we will go weakest to strongest) 1) Dispersion force- -Often called London Force after Fritz London. -weakest of three covalent forces. -only force that keeps non- polar molecules together since they have no true + or - attraction. But dispersion forces occur in all molecule types. -the larger the molecule, the more dispersion force it will have (more electrons).
- 4. 2) Dipole-Dipole Force- -stronger than dispersion forces. -occurs in weaker polar molecules because of their partial positive and negative charges. (δ+ and δ-) animation Draw HCl and show charges. Hδ +—Clδ - Hδ +—Clδ - Hδ +—Clδ - -dipole-dipole is for all polar molecules except H-F, H-O or H-N. (they have a stronger force)
- 5. 3) Hydrogen Forces- strongest IM covalent bond -”Hydrogen forces are a lot of FON” (hydrogen with F,O and N only) -the ΔEN is so great between H and FON that the whole molecule has a very strong δ+ and δ- end. H = 2.1 F = 4.0 ΔEN = 1.9 (is almost ionic!!!)
- 6. -these stronger δ+ and δ- ends create a greater force than dipole-dipole which has weaker partial charges. Ex. Water -hydrogen forces are essential for making the molecules of life… DNA and proteins.